Philly Fed Survey Valuable To Investors
Post on: 25 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
# Of Up Periods / Down Periods: Indicates the number of quarters the portfolio has generated a positive / negative return over the given time period.
An AAA rating is the highest possible rating assigned to the bonds of an issuer by credit rating agencies. An issuer that is rated AAA has an exceptional degree of creditworthiness and can easily meet its financial commitments. Ratings agencies such as Standard & Poors and Fitch Ratings use AAA to indicate the highest credit quality, while Moodys uses Aaa.
An AA+ rating is generally one step below the highest rating (AAA) assigned to the bonds of an issuer by credit rating agencies. This rating signifies that there is little to no risk of default and is often assigned to securities that have some type of insurance backing.
The return that an asset achieves over a certain period of time. This measure looks at the appreciation or depreciation (expressed as a percentage) that an asset usually a stock or a mutual fund achieves over a given period of time. Absolute return differs from relative return because it is concerned with the return of a particular asset and does not compare it to any other measure or benchmark.
ADP National Employement Report
The ADP National Employment Report®, sponsored by ADP®, was developed and is maintained by Macroeconomic Advisers, LLC. It is a measure of employment derived from an anonymous subset of roughly 500,000 U.S. business clients. During the twelve-month period through December 2009, this subset averaged over 360,000 U.S. business clients and over 22 million U.S. employees working in all private industrial sectors.
ADP Private Jobs Report
The ADP National Employment Report (ADP Private Jobs Report) provides a monthly snapshot of U.S. nonfarm private sector employment based on actual transactional payroll data. The report is based on payroll data from over half of ADPs U.S. business clients, which represents about 24 million employees from all 19 of the major North American Industrial Classification (NAICS) private industrial sectors.
Alpha: Measures the difference between a portfolio’s actual returns and its expected performance, given its level of risk as measured by Beta. A positive (negative) Alpha indicates the portfolio has performed better (worse) than its Beta would predict.
American Association of Individual Investors
American Association of Individual Investors (AAII) is a nonprofit organization that arms individual investors with the education and tools they need to build wealth. From stock investing to financial planning and retirement funding, AAII covers all your needs.
An Annuity is a financial product sold by financial institutions that is designed to accept and grow funds from an individual and then, upon annuitization, pay out a stream of payments to the individual at a later point in time. Annuities are primarily used as a means of securing a steady cash flow for an individual during their retirement years.
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is a regional economic forum established in 1989 to help foster trade and cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region.
Asset-Backed Securities
Asset-backed securities are bonds or notes backed by financial assets such as non-mortgage loans including credit card receivables, auto loans, manufactured-housing contracts, and home-equity loans.
An Asset Class is a group of securities that exhibit similar characteristics, behave similarly in the marketplace, and are subject to the same laws and regulations. The three main asset classes are equities (stocks), fixed-income (bonds) and cash equivalents (money market instruments).
Average Duration: A common gauge of the price sensitivity of a fixed income asset or portfolio to a change in interest rates
Average Up / Down Return: Measures the average return generated during quarters that the portfolio had a positive /negative return.
The BAA spread refers to the yield on corporate bonds above the rate on comparable maturity Treasury debt, and is a market-based estimate of the amount of fear in the bond market. BAA-rated bonds are the lowest quality bonds still considered investment-grade, rather than high-yield. Therefore, they best reflect the stresses across the quality spectrum. A rise in BAA spreads acts as a negative for the CCI.
Balanced portfolio is a method of portfolio allocation designed to provide both income and capital appreciation while avoiding excessive risk.
Bank Loan portfolios primarily invest in floating-rate bank loans instead of bonds. In exchange for their credit risk, these loans offer high interest payments that typically float above a common short-term benchmark such as the London Interbank Offered Rate, or LIBOR.
Barclay’s Aggregate Bond index
The Barclays Aggregate Bond Index represents securities that are SEC-registered, taxable, and dollar denominated. The index covers the U.S. investment-grade fixed rate bond market, with index components for government and corporate securities, mortgage pass-through securities, and asset-backed securities.
Barclay’s High-Yield Bond Index
Barclays High-Yield Bond Index is an unmanaged index of corporate bonds rated below investment grade by Moody’s, S&P or Fitch Investor Service. The index also includes bonds not rated by the ratings agencies.
Barclay’s Municipal Bond Index
The Barclays Municipal Bond Index is a market capitalization-weighted index of investment-grade municipal bonds with maturities of at least one year. All indices are unmanaged and include reinvested dividends. One cannot invest directly in an index. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Basel III is a comprehensive set of reform measures designed to improve the regulation, supervision and risk management within the banking sector. The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision published the first version of Basel III in late 2009, giving banks approximately three years to satisfy all requirements. Largely in response to the credit crisis, banks are required to maintain proper leverage ratios and meet certain capital requirements.
Basis Points are a unit relating to interest rates that is equal to 1/100th of a percentage point. It is frequently but not exclusively used to express differences in interest rates of less than 1%.
Batting Average is a statistical measure used to measure an investment managers ability to meet or beat an index. Batting average is calculated by dividing the number of days (or months, quarters, etc.) in which the manager beats or matches the index by the total number of days (or months, quarters, etc.) in the period of question and multiplying that factor by 100.
An obligation rated BBB exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
The Beige Book is a commonly used name for the Fed report called the Summary of Commentary on Current Economic Conditions by Federal Reserve District. It is published just before the FOMC meeting on interest rates and is used to inform the members on changes in the economy since the last meeting.
Best Quarter / Worst Quarter Return: Indicates the highest / lowest quarterly rate of return generated by the portfolio.
Beta measures a portfolios volatility relative to its benchmark. A Beta greater than 1 suggests the portfolio has historically been more volatile than its benchmark. A Beta less than 1 suggests the portfolio has historically been less volatile than its benchmark.
Breakeven yield is the point at which the money brought in from the sale of a product or service is equal to the cost of marketing the product or services. The breakeven point is the point at which no profit or loss is being derived. Breakeven yield allows a decision-maker to have knowledge about the minimum volume yield required to earn a specific rate of return on a product or service.
Bubble describes an economic cycle characterized by rapid expansion followed by a contraction.
Build America Bonds
The issuance of Build America Bonds (BAB) began in April of 2009. They were authorized by the ARRA economic stimulus of 2009 and can be issued for qualifying infrastructure projects. They are taxable municipal bonds and are considered a category of bonds.
