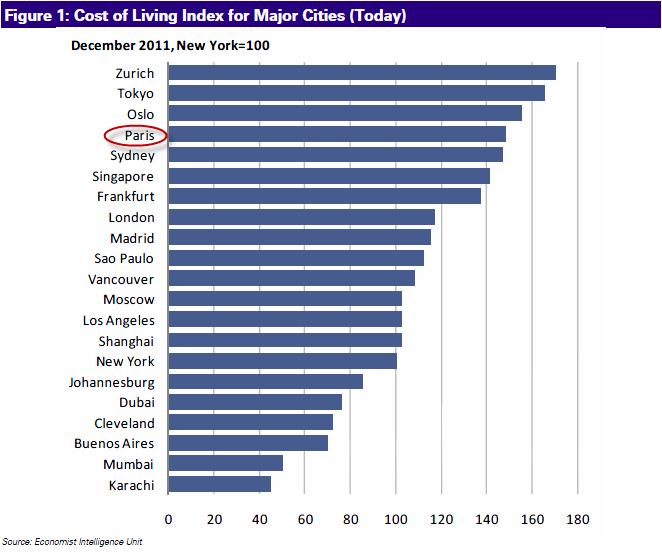
What is the Big Mac Index
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
McDonalds as a Purchasing Power Parity Index
Aping Vision / STS/ Digital Vision/ Getty Images
The Big Mac Index is an index created by The Economist based on the theory of purchasing power parity (PPP). Over the long-term, the PPP theory states that currency exchange rates should equal the price of a basket of goods and services in different countries. And what better basket of goods than McDonald’s Big Mac — or at least its equivalent — in various countries?
In theory, the price of a Big Mac reflects a number of local economic factors, ranging from the cost of the ingredients to the cost of local production and advertising. The resulting PPP metric is therefore considered by many economists to be a reasonable measurement of real world purchasing power. But investors should remember that there are some exceptions to the rule.
How the Big Mac Index Works
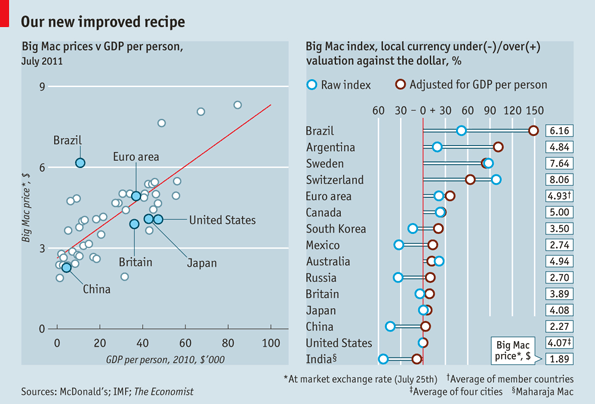
The Big Mac Index is calculated by dividing the price of a Big Mac in one country by the price of a Big Mac in another country in their respective local currencies. The resulting value is then compared to the official exchange rate between the two currencies to determine if either currency is undervalued or overvalued according to the PPP theory.
For example, suppose that a Big Mac in the U.S. costs one U.S. dollar and one in the eurozone costs two euros. The Big Mac Index valuation for EUR/USD would be 2.0, or two divided by one, which could then be compared to the EUR/USD exchange rate. If the exchange rate was 1.5, investors could predict that the euro was undervalued by 0.5 euros per U.S. dollar.
There are also many variants of the Big Mac Index that may be useful for investors. For instance, UBS Wealth Management expanded the index to include the number of hours that an average worker must work to earn enough to buy a Big Mac. Other groups created separate indexes for everything from Apple iPods to Starbucks coffees to Ikea Billy bookshelves.
Using the Big Mac Index
Investors in the United States may not see much need for the Big Mac Index, since there are already a number of reputable price indexes available, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI). But the index becomes useful in other countries where reliable indexes aren’t available, such as those that manipulate government statistics or those that don’t publish official data.
For example, many economists believed that Argentina had been modifying its official consumer price data to understate its true rate of inflation between 2010 and 2012. So, The Economist used its Big Mac Index to find that the average annual rate of burger inflation was 19% compared to the country’s official 10% rate of inflation in January of 2011.
Investors can use data from the Big Mac Index in many different ways. For instance, they can use the values to determine if a currency is overvalued or undervalued relative to others and trade based on that data in the foreign exchange market. Similarly, investors can measure changes in values over time to determine rates of inflation and compare that to official records.
Key Takeaway Points
- The Big Mac Index is an index created by The Economist based on the theory of purchasing power parity (PPP).
- The Big Mac Index is calculated by dividing the price of a Big Mac in one country by the price of a Big Mac in another country in their respective local currencies.
- Investors can use data from the Big Mac Index in many different ways, ranging from determining rates of inflation to comparing currency valuations.














