Residual method
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment

A method of allocating the purchase price for the acquisition of another firm among the acquired assets .
Similar financial terms
Usually refers to the value of a lessor’s property at the time the lease expires.
Lost wealth of the shareholders due to divergent behavior of the managers.
An approach that suggests that a firm pay dividends if and only if acceptable investment opportunities for those funds are currently unavailable.
Assets that remain after sufficient assets are dedicated to meet all senior debtholder’s claims in full.
(a) Parts of stock returns not explained by the explanatory variable (the market-index return). They measure the impact of firm-specific events during a particular period. (b) Remainder cash flows generated by pool collateral and those needed to fund bonds supported by the collateral.
Under this currency translation method, the choice of exchange rate depends on the underlying method of valuation. Assets and liabilities valued at historical cost (market cost) are translated at the historical (current market) rate.
A method of cash budgeting that is organized along the lines of the cash flow statement.
A method of calculating the growth rate by relating the terminal value to the initial value and assuming a constant percentage annual rate of growth between these two values.
Accounting for an acquisition using market value for the consolidation of the two entities’ net assets on the balance sheet. Generally, depreciation/amortization will increase for this method compared with pooling and will result in lower net income.
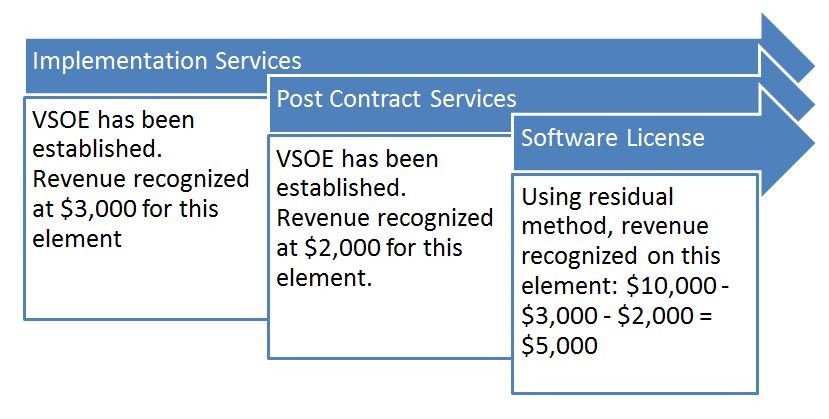
The practice of making a charge in the income account equivalent to the tax savings realized through the use of different depreciation methods for shareholder and income tax purposes, thus washing out the benefits of the tax savings reported as final net income to shareholders.
Under this translation method, monetary items (e.g. cash, accounts payable and receivable, and long-term debt) are translated at the current rate while non-monetary items (e.g. inventory, fixed assets, and long-term investments) are translated at historical rates.
A statistical technique for fitting a curve to a set of data points. One of the variables is transformed by taking its logarithm, and then a straight line is fitted to the transformed set of data points.
A method of constructing a replicating portfolio in which the manager purchases a number of the largest-capitalized names in the index stock in proportion to their capitalization.
Under this currency translation method, all of a foreign subsidiary’s current assets and liabilities are translated into home currency at the current exchange rate while noncurrent assets and liabilities are translated at the historical exchange rate, that is, the rate in effect at the time the asset was acquired or the liability incurred.
Under this currency translation method, all foreign currency balance-sheet and income statement items are translated at the current exchange rate.














