The Professional Interbank Forex Market
Post on: 23 Июль, 2015 No Comment
Updated: May 16, 2013 at 10:56 AM
The largest forex trading volumes by far go through the network of professional forex dealers known collectively as the Interbank forex market.
As the name implies, these Interbank dealers usually work for major forex market making banks, their forex brokers or their customers. These larger players tend to trade amounts more than $1 million and execute transactions based on credit lines that banks extend to each other and their customers.
Despite not having a centralized exchange or much formal regulation, this huge currency trading market usually manages to function in an orderly way and provides enough liquidity for almost all commercial forex trades.
As a result, those able to access the Interbank forex market tend to enjoy the best dealing spreads under most trading conditions, although some exceptions do apply such as after major economic data releases as the market digests the new information and adjusts exchange rates accordingly.
Communication in the Interbank Market
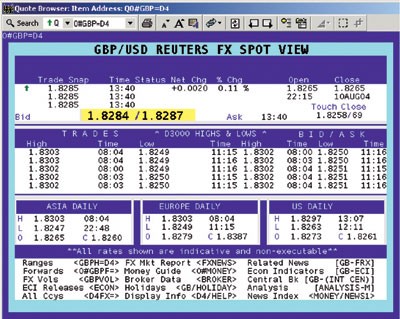
This over the counter or OTC network of forex traders and advisors has traditionally communicated via telephones and direct phone lines to other counterparties in the market. Also, forex brokers often communicate Interbank market prices and dealing activity in the most active currency pairs orally using voice broker boxes.
Nevertheless, recent technologically advances have made electronic trading increasingly popular in the Interbank market. This includes transactions done via professional dealing networks like the Electronic Broking Services or EBS Spot Dealing system and the Reuters Dealing 3000 Spot Matching system.
Who Trades Forex in the Interbank Market and Why
The professional Interbank forex market includes a variety of participants that trade foreign exchange for a number of different reasons.
These forex traders might include individuals working at major commercial banks, central banks, fund managers, international corporations, as well as high net worth individuals.
Most of them either deal forex for hedging or speculative purposes like corporations and hedge funds respectively. Nevertheless, many large banks are market makers that provide liquidity to the market. Also, central banks often adjust their currency reserves and intervene to stabilize their currencies.
Other common reasons to trade forex include:
Handling the import and export requirements of corporations and individuals
Facilitating foreign security or real estate investment transactions
Profiting from short-term changes in the level of forex rates
Managing existing currency positions
Customers of the Interbank Market
Customers with access to the OTC Interbank market via a bank might include large international corporations, fund managers and government’s central banks, as well as high-net-worth individuals that generally deal forex in transaction amounts of more than $1 million.
These customers of banks participating in the professional Interbank forex market tend to deal over the telephone with a particular forex advisor who works on the bank’s dealing desk.
The advisor might call their client regularly with timely market commentary or sometimes even visit with the client in order to offer tailored hedging or trading strategy advice
Furthermore, despite being largely unregulated, the OTC forex market manages to maintain a substantial degree of liquidity as demonstrated by tight dealing spreads and the ability to absorb large transactions without much price movement. This fact illustrates how people acting freely and in their own best interest can still provide an orderly market under most conditions.
Please also see:
Risk Statement: Trading Foreign Exchange on margin carries a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. The possibility exists that you could lose more than your initial deposit. The high degree of leverage can work against you as well as for you.














