Your Personal Investment Portfolio Asset Allocation Strategy
Post on: 4 Май, 2015 No Comment

As you may know, asset allocation is the number one factor to consider when structuring a successful investment portfolio. The goal of most investors should be to build a diversified portfolio that will allow them to weather the ups and downs of the market.
However, you cannot properly construct your portfolio until you know exactly what kind of investor you are. This requires looking at a number of different factors and answering some important questions so that you can find the optimal mix for your investment portfolio.
Below are the 3 most important factors that you need to consider in order to properly structure your portfolio:
1. Determine Your Investment Strategy
Determining your investment strategy is the first thing you need do before you invest a single cent in any stock, bond, or mutual fund. Ask yourself the following questions and make a list so that you can map out your investment strategy.
- What purpose am I investing for?
- Am I investing to create a side income stream to supplement my retirement plan ?
- Or am I investing to build a massive sum of money that I can rely on in my golden years?
- Will I need to access this money in the next 1, 5, or 10 years?
- Am I more interested in passive investing or active investing ?
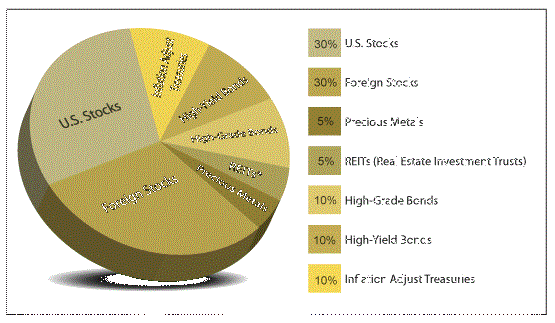
There is a big difference between the strategies of someone who is investing for supplemental income outside of a pension plan and an individual who is totally dependent on their 401k for income after retirement. Once you know the purpose for which youre investing, you can then determine the assets that you need to invest in to meet your goals.
2. Assess Your Risk Tolerance
Believe it or not, all investors believe that they are risk takers when first starting out. They want to actively invest in the next great stock or aggressive growth mutual fund that will make them a millionaire by the age of 40. That is, until these extra risky investments start dropping in value. So-called risk takers learn the hard way that they are actually conservative investors who would rather put their money in safe investment options like bonds .
This step requires that investors be honest with themselves about the magnitude of risk (and potential losses) that they would be comfortable taking. Will you be able to sleep at night if your portfolio is down 20 to 30%? Can you ride out the market dips so that you can see the market tops? The average investor is not a natural risk taker, which is why they buy during the market peaks and sell during the market troughs. If you want to know your investing temperament, look at how you responded during the market crash of 2008. Did you sell, hold or buy more shares?
3. How Old Are You? Age Matters
I know this not a popular statement but age does matter. If you are 50 or older with sizeable assets, the bulk of them should be in more conservative investments. The rule of thumb to follow is that younger investors should invest heavily in risky assets like stocks and older investors should primarily invest in fixed-income assets. Younger investors should be focused on capital appreciation while older investors should concentrate on capital preservation.
If youre very young (under 30), start saving and investing as soon as possible. Its extremely beneficial to start saving for retirement at a young age .
Here is a quick age-adjusted asset allocation tool that you can use:
- If youre a conservative investor, subtract your age from 100.
- If youre a risk taker, subtract your age from 120.
This is the percentage of money that you should invest in stocks. For example, if youre a 25 year old and have recently discovered that youre a risk taker when it comes to investing, you should put 95% of your assets in stocks (120-25=95). On the other hand, if youre 60 years old, nearing retirement and very conservative, you should only have 40% of your assets in stocks (100-60=40).
There are some exceptions to this rule, however. For example, if you are in your 50s and have only saved $20,000 for retirement, then you will have to adopt a much more aggressive strategy than the average 50 year old investor. This is because you will most likely need to work another 15 years minimum and focus on capital appreciation to make up for lost time. Ask yourself, how much money do I need to retire? and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Final Word
Remember that no two investors are exactly alike. Your investment portfolio should be structured based on your goals, strategy, risk tolerance, age. and number of years to retirement. If you take all of these factors into account, you should be well on your way to building the right portfolio for your retirement investment plan !