The Business Cycle is recurring and fluctuating levels of economic activity that an economy experiences over a long period of time. The five stages of the business cycle are growth (expansion), peak, recession (contraction), trough and recovery. At one time, business cycles were thought to be extremely regular, with predictable durations, but today they are widely believed to be irregular, varying in frequency, magnitude and duration.
Business inventories
Business inventories are the dollar amount of inventories held by manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers. The level of inventories in relation to sales is an important indicator of the near-term direction of production activity.
The Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (CCAR) is an annual exercise by the Federal Reserve to assess whether the largest bank holding companies operating in the United States have sufficient capital to continue operations throughout times of economic and financial stress and that they have robust, forward-looking capital-planning processes that account for their unique risks.
Challenger, Gray & Christmas
Challenger, Gray & Christmas is the oldest executive outplacement firm in the United States. The firm conducts regular surveys and issues reports on the state of the economy, employment, job-seeking, layoffs, and executive compensation.
Chicago Fed National Activity Index
The Chicago Fed National Activity Index (CFNAI) is a monthly index designed to gauge overall economic activity and related inflationary pressure.
Chicago Purchasing Managers Index (CFMMI)
The Chicago Area Purchasing Manager Index that is read on a monthly basis to gauge how manufacturing activity is performing. This index is a true snapshot of how manufacturing and corresponding businesses are performing for a given month. A reading of 50 or above is considered a positive reading. Anything below 50 is considered to indicate a decline in activity. Readings of the index have the ability to shift the days trading session one way or another based on the results.
Chicago Fed Midwest Manufacturing Index (CFMMI)
The Chicago Fed Midwest Manufacturing Index (CFMMI) is a monthly estimate by major industry of manufacturing output in the Seventh Federal Reserve District states of lllinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan and Wisconsin. It is a composite index of 15 manufacturing industries that uses hours worked data to measure monthly changes in regional activity.
A short-term unsecured promissory note issued by a finance company or a relatively large industrial firm. The notes are generally sold at a discount from face value with maturities ranging from 30 to 270 days. Although the large denominations ($25,000 minimum) of these notes usually keep individual investors out of this market, the notes are popular investments for money market mutual funds. Used interchangeably with the term paper.
A commodity is a basic good used in commerce that is interchangeable with other commodities of the same type. Commodities are most often used as inputs in the production of other goods or services. The quality of a given commodity may differ slightly, but it is essentially uniform across producers.
Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office is a non-partisan arm of Congress, established in 1974, to provide Congress with non-partisan scoring of budget proposals.
Consumer Confidence Index
The Consumer Confidence Index is based on consumers perceptions of current business and employment conditions, as well as their expectations for six months hence regarding business conditions, employment, and income. Three thousand households across the country are surveyed each month. In general, while the level of consumer confidence is associated with consumer spending, the two do not move in tandem each and every month.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services.
Consumer Price Inflation
Consumer Price Inflations is the retail price increase as measured by a consumer price index (CPI).
Consumer Sentiment Report
The Consumer Sentiment report refers to a report published by the University of Michigan, in which the University’s Consumer Survey Center questions 500 households each month on their financial conditions and attitudes about the economy. Consumer sentiment is important because it is directly related to the strength of consumer spending. Preliminary estimates for a month are released at mid-month. Final estimates for a month are released near the end of the month.
Core CPI is a subset of the total Consumer Price Index (CPI) that excludes the highly volatile food and energy prices. It is released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics around the middle of each month. Compare to Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE); Core PPI; Producer Price Index (PPI).
Core Inflation is a measure of inflation that excludes certain items that face volatile price movements. Core inflation eliminates products that can have temporary price shocks because these shocks can diverge from the overall trend of inflation and give a false measure of inflation.
Correlation is a statistical measure of how two securities move in relation to each other. Correlations are used in advanced portfolio management.
Credit Default Swap (CDS)
A Credit Default Swap (CDS) is designed to transfer the credit exposure of fixed income products between parties. The buyer of a credit swap receives credit protection, whereas the seller of the swap guarantees the credit worthiness of the product. By doing this, the risk of default is transferred from the holder of the fixed income security to the seller of the swap.
Credit Quality is one of the principal criteria for judging the investment quality of a bond or bond mutual fund. As the term implies, credit quality informs investors of a bond or bond portfolios credit worthiness, or risk of default.
Credit ratings are published rankings based on detailed financial analyses by a credit bureau specifically as it relates the bond issues ability to meet debt obligations. The highest rating is AAA, and the lowest is D. Securities with credit ratings of BBB and above are considered investment grade.
Credit risk is the risk of loss of principal or loss of a financial reward stemming from a borrowers failure to repay a loan or otherwise meet a contractual obligation. Credit risk arises whenever a borrower is expecting to use future cash flows to pay a current debt. Investors are compensated for assuming credit risk by way of interest payments from the borrower or issuer of a debt obligation. Credit risk is closely tied to the potential return of an investment, the most notable being that the yields on bonds correlate strongly to their perceived credit risk.
The credit spread is the yield the corporate bonds less the yield on comparable maturity Treasury debt. This is a market-based estimate of the amount of fear in the bond market Bass-rated bonds are the lowest quality bonds that are considered investment-grade, rather than high-yield. They best reflect the stresses across the quality spectrum.
Currency Forward is a forward contract in the forex market that locks in the price at which an entity can buy or sell a currency on a future date. Also known as outright forward currency transaction, forward outright or FX forward.
Current Conditions Index (CCI)
The Current Conditions Index (CCI) is a weekly measure of the conditions that underpin LPL Financial Research’s outlook for the markets and economy. It provides real-time insight into the trends that shape our recommended actions to manage portfolios and has proven to be a useful investment decision-making tool. This index is not intended to be a leading index or predict future conditions; it is a coincident measure of where they are now. Because our index is tailored to the current environment, the components of the CCI are periodically changed to retune the index to those factors most critical to the markets and economy, so it may continue to be a valuable investment decision-making tool.
Current account is the difference between a nation’s savings and its investment.
Dallas Fed Manufacturing Index
The Dallas Fed conducts the Texas Manufacturing Outlook Survey monthly to obtain a timely assessment of the state’s factory activity. Firms are asked whether output, employment, orders, prices, and other indicators increased, decreased, or remained unchanged over the previous month. Survey responses are used to calculate an index for each indicator.
The Deutscher Aktien Index (DAX) is a stock index that represents 30 of the largest and most liquid German companies that trade on the Frankfurt Exchange.
The debt ceiling refers to the maximum amount of money the United States Federal Government can borrow, and is set by law (created under the Second Liberty Bond Act of 1917).
