The Difference Between Common and Preferred Stocks is Risk
Post on: 27 Май, 2015 No Comment
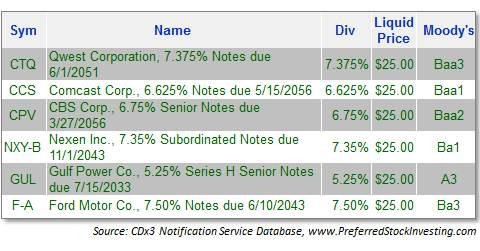
The Simple Way to Plan, Manage, and Organize Your Money
April 19, 2010
The Difference Between Common and Preferred Stocks is Risk
The most important distinction between common and preferred stocks is risk.  Common stocks carry considerably more risk than their preferred cousins and at no time in recent history has this been as clear.  The chart above from Yahoo! Finance shows the two year price chart of Citigroup common stock in the red and Citigroup 6% preferreds in the blue.
In looking at this chart, youll see that both started at the same place, and in mid-September of 2008 (after the fall of Lehman Brothers), both the common and preferreds moved sharply lower in tandem.  This continued until March of 2009 when the market finally reached bottom.  Since then, however, there is a marked difference in performance.
An investment in each made two years ago would have the preferreds down a few percentage points with common shares down over 80%.  So what accounts for this dramatic difference in performance?  Risk.
Why Preferreds are Less Risky
A preferred stock can have any of a number of unique features. but all share something in common — priority.  In the event of an issuing company going bankrupt, preferred shareholders are paid before common stockholder and after bondholders.  This means that preferred shareholders are more likely to receive something in the event of liquidation — implying there is less risk in preferreds .
Beyond this, preferreds also pay dividends.  In this case, Citi pays a 6% annualized dividend to holders of its preferred stock.  This dividend isnt like a dividend paid to common stockholders.  Instead, preferreds typically bind the company to paying a dividend at a stated rate at regular intervals whereas dividends to common stockholders are at the sole discretion of the company.
Applied Learning
The two critical points made above can be applied to the chart for Citi common and preferred.  When the Panic of 2008-09 was in its early stages, few thought major banks were at risk of going under.  However, once Lehman Brothers failed, fear spread throughout the market and Citi common and preferred nosedived.  The downward spiral continued until March of 2009 when the market finally found a bottom.
During this descent, both common and preferred investors feared not only dividends wouldnt be paid, but also feared for the very life of the company.  Though preferreds have priority over common in the event of liquidation, the chart shows that neither common nor preferred shareholders believed they would receive much of anything in a bankruptcy.  Thus they moved together during the panic.
But, once the market bottomed, it appeared that the company would not fail.  This meant that preferred shareholders no longer had the major risk of a corporate bankruptcy and it made dividend payments more assured.  For common shareholders, the value of the stock was decimated — while the company would not fail, it also was unlikely to return to profits anytime soon.

If youll recall, there are only two ways to make money on stocks — dividends and price appreciation.  Since common stock dividends are at the discretion of the issuing company, a company going through turbulent times like Citi is unlikely to pay a dividend to common stockholders.  This means that the value of Citi common stock was almost completely dependent upon price appreciation — a tough proposition considering the massive problems in the financial industry.
However, since Citi was contractually bound to pay on preferreds, there is a greater certainty of getting a 6% return on the preferred shares, making the value of the stock less dependent on price appreciation.  It is this difference in the dividends that allowed Citi preferred shares to rebound to near pre-panic levels in August while common shares continue to languish more than 80% lower than their price just two years ago.
Critical Thinking
Having seen this example, consider these questions:
- Are common stocks more or less risky than preferred stocks?  Why?
- During a calamitous market that sees preferred stocks decline like common stocks, which type of stock offers the best opportunity to make money?
- After this two year period, is it likely that Citi preferreds will continue to rise?  Why not?
Related Posts














