Dow Jones Industrial Average The Full Story from Profit Confidential
Post on: 8 Август, 2015 No Comment
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a weighted index representing the stock price action of 30 of the largest U.S. corporations. The world’s most widely followed stock market index, the DJIA was created on May 26, 1896 by Charles Dow and Edward Jones. When it was first launched, the Dow Jones stood at 40.94.
The DJIA is calculated by taking the average price of the listed stocks and dividing that figure by a number called the divisor. The divisor is there to take into account stock splits and mergers, and it changes frequently.
Much broader U.S. stock market indexes have since been created, including the S&P 500 index (which monitors the stock prices of the top 500 U.S. corporations); and the Wilshire 5000 (an index based on the market capitalization of 4,100 stocks actively traded in the U.S.).
The earnings and revenues of large corporations are often leading economic indicators. Hence, economists often look at the DJIA as an indicator of economic activity. If the index is hitting new highs, economic activity can be expected to be brisk in the next six months. Comparatively, if the index is falling to new lows, poor economic times could lie ahead. When news sources declare the markets up or down, they are generally referring to the DJIA.
What does it take to get included on the DJIA? There are no specific rules for inclusion; rather, there is a set of broad guidelines that require large, respected, substantial enterprises that represent a significant portion of the economic activity in the United States.
When the DJIA was launched, the index comprised 12 industrial companies.
Most of the original companies listed on the Dow are still in existence, though, after 100 years, not necessarily in the same form. Early industrial companies included: American Cotton Oil, American Tobacco, Chicago Gas, Tennessee Coal Iron and RR, U.S. Leather, and United States Rubber. The only component still trading in its original form and currently on the DJIA is General Electric Company (NYSE/GE).
In 1916, the DJIA was updated to 20 stocks. Some of the new companies included: American Beet Sugar, American Locomotive, Goodrich, Republic Iron & Steel, Studebaker, Westinghouse, and The Western Union Company (NYSE/WU).
The DJIA reached its current 30 components in 1928. The 30 companies occasionally changed to adapt to the evolving market.
During the stock market crash of 1929, the DJIA lost nearly 90% of its peak value, and would not surpass that (inflation-adjusted) peak again until 1954.
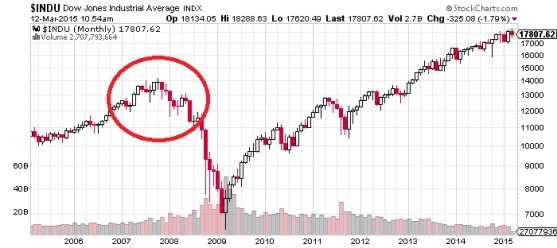
The Dow first passed the 1,000 mark in November 1972; it crossed 10,000 for the first time on March 29, 1999. This growth trend would extend into the 1990s. At the turn of the millennium, the average began to level off near 10,500.
On October 9, 2007, the DJIA peaked at 14,165. This was followed by the 2008 financial crisis. On March 9, 2009, the Dow Jones index hit bottom at 6,547, or 55% below its October 2007 high.
After March 9, 2009, the Dow Jones began another bull run after investors, for better or for worse, accepted that the Federal Government and Quantitative Easing had stopped another Great Depression.
Since May 26, 1896, the Dow Jones list of companies has been reconfigured 49 times. Most recently, Kraft Foods Group, Inc. (NASDAQ/KRFT) was removed from the list in favor of UnitedHealth Group Incorporated (NYSE/UNH).
A broader index than the name implies, the most recent configuration of the DJIA includes: Bank of America Corporation (NYSE/BAC), Caterpillar Inc. (NYSE/CAT), E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Company (NYSE/DD), Exxon Mobile Corporation (NYSE/XOM), JPMorgan Chase & Co. (NYSE/JPM), International Business Machines Corporation (NYSE/IBM), Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ/MSFT), The Procter & Gamble Company (NYSE/PG), Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (NYSE/WMT), and The Walt Disney Company (NYSE/DIS).
There are several ways in which investors can trade the bull and bear markets on the DJIA. Several equities are designed to trade at par with or on the inverse of the DJIA. Investors can also purchase futures and options through the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE).