Debt-to-GDP is a measure of a countrys federal debt in relation to its gross domestic product (GDP). By comparing what a country owes and what it produces, the debt-to-GDP ratio indicates the countrys ability to pay back its debt. The ratio is a coverage ratio on a national level.
Default Rate is the interest rate charged to a borrower when payments on a revolving line of credit are overdue. This higher rate is applied to outstanding balances in arrears in addition to the regular interest charges for the debt.
Default rate is the rate in which debt holders default on the amount of money that they owe. It is often used by credit card companies when setting interest rates, but also refers to the rate at which corporations default on their loans. Default rates tend to rise during economic downturns, since investors and businesses see a decline in income and sales while still required to pay off the same amount of debt.
Default Risk is when companies or individuals will be unable to make the required payments on their debt obligations. Lenders and investors are exposed to default risk in virtually all forms of credit extensions. To mitigate the impact of default risk, lenders often charge rates of return that correspond the debtors level of default risk. The higher the risk, the higher the required return, and vice versa.
Deflation is a general decline in prices, often caused by a reduction in the supply of money or credit.
A security whose price is dependent upon or derived from one or more underlying assets. The derivative itself is merely a contract between two or more parties. Its value is determined by fluctuations in the underlying asset. The most common underlying assets include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates and market indexes.
Dow Jones Industrial Average is the most widely used indicator of the overall condition of the stock market, a price-weighted average of 30 actively traded blue chip stocks, primarily industrials. The 30 stocks are chosen by the editors of the Wall Street Journal. The Dow is computed using a price-weighted indexing system, rather than the more common market cap-weighted indexing system.
Dow Jones Industrial Average Index
The Dow Jones Industrial Average Index is comprised of U.S.-listed stocks of companies that produce other (non-transportation and non-utility) goods and services. The Dow Jones Industrial Averages are maintained by editors of The Wall Street Journal. While the stock selection process is somewhat subjective, a stock typically is added only if the company has an excellent reputation, demonstrates sustained growth, is of interest to a large number of investors and accurately represents the market sectors covered by the average. The Dow Jones averages are unique in that they are price weighted; therefore their component weightings are affected only by changes in the stocks’ prices.
Dow Jones Transportation Average Index
The Dow Jones Transportation Average is a price-weighted index that covers twenty companies in the transportation industry.
The discount rate: The rate at which member banks may borrow short term funds directly from a Federal Reserve Bank. The discount rate is one of the two interest rates set by the Fed, the other being the Federal funds rate. The Fed actually controls this rate directly, but this fact does not really help in policy implementation, since banks can also find such funds elsewhere.
The DuPont method of performance measurement that was started by the DuPont Corporation in the 1920s. With this method, assets are measured at their gross book value rather than at net book value in order to produce a higher return on equity (ROE). It is also known as DuPont identity.
Durable Goods Orders
Durable goods orders refer to an economic indicator released monthly by the Bureau of Census that reflects new orders placed with domestic manufacturers for delivery of factory hard goods (durable goods) in the near term or future. Durable goods orders come in two releases per month: the advance report on durable goods and the manufacturers shipments, inventories and orders.
Duration is a measure of the sensitivity of the price (the value of principal) of a fixed-income investment to a change in interest rates. It is expressed as a number of years. Rising interest rates mean falling bond prices, while declining interest rates mean rising bond prices. The bigger the duration number, the greater the interest-rate risk or reward for bond prices.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization EBITDA
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA) is essentially net income with interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization added back to it, and can be used to analyze and compare profitability between companies and industries because it eliminates the effects of financing and accounting decisions.
Eurodollars are U.S. dollar denominated time deposits held at foreign banks. Given that they are held outside the country, they are not under the jurisdiction of the Federal Reserve.
European Central Bank (ECB)
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central bank responsible for the monetary system of the European Union (EU) and the euro currency. The bank was formed in Germany in June 1998 and works with the other national banks of each of the EU members to formulate monetary policy for the European Union.
An emerging market is a nation that is progressing toward becoming advanced, as shown by some liquidity in local debt and equity markets and the existence of some form of market exchange and regulatory body.
Emerging Market Debt (EMD)
Emerging market debt (EMD) is a term used to describe bonds issued by less developed countries. This type of debt is primarily issued by sovereign (government) issuers, and may be denominated in local currencies, or more heavily used currencies such as the Dollar or Euro.
Empire State Manufacturing Index
The Empire State Manufacturing Index is a seasonally adjusted index that tracks the results of the Empire State Manufacturing Survey. The survey is distributed to roughly 175 manufacturing executives and asks questions intended to gauge both the current sentiment of the executives and their six-month outlook on the sector.
Empire State Manufacturing Survey
Empire State Manufacturing Survey is a monthly survey of manufacturers in New York State conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Employment Situation Report
The monthly jobs report (known as the employment situation report) is a set of labor market indicators based on two separate surveys distributed in one monthly report by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The report includes the unemployment rate, non-farm payroll employment, the average number of hours per week worked in the non-farm sector, and the average basic hourly rate for major industries.
Earnings per share (EPS) is the portion of a companys profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. EPS serves as an indicator of a companys profitability. Earnings per share is generally considered to be the single most important variable in determining a shares price. It is also a major component used to calculate the price-to-earnings valuation ratio.
Equity Sensitivity: As investors move further down in the capital structure, equity sensitivity begins to play a larger role. When investors look for less yield and more total return (capital appreciation) in certain asset classes, the equity sensitivity also plays an increasing role in absolute risk. Investments such as convertible bonds, preferred stocks, and dividend-paying stocks have higher correlation to the equity markets and are more subject to equity sensitivity than fixed income investments such as U.S. Treasuries.
Euro Interbank Offer Rate (EURIBOR)
The rate of interest at which prime banks borrow funds from other prime banks in the European Union (EU) interbank market.
Eurozone Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)
Eurozone Unemployment
Eurozone Retail sales
Euro STOXX 50 Index
The EURO STOXX 50 Index is a blue-chip index for the Eurozone, which covers 50 stocks from 12 Eurozone countries: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal and Spain.
Excess Returns are the returns in excess of the risk-free rate or in excess of a market measure, such as an index fund.
Existing Home Sales
Existing home sales is a measure of the number and price of sales of single family homes other than new construction.
