Dividend Capture using Covered Calls
Post on: 10 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
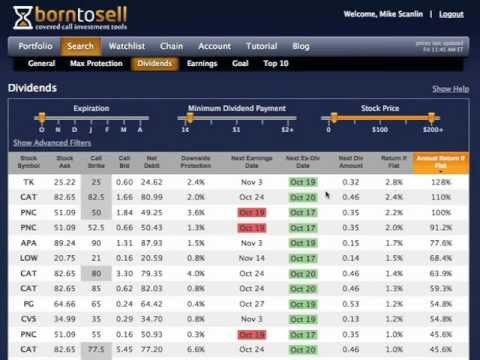
Some stocks pay generous dividends every quarter. You qualify for the dividend if you are holding on the shares before the ex-dividend date.
Many people have tried to buy the the shares just before the ex-dividend date simply to collect the dividend payout only to find that the stock price drop by at least the amount of the dividend after the ex-dividend date, effectively nullifying the earnings from the dividend itself.
There is, however, a way to go about collecting the dividends using options. On the day before ex-dividend date, you can do a covered write by buying the dividend paying stock while simultaneously writing an equivalent number of deep in-the-money call options on it. The call strike price plus the premiums received should be equal or greater than the current stock price.
On ex-dividend date, assuming no assignment takes place, you will have qualified for the dividend. While the underlying stock price will have drop by the dividend amount, the written call options will also register the same drop since deep-in-the-money options have a delta of nearly 1. You can then sell the underlying stock, buy back the short calls at no loss and wait to collect the dividends.
The risk in using this strategy is that of an early assignment taking place before the ex-dividend date. If assigned, you will not be able to qualify for the dividends. Hence, you should ensure that the premiums received when selling the call options take into account all transaction costs that will be involved in case such an assignment do occur.
Example
In November, XYZ company has declared that it is paying cash dividends of $1.50 on 1st December. One day before the ex-dividend date, XYZ stock is trading at $50 while a DEC 40 call option is priced at $10.20. An options trader decides to play for dividends by purchasing 100 shares of XYZ stock for $5000 and simultaneously writing a DEC 40 covered call for $1020.
On ex-dividend date, the stock price of XYZ drops by $1.50 to $48.50. Similarly, the price of the written DEC 40 call option also dropped by the same amount to $8.70.
As he had already qualified for the dividend payout, the options trader decides to exit the position by selling the long stock and buying back the call options. Selling the stock for $4850 results in a $150 loss on the long stock position while buying back the call for $870 resulted in a gain of $150 on the short option position.
As you can see, the profit and loss of both position cancels out each other. All the profit attainable from this strategy comes from the dividend payout — which is $150.
More Articles
Your new trading account is immediately funded with $5,000 of virtual money which you can use to test out your trading strategies using OptionHouse’s virtual trading platform without risking hard-earned money.
Once you start trading for real, your first 150 trades will be commission-free! (Make sure you click thru the link below and quote the promo code ’90FREE’ during sign-up)














