Examining cyclical and non cyclical sectors of Investment
Post on: 29 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
Investment professionals often lump investment such as stocks or bonds into one of two categories that is cyclical and non-cyclical sectors. understanding of this two type of investment will help investor make wise investment and market timing decisions, and this can increase the return on investor’s investment while reducing overall level of risk. so mean that understanding cyclical and non-cyclical investment can conduct a more perfect portfolio in our investment.
Non-cyclical bonds are famous among investor for their good performance even in economic downturns. that is because the fact that the items and service included in this classification enjoy constant consumption by customers. However, during economy is growing, these kind of investment tend to lag behind.
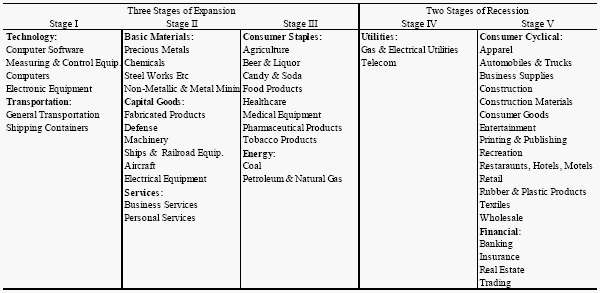
When investment professionals speak of investment that are cyclical and non-cyclical, they are referring to how sensitive a particular sector is to changes in the business cycle. period of economic expansion and retraction are inevitable, and each sector of the economy reacts differently when the economy enters a recession. Stocks or bonds that are less affected by economic slowdown than the market are considered as non-cyclical investment.
The classic example of non-cyclical investment is food consumption. No matter what the conditions of the economy are, people will still consume food to provide for their existence. Another example is the utilities sector and the same applies for electricity, water and gas consumption. Company to luxuries, when the business cycle turns down, people tend to cut down on their discretionary spending. those cutbacks in spending tend to send the stocks of luxury clothing retailer, high-end cars. these types of investment are generally considered cyclical because they are sensitive to things like consumer sentiment and the overall strength of the economy.
When the economy slows down and the interest rate rise, cyclical bonds companies suffer. Consumers put off buying the new car in the hopes of the situation improving.
Despite this eat, drink or smoke perception and despite modern-day developments, tobacco company have miraculously never disappeared or been wiped out. Not all food corporation are actually defensive stocks, but a good rule is that if the bulk of the sales comes from grocery stores, the investment is probably a defensive one.
Restaurant chains that cater to middle and upper-middle level incomes are not defensive sector at all, because a family can quite easily stay home for dinner two nights more per week instead going to a restaurant. Lower-end restaurants or fast food chains are somewhat defensive because consumer still have to eat and they can frequently feed a family at a lower cost there than they can at home. What commonly happens in most bust parts of the business boom and bust cycle is that consumers will just spend less going out no matter what and will try to spend money to eat at home.
Hence, the food manufacturers are the true defensive plays. Alcoholic beverage companies, bottled beverage companies, and water companies are all deemed defensive stocks. People still have to drink water, children and adults will still spend on the sodas, and it is doubtful that in hard times people will drink alcohol even more.
Water, gas and electric utilities are also deemed defensive sectors. How many citizens in the population will live inside their houses without electricity, gas and water? Perhaps some, but very few. The utility business are thought of also benefiting from slower economic environments because interest rates tend to be lower and their competition to borrow funds is much less.
In the past, telephone utility was deemed as a defensive stock, but the problem with this argument now is that telecom competition is no longer deemed a utility. Most markets tend to have one option for power and gas, but now the competition with competitive local exchange carriers (CLEC), cable companies, wireless and copper line phone companies has altered this stigma.
Apartment real estate investment trusts (REITs) are also deemed defensive. Housing stocks are not defensive because there are times when the economy is deprived and very little building is taking place. Office building REITs or industrial park REITs are not defensive because if businesses slow down, the rate of defaults on leases rises.
The reason an apartment REIT is defensive that is because of the need for shelter, and as long as these are not ultra-high-end apartments, you can imagine that if citizens have to live anywhere besides a homeless shelter, they will choose to live in an apartment building. These also offer higher dividend income than treasury rates at almost all points of the business cycle. REITs are now much more common than they were 20 and 30 years ago, but in the modern world and for the foreseeable future these will still be around.
Drug investment are also part a historic defensive investment sector. This has greatly changed through time because of drug corporation relying heavily on major drugs that often have problems discovered down the road or because of new branded and generic competition that didn’t exist back in the early 1990s and before.
Generic drug makers may be the new defensive plays in modern times, but anyone who has owned either generic drug companies over the last 10 to 12 years can confirm that this defensive stock disgrace is not as true as the classical business models used to indicate.
Perhaps can lump other medical companies into this fray because society will still seek medical improvements, but if they have to spend their own money, that might not hold true and many of the device manufacturers haven’t put in the decades and centuries of these classical models remaining true.
Another assumption for compare non-cyclical bonds and cyclical bond is about the default level. Before we already discuss that the non-cyclical bond example is the utilities sector and the same applies for electricity, water and gas consumption. Every country the electricity, water and gas company is mainly issue by the government. That mean that the default risk levels compare to those cyclical bond is much lower. But lower the default risk level also effect the potential return. The higher the risk level, the higher the potential returns.
Another issue is about the maturity period. The mainly relationship is the same. The longer the maturity, the higher the chance for default, since the longer the bondholder is exposed to the market volatility.
An additional factor that can be used when evaluating the chances for default of a bond is the ranking that is given to it by one of the most reputable ranking services — Malaysia Rating Corporation Berhad.
The ranking services grade the trustworthiness of bonds on a scale starting from highest grade, passing through high grade, upper medium grade and ending at medium grade. Additionally, ranking is provided for low rated bonds. However, you should select bonds that fall in the ratings mentioned above. On the other hand, if you are a speculator, a low-rated bond may be of interest to you.
The real cases compare within the cyclical investment and the non-cyclical investment is the economic slowdown when year 2000 to year 2002. Below is a chart showing the performance of a highly cyclical company, the Ford Motor Co. (blue line), and a classic non-cyclical company, Florida Public Utilities Co. (red line). This chart clearly demonstrates how each company’s share price reacts to downturns in the economy.
Notice that the downturn in the economy from 2000 to 2002 drastically reduced Ford’s share price, whereas the growth of Florida Public Utilities’ share price hardly batted an eye at the slowdown.
myinvestingnotes.blogspot.com/2010/08/cyclical-versus-non-cyclical-stocks.html