Federal Reserve (Fed)
The central bank of the United States and the most powerful financial institution in the world. The Federal Reserve Bank was founded by the U.S. Congress in 1913 to provide the nation with a safe, flexible and stable monetary and financial system. It is based on a federal system that comprises a central governmental agency (the Board of Governors) in Washington, DC and 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks that are each responsible for a specific geographic area of the U.S. The Federal Reserve Bank is considered to be independent because its decisions do not have to be ratified by the President or any other government official. However, it is still subject to Congressional oversight and must work within the framework of the government’s economic and financial policy objectives. Often known simply as “the Fed.
Fed Funds Futures are a product offered by the Chicago Board of Trade which allow investors to speculate on what the Federal Reserve will do with interest rates.
Fed Funds Futures Curve
The Fed funds futures curve graphically represents the anticipated Fed funds rate at future points in time.
The Fed funds rate is the interest rate on loans by the Fed to banks to meet reserve requirements.
floating rate bank loan
Floating rate bank loans are loans issued by below investment grade companies for short term funding purposes with higher yield than short-term debt and involve risk.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is the branch of the Federal Reserve Board that determines the direction of monetary policy. The eleven-person FOMC is composed of the seven-member board of governors, and the five Federal Reserve Bank presidents. The president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York serves continuously, while the presidents of the other regional Federal Reserve Banks rotate their service in one-year terms.
Forward guidance is a tool used by a central bank to exercise its power in monetary policy in order to influence, with their own forecasts, market expectations of future levels of interest rates.
Forward Price To Earnings is a measure of the price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) using forecasted earnings for the P/E calculation. While the earnings used are just an estimate and are not as reliable as current earnings data, there is still benefit in estimated P/E analysis. The forecasted earnings used in the formula can either be for the next 12 months or for the next full-year fiscal period.
Free cash flow (FCF) measure of financial performance calculated as operating cash flow minus capital expenditures. FCF represents the cash that a company is able to generate after laying out the money required to maintain or expand its asset base. Free cash flow is important because it allows a company to pursue opportunities that enhance shareholder value. Without cash, its tough to develop new products, make acquisitions, pay dividends and reduce debt.
The FTSE 100 is an index of blue-chip stocks on the London Stock Exchange.
The term Futures refers to future contracts, a financial contract obligating the buyer to purchase an asset (or the seller to sell an asset) at a predetermined future date and price. Contracts detail the quality and quantity of the underlying asset, and are standardized to facilitate trading on a futures exchange. Futures are used to either hedge or speculate on the price movement of an underlying asset, such as a physical commodity or financial instrument.
The Group of Twenty (G-20) Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors is the premier forum for our international economic development that promotes open and constructive discussion between industrial and emerging-market countries on key issues related to global economic stability. By contributing to the strengthening of the international financial architecture and providing opportunities for dialogue on national policies, international co-operation, and international financial institutions, the G-20 helps to support growth and development across the globe.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the monetary value of all the finished goods and services produced within a countrys borders in a specific time period, though GDP is usually calculated on an annual basis. It includes all of private and public consumption, government outlays, investments and exports less imports that occur within a defined territory.
General Obligation Bonds
General Obligation(GO) bonds are municipal bonds backed by the credit and taxing power of the issuing jurisdiction rather than the revenue from a given project.
Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS): A standardized classification system for equities developed jointly by Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) and Standard & Poors. The GICS methodology is used by the MSCI indexes, which include domestic and international stocks, as well as by a large portion of the professional investment management community. The GICS hierarchy begins with 10 sectors and is followed by 24 industry groups, 67 industries and 147 sub-industries. Each stock that is classified will have a coding at all four of these levels. The 10 GIC Sectors are as follows: Energy, Materials, Industrials, Consumer Discretionary, Consumer Staples, Health Care, Financials, Information Technology, Telecommunication Services, and Utilities.
Global Macro Strategy
Global Macro Strategy is a hedge fund strategy that bases its holdingssuch as long and short positions in various equity, fixed income, currency, and futures marketsprimarily on overall economic and political views of various countries (macroeconomic principles).
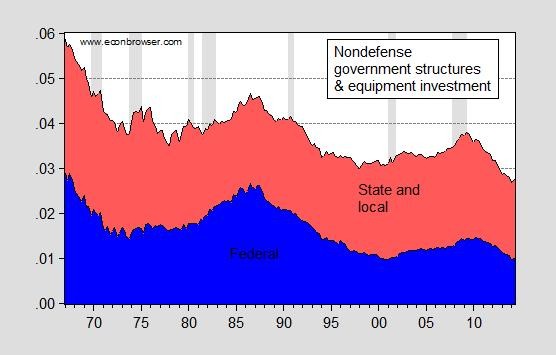
Government Employment vs Private Employment
Private employment includes persons employed at nonfarm establishments outside federal, state and local government. Government or public sector employment includes employees at Federal, state and local governments.
Gross Expense Ratio
The gross expense ratio is the funds total annual operating expense ratio. It is gross of any fee waivers or expense reimbursements.
Guaranteed Lifetime Withdrawal Benefit (GLWB)
Guaranteed Lifetime Withdrawal Benefit (GLWB) is a rider on a variable annuity that allows minimum withdrawals from the invested amount without having to annuitize the investment. The amount that can be withdrawn is based on a percentage of the total amount invested in the annuity.
The Hang Seng index is a market capitalization weighted index which tracks daily changes of the 48 largest companies in the Hong Kong stock market.
Housing starts are the number of new residential construction projects that have begun during any particular month.
The presidents of regional Federal Reserve Banks are commonly classified as hawks or doves. Hawks generally favor tighter monetary policy, with less monetary support from the Federal Reserve. Doves are the opposite, generally favoring easing of monetary policy.
High Yield bond portfolios concentrate on lower-quality bonds, which are riskier than those of higher-quality companies. These portfolios generally offer higher yields than other types of portfolios, but they are also more vulnerable to economic and credit risk. These portfolios primarily invest in U.S. high-income debt securities where at least 65% or more of bond assets are not rated or are rated by a major agency such as Standard & Poors or Moodys at the level of BB (considered speculative for taxable bonds) and below.
High-Yield spread is the yield differential between the average yield of high-yield bonds and the average yield of comparable maturity Treasury bonds.
Industrial Production
The Federal Reserves monthly index of industrial production and the related capacity indexes and capacity utilization rates cover manufacturing, mining, and electric and gas utilities. The industrial sector, together with construction, accounts for the bulk of the variation in national output over the course of the business cycle. The industrial detail provided by these measures helps illuminate structural developments in the economy.
