Work Motivation What Drives Employees to Perform
Post on: 22 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
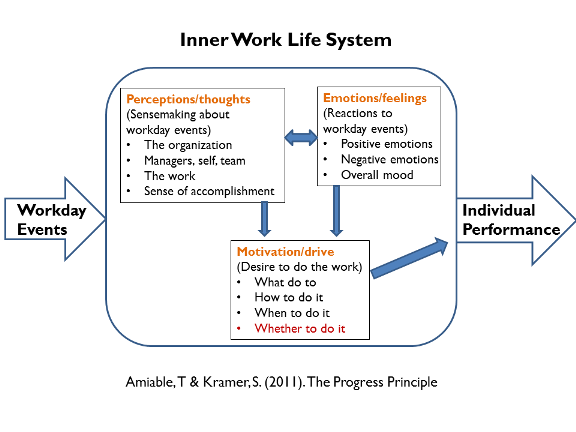
The purpose of the Research Translation is to provide HR professionals with a close-up view of current research from the academic community on different topics of interest in human resource management and to present “golden nuggets” that are thought-provoking and applicable to organizations both today and in the future.
Introduction
Research shows that a number of drivers affect work motivation. These drivers are closely tied to aspects such as perception, stress, change, expectations and personal and professional goals and values. Drivers of work motivation also directly influence job satisfaction. For example, key findings of the SHRM Job Satisfaction Series indicate that the top drivers of employee job satisfaction are benefits, communication between employees and management, compensation, work/life balance, job security and relationship with immediate supervisor. 1 Highlights from following three articles provide additional perspectives on the drivers that influence work motivation.
Re-Examining Salesperson Goal Orientations: Personality Influencers, Customer Orientation and Work Satisfaction
By Eric G. Harris, John C. Mowen, and Tom J. Brown 2
While scholars have pointed out the importance of relationship marketing and the key role of sales knowledge in the establishment of buyer-seller relationships, research regarding salesperson learning motivation has not been readily available. This study uses data from a sample of 190 real estate agents to test the hypothesis that there are relationships between personality influencers, goal motivation, customer/selling orientation and overall work satisfaction. In particular, the study results indicate that learning orientation is important and that the drive for performance positively influences selling motivation.
The Role of Work Context in Work Motivation: A Public Sector Application of Goal and Social Cognitive Theories
By Bradley E. Wright 3
The purpose of this study, based on data analysis from a state government employee survey, was to test a conceptual model that predicts how an organization’s work context may influence work motivation. This model of work motivation, developed by using goal and social cognitive theories, assesses whether aspects of the organization’s work context (e.g. procedural constraints, greater goal conflict, goal ambiguity) have a detrimental impact on work motivation due to their influence on three variables of work motivation: 1) job goal specificity; 2) job difficulty; and 3) self-efficacy. The study results indicate that this motivation model can identify specific leverage points to help increase work motivation—specifically, positively influencing productivity in the public sector.
Working Conditions in Projects: Perceptions of Stress and Motivation Among Project Team Members and Project Managers
By Margareta Gallstedt 4
In many cases, organizations today largely depend on the individual performance of their employees to meet their goals and objectives. Directly related to performance is the extent to which employee perceptions of working conditions are influenced by two key factors: motivation and stress. While projects may be motivating when there are clear goals, there may also be time pressure as a result of incidents such as loss of resources, changing preferences or priorities, or project closures that may lead to changes to earlier set goals. This study considered the impact of the perceptions of stress and motivation on both project team members and project team managers. Two questions were considered: 1) how do project managers and project team members perceive incidents that are typically encountered during the course of projects? and 2) how do they cope with the uncertainties as a result of these incidents? The study findings indicate that over the lifecycle of a project, incidents can result in changes. Further, the study findings also suggest that these changes affect both goals and employee perceptions of working conditions, tasks and the situation. To deal with these changes, employees use a variety of different coping strategies to help reduce stress and uncertainty.
HR Insights
In today’s competitive marketplace, organizations increasingly tie performance to compensation, using the talent of their workforce to maintain or expand strategic goals that benefit the company’s bottom line. HR professionals can best support organizational goals by providing the appropriate resources (e.g. staff with the required knowledge and skills) through strategic hiring and training. HR practitioners can also make a significant contribution to organizational goals by fostering a company culture that is communicative and resourceful and one that rewards innovation, creativity and teamwork.
Endnotes
1 Esen, E. (2004, August). SHRM job satisfaction series survey report. Alexandria, VA: Society for Human Resource Management.
2 Harris, E. G. Mowen, J. C. & Brown, T. J. (2005, Winter). Re-examining salesperson goal orientations: Personality influencers, customer orientation and work satisfaction. Academy of Marketing Science Journal, 33. 1, 19-36.
3 Wright, B. E. (2004, January). The role of work context in work motivation: A public sector application of goal and social cognitive theories. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 14. 1, 59+.
4 Gallstedt, M. (2003). Working conditions in projects: Perceptions of stress and motivation among project team members and project managers. International Journal of Project Management, 21. 6, 449+.
Author: Nancy R. Lockwood, SPHR, GPHR, SHRM Research Department














