Solo 401k
Post on: 28 Май, 2015 No Comment

401k plans are defined in the Internal Revenue Code (Section 401) as retirement savings trusts. A 401(k) Plan is an IRS approved qualified retirement plan. As the name implies, the Solo 401(k) plan is an IRS approved qualified 401(k) plan designed for a self-employed individual or the sole owner-employee of a corporation. It works best when there are no other employees or a very small number of employees.
In 2001, the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act (EGTRRA) was passed. This act clarified how a 401(k) could be used by a self employed person who has no full time employees. It also clarified that the self-employed 401(k) participant can make contributions as the role of employee and employer resulting in very high contribution limits.
To access these benefits an investor must meet two eligibility requirements:
1. The presence of self employment activity.
2. The absence of full-time employees.
A Solo 401(k) offers a self-employed business owner the ability to use his or her retirement funds to make virtually any type of investment on their own without requiring the consent of a custodian. The IRS only describes the type of investments that are prohibited, which are very few. In addition, a Solo 401(k) plan offers a high annual contribution limit (up to $59,000), allows you to borrow up to $50,000 for any purpose, and imposes no custodian fees.
The Advantages of Using a Solo 401(k)?
The Solo 401(k) plan offers most of the characteristics of the Self Directed IRA LLC, including having the ability to make almost any type of investments, including real estate, but without the need to establish an LLC or pay custodian fees. The Solo 401(k) Plan is the most tax-advantageous retirement plan available because of its very high annual contribution limits. The Solo 401K plan also allows you to borrow money from your retirement funds (up to $50,000) and use the funds for any purpose, including help finance your business or pay personal bills.
Am I Eligible to use the Solo 401K Plan?
The Solo 401(k) plan may be used by any individual who is already a business owner or who will be establishing a business and does not have, or plan to have, full-time employees. The Solo 401(k) plan is perfect for independent contractors, such as consultants, home businesses and real estate agents. The owners spouse may also contribute to the plan as long as he or she is an employee of the business.
Use the Solo 401K Plan to Take out a Loan
One of the advantages of the Solo 401K plan is that it allows you to take out a loan from your retirement account. Under Internal Revenue Code Section 72(p), a Solo 401(k) Plan participant is permitted to borrow up to 50% of the total 401(k) value or $50,000 whichever is less tax-free for any reason. Repayment of the loan is based on a schedule provided when the loan is initiated and must be paid back into the account (including interest) over a term of up to five years. Loan payments must be made at least quarterly and at a minimum interest rate of Prime (as of January 1, 2015, the Prime interest rate as per the Wall Street Journal is 3.25%). Failure to make the loan payments may cause a loan default causing taxes and IRS penalties.
For Real Estate Investors
Like the Self-Directed IRA LLC structure, the Solo 401K Plan offers participants the ability to invest in real estate tax-free! All income and gains generated by the investment will flow back to the 401(k) Plan tax-free!
In addition, in the case of an IRA using nonrecourse debt to finance a real estate purchase (only nonrecourse debt is permitted as recourse debt associated with an IRA investment would trigger a prohibited transaction), income or gains generally from the investment would trigger a penalty tax called the Unrelated Debt Financed Income (UDFI) tax. UDFI is a type of unrelated business taxable income which if triggered could subject the IRA to close to a 40% tax for 2015. However, a 401(k) Plan using nonrecourse financing for a real estate investment is exempt from the UDFI tax (Internal Revenue Code Section 514(c)(9).
How do I Initially fund the Solo 401K Plan?
Like the Self-Directed IRA LLC, to initially fund the Solo 401(k) you may rollover funds from Traditional IRAs, SEP Plans, previous employer 401(k) plans, Money Purchase plans, Profit Sharing plans, Keogh plans, Defined Benefit plans, 403(b) plans and Rollover IRAs tax-free! This is accomplished by setting up a Trust account for the Solo 401(k) and directly transferring the funds from the current Custodian to the trust bank account. The trust account can be opened at any local bank or credit union.
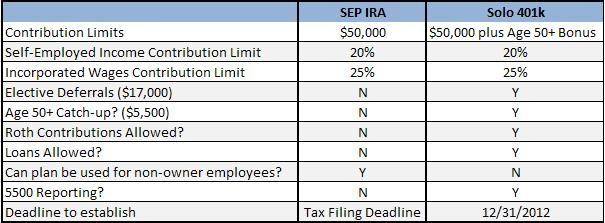
How much Money Can I Contribute to the Solo 401K Plan?
Under the 2015 Solo 401(k) contribution rules, a plan participant under the age of 50 can make a maximum employee deferral contribution in the amount of $18,000. That amount can be made in pre-tax or after-tax (Roth). On the profit sharing side, the business can make a 25% (20% in the case of a sole proprietorship or single member LLC) profit sharing contribution up to a combined maximum, including the employee deferral, of $53,000, an increase of $1,000 from 2014.
For plan participants over the age of 50, an individual can make a maximum employee deferral contribution in the amount of $24,000. That amount can be made in pre-tax or after-tax (Roth). On the profit sharing side, the business can make a 25% (20% in the case of a sole proprietorship or single member LLC) profit sharing contribution up to a combined maximum, including the employee deferral, of $59,000, an increase of $1,500 from 2014.