Information Ratio: A risk-adjusted return measure that indicates the risk of the portfolio relative to the benchmark. It is the excess return divided by the Tracking Error.
IFO Business Climate Index
The IFO Business Climate Index is a leading economic indicator in Germany. Data is compiled from surveys sent to 7000 participants from firms in construction, manufacturing, retailing, and wholesaling, who are asked to assess their current business situation as well as their business outlook for the next six months.
The Ifo Institute is one of the leading economic research institutes in Europe and at the same time the one most often quoted in the German media.
Initial Jobless Claims
Initial Jobless Claims is a measure of the number of jobless claims filed by individuals seeking to receive state jobless benefits. This number is watched closely by financial analysts because it provides insight into the direction of the economy. Higher initial claims correlate with a weakening economy.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
An initial Public Offering (IPO) is the first sale of stock by a private company to the public.
An Insured Bond is a bond with interest and principle payments insured by a third party. Insured bonds are usually found as a feature of municipal bonds; they are purchased, underwritten and repackaged by a financial guarantee company who then sells the issue to investors.
Interest Rate Risk is the risk that an investments value will change due to a change in the absolute level of interest rates, in the spread between two rates, in the shape of the yield curve or in any other interest rate relationship. Such changes usually affect securities inversely and can be reduced by diversifying (investing in fixed-income securities with different durations) or hedging (e.g. through an interest rate swap).
International Council of Shopping Centers (ISCS)
International Council of Shopping Centers (ISCS) measured nominal same-store or comparable store sales excluding restaurant and vehicle demand.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization created for the purpose of promoting global monetary and exchange stability, facilitating the expansion and balanced growth of international trade, and assisting in the establishment of a multilateral system of payments for current transactions.
Investment Company Institute (ICI)
The Investment Company Institute (ICI) is the national association of U.S. investment companies, including mutual funds, closed-end funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and unit investment trusts (UITs). Members of ICI manage total assets of $11.18 trillion and serve nearly 90 million shareholders.
Jobless Claims is the number of people who are filing or have filed to receive unemployment insurance benefits, as reported weekly by the U.S. Department of Labor. There are two categories of jobless claims initial, which comprises people filing for the first time, and continuing, which consists of unemployed people who have been receiving unemployment benefits for a while. Jobless claims are an important leading indicator on the state of the employment situation and the health of the economy. Average weekly initial jobless claims are one of the 10 components of The Conference Board Leading Economic Index.
Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) is a survey done by the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics to help measure job vacancies. It collects data from employers including retailers, manufacturers and different offices each month. Respondents to the survey answer quantitative and qualitative questions about their businesses employment, job openings, recruitment, hires and separations. The JOLTS data is published monthly and by region and industry.
JP Morgan Emerging Market Bond Index
The JPMorgan Emerging Markets Bond Index Global (EMBI Global) tracks total returns for traded external debt instruments in the emerging markets, and is an expanded version of the JPMorgan EMBI+. As with the EMBI+, the EMBI Global includes U.S. dollar-denominated Brady bonds, loans, and Eurobonds with an outstanding face value of at least $500 million. It covers more of the eligible instruments than the EMBI+ by relaxing somewhat the strict EMBI+ limits on secondary market trading liquidity
The Korea Composite Stock Price Index or KOSPI is the index of all common stocks traded on the Stock Market Division—previously, Korea Stock Exchange—of the Korea Exchange.
Korea Composite Stock Price Index
The Korea Composite Stock Price Index or KOSPI is the index of all common stocks traded on the Stock Market Division—previously, Korea Stock Exchange—of the Korea Exchange.
An economic indicator that changes before the economy has changed. Examples of leading indicators include production workweek, building permits, unemployment insurance claims, money supply, inventory changes, and stock prices. The Fed watches many of these indicators as it decides what to do about interest rates.
Leading Economic Index
The Leading Economic Index is a monthly publication from the Conference Board that attempts to predict future movements in the economy based on a composite of 10 economic indicators whose changes tend to precede changes in the overall economy.
By using a combination of assets, debt, equity, and interest payments, leverage ratios are used to understand a companys ability to meet it long-term financial obligations. The three most widely used leverage ratios are the debt ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and interest coverage ratio. The debt ratio gives an indication of a company’s total liabilities in relation to their total assets. The higher the ratio, the more leverage the company is using and the more risk it is assuming.
London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR): An interest rate at which banks can borrow funds, in marketable size, from other banks in the London interbank market. The LIBOR is fixed on a daily basis by the British Bankers Association. The LIBOR is derived from a filtered average of the worlds most creditworthy banks interbank deposit rates for larger loans with maturities between overnight and one full year.
Liquidity risk is the risk stemming from the lack of marketability of an investment that cannot be bought or sold quickly enough to prevent or minimize a loss.
The velocity of M1 is personal income divided by the M1 money supply. The M1 money supply consists of (1) currency outside the U.S. Treasury, Federal Reserve Banks, and the vaults of depository institutions; (2) travelers checks of nonbank issuers; (3) demand deposits at commercial banks (excluding those amounts held by depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign banks and official institutions) less cash items in the process of collection and Federal Reserve float; and (4) other checkable deposits (OCDs), consisting of negotiable order of withdrawal (NOW) and automatic transfer service (ATS) accounts at depository institutions, credit union share draft accounts, and demand deposits at thrift institutions.
The money supply is an economic term for the total amount of currency and other liquid assets available in an economy at a point in time. There are several ways to define this number. M1 includes physical money such as coins and currency, checking accounts (demand deposits), and Negotiable Order of Withdrawal (NOW) accounts. M2 includes all of M1, plus time-related deposits, savings deposits, and non-institutional money-market funds.
Low correlation means that different asset types have not performed in the same way: When returns on some asset types were declining, returns on others were gaining.
M3 is a measure of money supply that includes M2 as well as large time deposits, institutional money market funds, short-term repurchase agreements, and other larger liquid assets.
Machine Tool Orders
Machine orders data (also known as machine tool order data) is a figure issued by Japan Machine Tool Builders Association (JMTBA) every month. It serves as one indicator of the Japanese economy.
Managed Futures Funds
Managed Futures funds use systematic quantitative programs to find and invest in positive and negative trends
in the futures markets for financials and commodities. Historically, the benefit of managed futures have been
solid long-term returns with very low correlation to equities and fixed income securities.
Margin debt is debt used to purchase securities within an investment account. Margin debt carries an interest rate, and the amount of margin debt will change daily as the value of the underlying securities changes.
