Key Value Stock Fundamentals for Screening Stocks
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
The hardest part of deciding where to invest is actually deciding what criteria you want to look for in a company. I am a huge value investor, and look for solid companies that can be purchased at a discounted price (maybe due to bad short-term news). The trick to finding these companies is to use a stock screener. Most online brokerages have them, as does Yahoo! Finance or Money.com. What I highlight below are some key fundamentals you may want to look at when investing in a company.
Remember, a number or ratio may look good, but it is important to understand why that number looks good, or if it looks too good. These key value stock fundamentals will help you do just that.
Market Capitalization
While market capitalization may not matter too much for small investors, it can play a role in the types of companies that you will see. I prefer to exclude micro-cap companies, which are companies that have a capitalization of less than $300 million. The reason for this is that most are young start-ups or highly volatile companies, and as a result, it can skew some of the other measures that I like to screen by. However, it is also important to note that micro-cap companies do make up the bulk of the stock market. Right now, there are 5,678 micro-cap companies that are publicly traded, while there are only 2,489 small-cap and larger companies traded.
PEG Ratio
The reason I prefer this metric to the P/E ratio alone is that it provides a look at whether the P/E ratio is excessively high, or if it actually reflects the companys growth prospects. The main disadvantage to this measurement is that it doesnt work at the extremes (very low-growth or ultra-high growth). It also relies on the estimate of the companys growth rate, which is not a definite number. This is why it is only one criteria in the overall screen.
Profit Margin TTM
The profit margin is a great indicator about how the company is performing. When looking at this metric, it is important that you look at the TTM, or trailing twelve months. This gives you finite data non how the company performed over the past year. When looking at companies, it is extremely important that you compare the companys profit margin to the industry in which it operates. You cannot simply assign a margin amount that you want.
Each industry has different standards for profit margin. In high tech, the margins can be very high, but in industrial production, they may be much lower due to input costs. When screening for this category, you want to look for a company that consistently has above industry average profit margins, and you want to know why. This is key to possibly discovering the companys competitive advantage in the market. Does the company have a technology that lowers costs? Are there contracts in place for years that allow it to buy its inputs at below current market rates? The answers to these questions will allow you to make a very informed decision about the company.
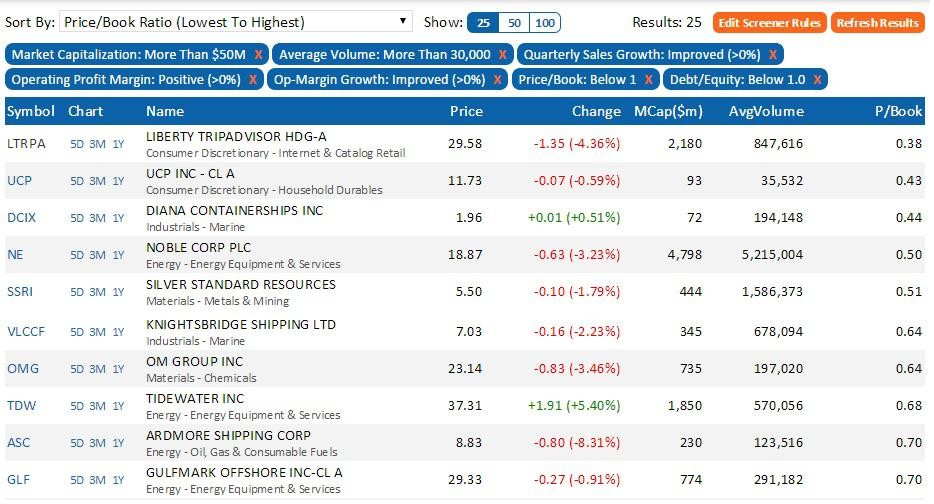
Price/Book Ratio
The next great indicator to look for is Price to Book Ratio. The book value of a company is the companys total tangible assets less its total liabilities. This ratio gives you an idea of how much an investor could have if the company went bankrupt immediately. A P/B Ratio of less than one can signal that a company is undervalued, or that the value of its assets minus liabilities is currently worth more than the share price. So, if the company went bankrupt immediately, you could actually make money (although highly unlikely).
The important thing to remember is that book value varies greatly for different industries. Also, a company in distress may have many more liabilities than assets, making this number meaningless. Finally, the book value does not include brands and intellectual property, which some companies use that their main asset. In such cases, the book value may also be meaningless.
Dividend Yield
I like a company with a positive dividend yield, even if it is very small. Dividends are great as they can show that the company is financially healthy enough to pay its shareholders. However, when looking at this metric, you may want to refer to our post about A Dividend Stock to Fear. In that post we discussed the payout ratio of stocks. It is important to look at the payout ratio of dividend paying stocks to ensure that the company is able to continue paying its dividend.














