How Leveraged ETFs Work
Post on: 6 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
S everal posts on this blog have dealt with ETFs including their suitability and terminology .
ETFs offer the diversification of mutual funds, trade on an exchange similar to stocks, and have lower MERs when compared to mutual funds. However, investment vehicles are updated and upgraded like software packages and there are new products released frequently; one such less commonly used product is the leveraged ETF .
What is a Leveraged ETF?
As would be evident from the name, it is an ETF with leverage involved to boost returns. Leveraged ETFs, like horizon betapro ETFs, track the performance of an index similar to a normal (no leverage) ETF. In addition, they use leverage through derivatives to double or triple returns and hold a corresponding inverse ETF as a short position. The leveraged ETFs have a target leverage amount of 2:1 or 3:1 that they maintain.
Performance of Leveraged ETFs
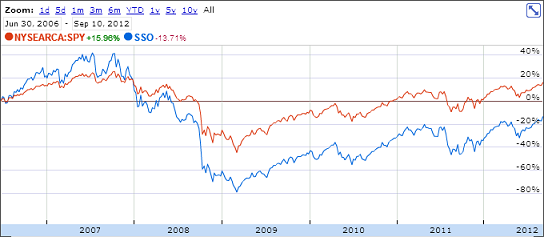
Leveraged ETFs do not have as long a history as regular ETFs but short-term data suggests that they are best suited for day traders with a short-term trading focus (think a day or a few days). To understand the performance of leverage ETFs, consider the example below.
Let us assume that the S&P 500 Index falls 5.0% on a trading day and rises 4.0% the next day during a volatile week. So, the underlying index would have lost 1.2% over those two trading days. A normal ETF tracking the S&P 500 Index would show a similar loss minus MER and tracking error, if any.
Overlooking MER and tracking error for simplicity, a 2X (double) leveraged ETF held during those same two trading days would have a loss of 2.8%. As you would see, a simple doubling of 1.2% should have yielded 2.4% but it will not. A double leveraged ETF in the above example that lost 10% (i.e. 5% * 2) on the first day would have to rise 11.1% on the second day to break even. Evidently the example above is capturing two volatile trading days but such small losses (i.e. 2.8% instead of the mere doubled value of 1.2%, i.e. 2.4%) compound over time.
Please check out this article to get a better understanding about leveraged ETF returns.
Pros and Cons
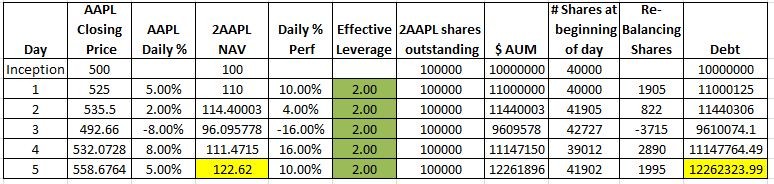
Readers would be able to recognize that leveraged investing to boost returns is a double-edged sword that will also magnify losses. Leveraged ETFs offer an easy way to increase returns; the higher the volatility on the positive side in the market, the better the return for the leveraged investor.
However, the longer the holding period for these leveraged ETFs, the poorer the returns (pdf) due to compounding errors. In addition, short-term holders are not immune to the losses that market volatility may bring. A leveraged ETF uses daily asset rebalancing as part of its operation that makes holders susceptible (see previous link). With low liquidity, the spread may also take a toll.
The Players
For people who have done their due diligence and decided that leveraged ETFs are a good fit for their investment portfolio, there are a few companies willing to lend a helping hand. Check out this Stock-Encyclopedia page and the Leveraged ETFsite for a list of available bull and bear 2X and 3X ETFs.
Do you use leveraged ETFs? How have your returns been? If you have had decent returns, do you plan to use the strategy for a while or are you going to take what you got till date and pack it in?
About the Author. Clark works in Saskatchewan and has been working to build his (DIY) investment portfolio, structured for an early retirement. He loves reading (and using the lessons learned) about personal finance, technology and minimalism. You can read his other articles here .