Master Limited Partnership (MLP)
Master Limited Partnership (MLP) is a type of limited partnership that is publicly traded. There are two types of partners in this type of partnership: The limited partner is the person or group that provides the capital to the MLP and receives periodic income distributions from the MLPs cash flow, whereas the general partner is the party responsible for managing the MLPs affairs and receives compensation that is linked to the performance of the venture.
Master Limited Partnership (MLP) Risk
Investing in MLPs involves additional risks as compared to the risks of investing in common stock, including risks related to cash flow, dilution and voting rights. MLPs may trade less frequently than larger companies due to their smaller capitalizations which may result in erratic price movement or difficulty in buying or selling. MLPs are subject to significant regulation and may be adversely affected by changes in the regulatory environment including the risk that an MLP could lose its tax status as a partnership. Additional management fees and other expenses are associated with investing in MLP funds.
McClellan Oscillator
A market breadth indicator that is based on the difference between the number of advancing and declining issues on the NYSE. It is primarily used for short and intermediate term trading.
Merger Arbitrage is a hedge fund strategy in which the stocks of two merging companies are simultaneously bought and sold to create a riskless profit. A merger arbitrageur looks at the risk that the merger deal will not close on time, or at all. Because of this slight uncertainty, the target companys stock will typically sell at a discount to the price that the combined company will have when the merger is closed. This discrepancy is the arbitrageurs profit.
The MICEX Index is a capitalization-weighted composite index calculated based on prices of the 50 most liquid Russian stocks.
The money supply is an economic term for the total amount of currency and other liquid assets available in an economy at a point in time. There are several ways to define this number. M1 includes physical money such as coins and currency, checking accounts (demand deposits), and Negotiable Order of Withdrawal (NOW) accounts. M2 includes all of M1, plus time-related deposits, savings deposits, and non-institutional money-market funds.
Monetary policy is the process through which the monetary authority (central bank, currency board, or other regulatory committee) of a country controls the size and rate of growth of the money supply, which in turn affects interest rates.
Mortgage-Backed Security (MBS) Definition
A mortgage-backed security (MBS) is a type of asset-backed security that is secured by a mortgage, or more commonly a collection (pool) of sometimes hundreds of mortgages. The mortgages are sold to a financial institution (a government agency or investment bank) that securitizes, or packages, the loans together into a security that can be sold to investors. The structure of the MBS may be known as pass-through, where the interest and principal payments from the borrower or homebuyer pass through it to the MBS holder, or it may be more complex, made up of a pool of other MBSs.
MSCI Asia Pacific Index
The MSCI Asia Pacific Index is comprised of more than 900 companies representing approximately 85% of market capitalization for 5 developed and 8 emerging markets countries in the Asia Pacific region.
The MSCI EAFE Index is made up of approximately 1,045 equity securities issued by companies located in 19 countries and listed on the stock exchanges of Europe, Australia, and the Far East. All values are expressed in U.S. dollars. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
MSCI Emerging Markets Index
The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is a free float-adjusted market capitalization index that is designed to
measure equity market performance of emerging markets. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index consists of the following 21 emerging market country indices: Brazil, Chile, China, Colombia, Czech Republic, Egypt,
Hungary, India, Indonesia, Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, Morocco, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Russia, South
Africa, Taiwan, Thailand, and Turkey.
A municipal bond is a debt security issued by a state, municipality, or county to finance its capital expenditures. These bonds are usually exempt from federal taxes, and may also be exempt from state and local taxes, especially if the investor lives in the state where the bond is issued.
Municipal Market Advisors
Municipal Market Advisors is an independent strategy, research and advisory firm.
Municipal-to-Treasury Yield Ratio
The Municipal-to-Treasury Yield compares the current yield of municipal bonds to US Treasuries of the same maturity. If
the ratio is at 100%, it indicates that the yield on a AAA-rated municipal bond is the same as a Treasury security of the same maturity. The ratio can be used as a gauge of price levels of municipal bonds relative to Treasuries.
Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board (MSRB)
The Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board (MSRB) writes investor protection rules and other rules regulating broker-dealers and banks in the United States municipal securities market, including tax-exempt and taxable municipal bonds, municipal notes, and other securities issued by states, cities, and counties or their agencies to help finance public projects or for other public policy purposes.
National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) Housing Market Index
The National Association of Home Builders Housing Market Index is based on a monthly survey of NAHB members designed to take the pulse of the single-family housing market. The survey asks respondents to rate market conditions for the sale of new homes at the present time and in the next 6 months as well as the traffic of prospective buyers of new homes.
The NASDAQ-100 is composed of the 100 largest domestic and international non-financial securities listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market. The Index reflects companies across major industry groups including computer hardware and software, telecommunications, retail/wholesale trade and biotechnology, but does not contain securities of financial companies.
National Association of State Budget Officers (NASBO)
The National Association of State Budget Officers is a professional membership organization for state finance officers, and is the instrument through which the states collectively advance state budget practices.
National Retail Federation (NRF)
The National Retail Federation (NRF) is a retail trade association with members from all types of retail suppliers. Members include department stores, specialty, discount, catalog, internet and independent retailers, restaurant chains and grocers, as well as businesses that supply goods and services to retailers. The NRF forms an umbrella over more than 100 other state, national and international retail associations.
Nelson A. Rockefeller
The Nelson A. Rockefeller Institute of Government is a public policy research institute that conducts studies and related projects on state and local government and finance, American federalism, public management, and New York State issues.
NFIB Small Business Optimism Index
The small business optimism index is compiled from a survey that is conducted each month by the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB) of its members. The index is a composite of ten seasonally adjusted components based on questions on the following: plans to increase employment, plans to make capital outlays, plans to increase inventories, expect economy to improve, expect real sales higher, current inventory, current job openings, expected credit conditions, now a good time to expand, and earnings trend.
The Nikkei 225 Stock Average is a price-weighted index comprised of the top 225 blue-chip companies on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
Non-rated refers to bonds that have not been assigned a credit rating by large credit rating agencies such as Standard & Poor’s or Moody’s
Non-rated bonds have not been issued a rating by bond rating agencies such as Standard and Poors and Moodys. Bonds that have not been rated by an agency are usually considered to be junk bonds or fall below investment grade.
Non-Financial Commercial Paper
Non-financial commercial paper is short term debt (maturities less than 270 days) issued by nonfinancial corporations.
Operation Twist is the name given to a Federal Reserve monetary policy operation that involves the purchase and sale of bonds. Operation Twist describes a monetary process where the Fed buys and sells short-term and long-term bonds depending on their objective.
