Investor Handbook for Water Risk Integration Ceres
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
A How To Guide and Resource for Institutional Investors
An Investor Handbook for Water Risk Integration:
Practices & Ideas Shared by 35 Global Investors
Many in the investment community recognize the growing challenges posed by resource scarcity, population growth, energy demands, climate change and increasing competition for freshwater resources. Water risks, in particular, are becoming more tangible. The World Economic Forum recently named water availability as the “top global risk.” Historic droughts, more pronounced extreme weather events and escalating water competition are all adding to the materiality of water as a financial risk.
Ceres recently interviewed 35 global asset owners and fund managers with over $6 trillion in collective assets under management on how they are integrating Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) factors and in particular water risks into investment decisions. The findings offer recommendations on how to integrate water into investment policies, portfolio management, strategic planning and client relationship building. It serves as a stepping-stone for managers just beginning to integrate (ESG) and water risks and opportunities into their thinking, as well as for advanced investors looking to deepen their practices
The “How to Guide” of ESG and Water Risk Integration follows the publication of the Ceres 21 st Century Investor: Blueprint for Sustainable Investing . which provides specific steps that help asset owners, and managers steer a sustainable investment course. It also follows the publication of the Ceres Aqua Gauge . which provides a framework for both companies and investors to evaluate their exposure to water risks and develop mitigation strategies across their value chains.
Download An Investor Handbook for Water Risk Integration
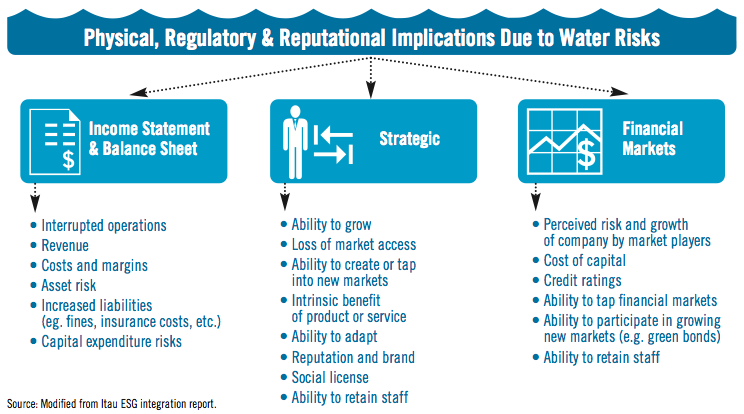
Key Elements of Corporate Water Risk
Corporate water risk exposure is a function of three variables:
- Company/sector-specific characteristics (e.g. water intensity of production),
- Water conditions in particular geographies (e.g. drought-prone or strictly regulated)
- Strength of corporate management (e.g. proactive vs. reactive) in mitigating risks.
More advanced survey participants reported capturing these variables in their analyses, looking specifically at relative levels of corporate water dependency, the security of relevant water resources and a company’s management of water risks – the building blocks of a corporate water risk dashboard framework .
Many managers reported capturing information such as the percentage of corporate facilities in high water risk areas, and how water-or waste-intensive a company or product is overall. Although capturing these sorts of metrics are an important step in understanding water risk exposure, many managers felt that their current approaches to analyzing corporate water dependency and security were still insufficient.
Overall, managers interviewed were most advanced in analyzing corporate responses to water risks. Many routinely assessed factors such as: Is management aware of water risks? Is the company measuring and disclosing water data? Do the board and upper management have oversight of water risks? Are they engaging stakeholders on water issues? Additionally, investors noted The United Nation’s recognition of the human right to clean drinking water and sanitation and its implications for corporations as an issue of growing importance.
To learn more, Download An Investor Handbook for Water Risk Integration
Key Findings and Recommendations
Despite challenges expressed in integrating water analysis, many managers surveyed recognize that water has material strategic, operating and financial implications for many global corporations and bond issuers. Many exemplary and innovative practices and ideas were shared and can be found below related to how to conduct corporate water risk analysis, applying water research to buy/sell decisions and beyond.
Opportunities for the Market
Although individual asset owners and fund managers have a direct role to play in deepening integration of water into investment decision-making, there are many opportunities to improve the broader research ecosystem to make water risk analysis more efficient and effective.
Ideas for improvements include:
- Establishing an effective and broadly-recognized investor framework for conceptualizing water risks.
- Further standardizing corporate water risk reporting and data gathering.
- Systematically capturing more location-specific corporate information.
- Integrating more water data into financial databases.
- Greater acceptance of the use of shadow water prices that reflect higher value of water in financial models.
- More efficiently aggregating NGO environmental and social research.
- Creating an independent body to conduct water risk analysis on behalf of investors.

Opportunities for Asset Owners and Fund Managers
Although there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to ESG and water integration, the Ceres’ recommendations outlined below can be selectively or collectively considered, depending on the unique needs of asset owners and fund managers.
