Country risk ratings Country risk inde risk credit ratings economic performance
Post on: 11 Май, 2015 No Comment
The future of the RMB
With falling oil prices sending the currencies of hydrocarbons producers tumbling, amid political instability, conflict risk and weak, unbalanced economies persisting, almost half the world’s sovereigns endured higher risk in 2014.
 
About Euromoney’s Country risk ratings
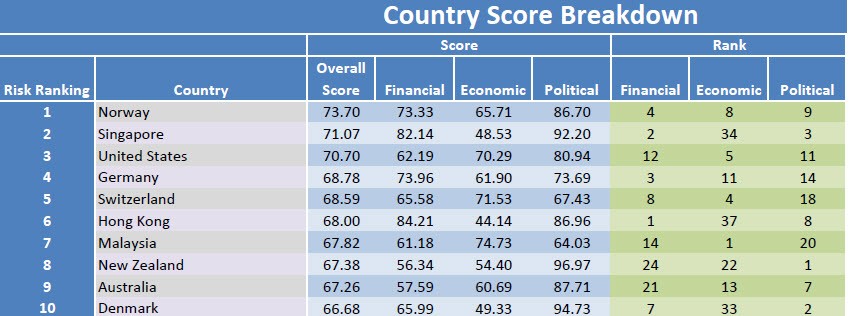
Country risk survey monitoring political and economic stability of countries around the globe.
Euromoney Country Risk evaluates the investment risk of a country, such as risk of default on a bond, risk of losing direct investment, risk to global business relations etc, by taking a qualitative model, which seeks an expert opinion on risk variables within a country (70% weighting) and combining it with three basic quantitative values (30% weighting).
Factors included in the ranking of countries by risk: 
    Political risk 
    Structural assessment
    Debt indicators 
    Credit Ratings 
    Access to bank finance 
    Access to capital markets 
Find out more about Euromoney Country Risk
List of countries ranked
Combined Euromoney Country Risk score
To obtain the overall ECR country risk score, Euromoney assigns a weighting to six categories. The three qualitative expert opinions are political risk (30% weighting), economic performance (30%), and structural assessment (10%). The three quantitative values are debt indicators (10%), credit ratings (10%), access to bank finance/capital markets (10%).
 • The qualitative average
The qualitative average is produced by combining evaluations of political, economic, and structural assessments from experts around the world.
When applying political, economic, and structural assessments to a 100 point scale for the qualitative average only (rather than the full Euromoney Country Risk score), the following weighting is used: political 43%, economic 43%, and structural 14%.
Qualitative assessments
Economic risk: participants rate each country for which they have knowledge from 0-10 across 6 sub factors to equal a score out of 100. The categories of economic risk scored are as follows: bank stability/ risk; GNP outlook; unemployment rate; government finances; monetary policy/ currency stability.
Political risk: participants rate each country for which they have knowledge from 0-10 across 5 sub factors to equal a score out of 100. The categories of political risk scored are as follows: corruption; government non-payments/ non-repatriation; government stability; information access/ transparency; institutional risk; regulatory and policy environment.
Structural risk: participants rate each country for which they have knowledge from 0-10 across 4 sub factors to equal a score out of 100. The categories of structural risk scored are as follows: demographics; hard infrastructure; labour market/ industrial relations; soft infrastructure.
Individual experts must apply a value to each sub factor before their score is accepted into the system.
Individual experts can also modify the sub factor weights to modify their effect on the overall score of 100. The weight of an individual sub factor can be lowered to a minimum of 10% and to a maximum of 30%. This allows the system to capture a second attribute along side of the evaluation of that category, which is the estimated effect of the category. For instance, a user may make a judgement that the single most important issue facing a given country is maintaining the stability of its currency, and so decide to increase the weighting of the monetary policy/ currency stability category from 20% to 30%.
Within each sub factor, ECR also asks experts for further information on the reasons behind each individual score, and these fall under the category of related factors. These are more like poll points, and do not directly affect the score. Instead, they inform a change made to a sub factor score and weight. For example, within the economic risk category of bank stability lie four further related factors: regulatory risk, trading exposures, asset quality and undercapitalisation. Individual experts are able to add more related factors and ignore ones which are not applicable.
The quantitative score factors
• Access to bank finance/capital markets: participants rate each country’s accessibility to international markets on a scale of 0-10 (0=no access at all and 10=full access). These scores are averaged and then weighted to 10%.
• Debt indicators: calculated using the folloiwng ratios from the World Bank’s Global Development Finance figures: total debt stocks to GNP (A), debt service to exports (B); current account balance to GNP (C). Developing countries which do not report complete debt data get a score of zero.
• Credit ratings: nominal values are assigned to sovereign ratings from Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s and Fitch IBCA. The ratings are converted into a score using a set scoring chart. This score is then averaged and the score weighted to 10%. The higher the average value the better.
Where there is no rating, countries score zero.
For full methodology and scoring guidelines, visit  www.euromoneycountryrisk.com/Methodology.aspx . 