Outright Monetary Transactions (OMT)
A program of the European Central Bank under which the bank makes purchases (outright transactions) in secondary, sovereign bond markets, under certain conditions, of bonds issued by Eurozone member-states.
P/B Multiple Compares a stocks market value to the value of total assets less total liabilities (book value). Determined by dividing current stock price by common stockholder equity per share (book value), adjusted for stock splits.
The P/E ratio (price-to-earnings ratio) is a measure of the price paid for a share relative to the annual net income or profit earned by the firm per share. It is a financial ratio used for valuation: a higher P/E ratio means that investors are paying more for each unit of net income, so the stock is more expensive compared to one with lower P/E ratio.
A tool for comparing the prices of different common stocks by assessing how much the market is willing to pay a share of each corporation’s estimated future earnings. It is calculated by dividing the current market price of a stock by the earnings per share estimate for the future period.
Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE)
Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) is a measure of price changes in consumer goods and services, targeted towards goods and services consumed by individuals. PCE is released monthly by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
Personal income is the dollar value of income from all sources by individuals in the U.S. and is reported monthly along with personal spending (or personal outlays) by the United States Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
Personal spending is the dollar value of purchases of durable and non-durable goods and services by consumers in the U.S. and is reported monthly along with personal income by the United States Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
Philadelphia Fed Index
Philadelphia Federal Index is a regional federal-reserve-bank index measuring changes in business growth. The index is constructed from a survey of participants who voluntarily answer questions regarding the direction of change in their overall business activities. The survey is a measure of regional manufacturing growth. When the index is above 0 it indicates factory-sector growth, and when below 0 indicates contraction.
The Philadelphia Fed Survey is a business outlook survey used to construct an index that tracks manufacturing conditions in the Philadelphia Federal Reserve district. The Philadelphia Fed survey is an indicator of trends in the manufacturing sector, and is correlated with the Institute for Supply Management (ISM) manufacturing index, as well as the industrial production index.
Porters five forces is a framework for the industry analysis and business strategy development developed by Michael E. Porter of Harvard Business School in 1979. It draws upon Industrial Organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of a market. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An unattractive industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching pure competition, in which available profits for all firms are driven down to zero.
Producer Price Index is an inflationary indicator published by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics to evaluate wholesale price levels in the economy.
Price to book ratio is the stocks capitalization divided by its book value. The value is the same whether the calculation is done for the whole company or on a per-share basis. This ratio compares the markets valuation of a company to the value of that company as indicated on its financial statements.
Price to Book Value
Price to Book Value is a ratio used to compare a stock’s market value to its book value.
Price to Cash Flow is a measure of the market’s expectations of a firm’s future financial health.
Price to Dividends is the ratio of the price of a share on a stock exchange to the dividends per share paid in the previous year, used as a measure of a company’s potential as an investment
Price to Forward Earnings
Price to Forward Earnings is a measure of the price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) using forecasted earnings for the P/E calculation.
Price to Net Asset Value
Price to Net Asset Value per share ratio is calculated as the previous days closing share price divided by net tangible asset value (NTAV) per share.
Principal-Protected Note PPN
Principal-Protected Note PPN is a fixed-income security that guarantees a minimum return equal to the investors initial investment (the principal amount).
Private equity is money invested in companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange or that is invested as part of buyouts of publicly traded companies in order to make them private companies.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
The Producer Price Index (PPI) of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a series of indexes that measure the average change over time in the prices received by domestic producers of goods and services. PPIs measure price change from the perspective of the seller. The headline PPI (for finished goods) is a measure of the average price level for a fixed basket of capital and consumer goods for prices received by producers.
Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)
Purchasing Managers Indexes are economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies, and are intended to show the economic health of the manufacturing sector. A PMI of more than 50 indicates expansion in the manufacturing sector, a reading below 50 indicates contraction, and a reading of 50 indicates no change. The two principal producers of PMIs are Markit Group, which conducts PMIs for over 30 countries worldwide, and the Institute for Supply Management (ISM), which conducts PMIs for the US.
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is an economic theory that estimates the amount of adjustment needed on the exchange rate between countries in order for the exchange to be equivalent to each currencys purchasing power.
Purchasing power risk or Inflation risk
Purchasing power risk is the risk that unexpected changes in consumer prices will penalize an investors real return from holding an investment. Because investments from gold to bonds and stock are priced to include expected inflation rates, it is the unexpected changes that produce this risk. Fixed income securities, such as bonds and preferred stock, subject investors to the greatest amount of purchasing power risk since their payments are set at the time of issue and remain unchanged regardless of the inflation rate.
Quantitative Easing (QE)
Quantitative Easing (QE) refers to the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) current and/or past programs whereby the Fed purchases a set amount of Treasury and/or Mortgage-Backed securities each month from banks. This inserts more money in the economy (known as easing), which is intended to encourage economic growth.
Relative Strength Index
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a technical momentum indicator that compares the magnitude of recent gains to recent losses in an attempt to determine overbought and oversold conditions of an asset.
Retail sales measure the total receipts at retail and food services stores that sell merchandise and related services to final consumers. Data are collected from the Monthly Retail Trade Survey conducted by the U.S. Bureau of the Census. Retail sales cover both the durables and nondurables portions of consumer spending, which together typically accounts for about two-thirds of GDP, and is therefore a key element in economic growth.
An indicator of how profitable a company is relative to its total assets. ROA gives an idea as to how efficient management is at using its assets to generate earnings. Calculated by dividing a companys annual earnings by its total assets, ROA is displayed as a percentage.
The amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders equity. Return on equity measures a corporations profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested.
A calculation used to assess a companys efficiency at allocating the capital under its control to profitable investments. The return on invested capital measure gives a sense of how well a company is using its money to generate returns.
R-Squared: Indicates what percentage of a manager’s movement in performance is explained by movement in performance in its benchmark. R-squared ranges from 0 to 100 and a score of 100 suggests that all movements of a manager’s performance are completely explained by movements in the index.
Russell 1000 Growth Index
Russell 1000® Growth Index measures the performance of those Russell 1000 companies with higher price-to-book ratios and higher forecasted growth values.
The Russell 2000 Index is an unmanaged index generally representative of the 2,000 smallest companies in the Russell Index, which represents approximately 10% of the total market capitalization of the Russell 3000 Index.