This report identifies 10 recommendations as most critical to advancing water risk integration in the near- and long-term including:
Strategic Recommendations
- Integrate water into investment beliefs, investment policy, RFPs (request for proposals) and manager evaluations. Clear mandates on the importance of water risk integration aligns internal integration efforts, and is also fundamental in setting clear expectations with managers, consultants and research providers. Aligning compensation structures related to integration or toward longer-term performance can also be an important component.
- Promote upper management support for ESG and water risk integration. High-level institutional support, in the form of investing in research and communication infrastructure and signaling internal high-level commitment, are additional building blocks in driving integration.
- Engage standard-setting and regulatory bodies and key stakeholder institutions on the importance of material ESG and water risks. This includes working with national regulators, standard-setting bodies, finance industry associations, investor networks and academic institutions to drive improvements in disclosure and integration of material ESG and water risks.
- Encourage asset owners to communicate to consultants and fund managers on how ESG and water risk integration is taking place. Stronger information flows on ESG and water risk analysis practices will move the conversation beyond checking boxes on “if” integration is taking place to a deeper understanding on the depth of the practices.
- View ESG and water integration as an opportunity to deepen relationships between asset owners and investment managers and evolve new products. In many cases, constructive
Portfolio-Level Recommendations
- Apply ESG and water risk integration to buy/sell decisions through whatever approach fits best with client and institutional goals. Possible approaches include embedding water analysis into ESG scores, shrinking the investment universe, conducting scenario analysis in financial models or any number of other methods shared in this report and beyond.
- When conducting corporate water risk analysis, capture elements of water dependency, security and management response. Gain an understanding of sector-specific water dependencies and risks and as well as information on operating or financial exposure in regions with high water risk. Assess corporate water management plans to counter and proactively deal with material water risks. Engage scientific community, investor networks and institutions which have expertise, tools and resources on ESG and water issues (many such experts are listed in this report).
- Engage portfolio companies on how they manage water risks. Leverage existing collaborative investor water engagement efforts when appropriate. Embed water into proxy voting guidelines and publish corporate water management expectations guidelines.
- Apply water analysis to risks and opportunities across-asset classes. By applying water analysis as a global mega theme that will affect all asset classes, more comprehensive and strategic risk mitigation and opportunity planning can be facilitated within an entire organization.
- Conduct a portfolio-level water footprint analysis to assess sectors, geographies and portfolio companies with high water risk exposure. A portfolio-level view of water risk exposure will establish regions, sectors and stocks with particularly high water risks and help prioritize research, engagement and risk mitigation strategies.
To learn more, Download An Investor Handbook for Water Risk Integration
Shareholder Resolutions Linked to Water Risk
Filing a shareholder resolution is an engagement tool used to try and influence corporate behavior and mitigate financial risks. Resolutions provide an opportunity to highlight substantive risk and management issues, and provide an opportunity to ask for increased disclosure, policies and action on a particular issue. Ultimately, resolutions are often a means to engender a productive dialogue between investors and company management to eventually lead towards better corporate management.
There are many resources and organizations available to aid investors on filing shareholder resolutions. In a separate study, Ceres analyzed U.S. shareholder resolution trends since 2003 and found that there have been 238 shareholder resolutions linked to water, either directly (75 with “water” in the resolve clause) or indirectly (163 with “water” in supporting language). The majority of targeted companies were in the oil and gas, electric utilities, coal, food and agriculture sectors.
Most frequently, resolutions involved requests for sustainability reports and risk disclosure related to hydraulic fracturing (with both, on average, gaining over 30 percent support), followed by human rights and community impact concerns and risks. There were also a large number of resolutions related to water contamination concerns in the coal industry. Full resolution texts and data is available here.
Establishing proxy-voting guidelines on water helps guide corporate engagement and sets clear expectations to clients, consultants and corporate management. Ceres has identified 30 institutions with water-related language in their proxy voting guidelines. This language directly encourages responsible and consistent voting on water-related shareholder proposals.
To learn more, Download An Investor Handbook for Water Risk Integration
What Are Investors Saying?
INSIGHTS FROM SURVEY PARTICIPANTS
Water is very emotive; you have to be aware of stakeholders and the greater community. Companies without active stakeholder engagement on water in high-risk sectors are exposed to considerable risks.
Investor environmental and water risk analysis is too often driven by issues in the media. A better approach would be to systematically assess industry and corporate risks and impacts on water resources.
We team up with international water experts using their knowledge, including expertise in water resource economics and natural resource risk assessments, to determine if the right corporate response programs are in place.
Water variability and delivery are amplified by climate change. It would be good if every passive and active investor were asking companies: “What is your water policy in the context of climate change?”
In our methods, we investigate the nature of a company’s product and if that product is solving a sustainability challenge.
I believe that water is the most mis-priced and misunderstood asset on this planet. The problem is that it consistently comes out of a faucet, with few people, investors included, aware of what is required to make that happen.
We really capture the attention of corporate management when we show them how much the company’s market capitalization may be impacted under a scenario of higher water prices.