An abbreviation of the Bombay Exchange Sensitive Index (Sensex) the benchmark index of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). It is composed of 30 of the largest and most actively-traded stocks on the BSE. Initially compiled in 1986, the Sensex is the oldest stock index in India
The Russell 2000 Index is an unmanaged index generally representative of the 2,000 smallest companies in the Russell Index, which represents approximately 10% of the total market capitalization of the Russell 3000 Index.
The SET index is an index calculated based on the prices of all common stocks that trade on the main board of the Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET), other than those that have been suspended more than one year.
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
A simple moving average (SMA) is a simple, or arithmetic, moving average that is calculated by adding the closing price of the security for a number of time periods and then dividing this total by the number of time periods. Short-term averages respond quickly to changes in the price of the underlying, while long-term averages are slow to react.
Shanghai Composite Index
The Shanghai Stock Exchange Composite Index is a capitalization-weighted index. The index tracks the daily price performance of all A-shares and B-shares listedon the Shanghai Stock Exchange. The index was developed on December 19, 1990 with a base value of 100. Index trade volume on Q is scaled down by a factor of 1000.
Sharpe Ratio: A risk-adjusted measure of performance evaluation. It compares the return above the risk-free rate earned as compared to the corresponding risk assumed by the portfolio, as measured by standard deviation. Good risk-adjusted performance is indicated by a higher Sharpe Ratio
Short selling (also known as shorting or going short) is the practice of selling assets, usually securities, that have been borrowed from a third party (usually a broker) with the intention of buying identical assets back at a later date to return to the lender. The short seller hopes to profit from a decline in the price of the assets between the sale and the repurchase, as the seller will pay less to buy the assets than the seller received on selling them.
Spread is the difference between the bid and the ask price of a security or asset.
Spread (High-Yield)
High-Yield spread is the yield differential between the average yield of high-yield bonds and the average yield of comparable maturity Treasury bonds.
S&P/Case-Shiller Home Price Index
The S&P/Case-Shiller home price index tracks monthly changes in the value of residential real estate in 20 metropolitan regions across the U.S. The composite indexes and the regional indexes are seen by the markets as measuring changes in existing home prices and are based on single-family home re-sales.
The Standard & Poor’s 500 Index is a capitalization-weighted index of 500 stocks designed to measure performance of the broad domestic economy through changes in the aggregate market value of 500 stocks representing all major industries.
Sovereign Debt is the amount of money that a countrys government has borrowed, typically issued as bonds denominated in a reserve currency.
Standard deviation is a historical measure of the variability of returns relative to the average annual return. A higher number indicates higher overall volatility.
The STOXX Europe 600 Index is derived from the STOXX Europe Total Market Index (TMI) and is a subset of the STOXX Global 1800 Index. With a fixed number of 600 components, the STOXX Europe 600 Index represents large, mid and small capitalization companies across 18 countries of the European region: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.
The strategic asset allocation process projects a three- to five-year time period. While the strength of the asset allocation decisions is retested often, we do not anticipate making adjustments until midway through the strategic time frame, which generally is about every two to three years. If significant market fluctuations warrant a change, adjustments may be made sooner.
Swap is a derivative in which counterparties exchange certain benefits of one partys financial instrument for those of the other partys financial instrument. The benefits in question depend on the type of financial instruments involved.
The Tankan Survey is an economic survey conducted by the Bank of Japan of thousands of Japanese businesses, where businesses are asked about current trends and conditions, as well as business expectations for the next quarter and year.
Tapering refers to the Federal Reserve (Fed) slowing the pace of bond purchases in their Quantitative Easing (QE) program. To execute QE, the Fed purchases a set amount of Treasury and Mortgage-Backed bonds each month from banks. This inserts more money in the economy (known as easing), which is intended to encourage economic growth. Lowering the amount of purchases (tapering) would indicate less easing of monetary policy.
Tactical portfolios are designed to be monitored over a shorter time frame to potentially take advantage of opportunities as short as a few months, weeks, or even days. For these portfolios, more timely changes may allow investors to benefit from rapidly changing opportunities within the market.
Tax Awareness: In the Tax Aware portfolios, LPL Financial Research places an emphasis on minimizing the impact of taxes. These portfolios employ investments and strategies that attempt to limit the effect of taxes.
The TED Spread measures the difference between 3-month LIBOR rate and the yield on 3-month Treasury bills. This is an effective measure of the liquidity available to banks. With bank capital adequacy near the center of the current crisis this is an important auge of the stress in the banking system. A rise in the TED Spread acts as a negative on the CCI.
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating securities by analyzing statistics generated by market activity, such as past prices and volume. Technical analysts do not attempt to measure a securitys intrinsic value, but instead use charts and other tools to identify patterns that can suggest future activity.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis is a division of the U.S. federal governments Department of Commerce that is responsible for the analysis and reporting of economic data used to confirm and predict economic trends and business cycles. Reports from the Bureau of Economic Analysis are the foundation upon which many economic policy decisions are made by government, and many investment decisions are made in the private sector by companies and individual investors.
The Bureau Of Labor Statistics
The Bureau Of Labor Statistics is a government agency that produces economic data that reflects the state of the U.S. economy. This data includes the Consumer Price Index, the unemployment rate and the Producer Price Index.
The Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
The Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act is a federal statute in the United States that was signed into law by President Barack Obama on July 21, 2010. The Act implements financial regulatory reform sponsored by the Democratically controlled 111th United States Congress and the Obama administration. Passed as a response to the late-2000s recession.
The Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States. Its unique structure includes a federal government agency, the Board of Governors, in Washington, D.C. and 12 regional Reserve Banks (Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Cleveland, Dallas, Kansas city, Minneapolis, New York, Philadelphia, Richmond, San Francisco, and St. Louis).
The Federal Reserve Bank
The Federal Reserve Bank is the banks that carry out Fed operations, including controlling the money supply and regulating member banks. There are 12 District Feds, headquartered in Boston, New York, Philadelphia, Cleveland, St. Louis, San Francisco, Richmond, Atlanta, Chicago, Minneapolis, Kansas City and Dallas.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF)
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world.
The Irish Stock Exchange (ISEQ)
The Irish Stock Exchange (ISEQ) is a limited company trading equities, government and corporate bonds, investment funds, and specialist securities such as asset-backed debt, securitized bonds, and warrants. Most company securities trade on ISE Xetra, the exchanges electronic trading system, and are settled in CREST. Irish government bonds are traded on EuroMTS, the electronic trading system for market makers in Irish government bonds, and are settled through Euroclear.
The Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
The Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) brings together the governments of countries committed to democracy and the market economy from around the world to support sustainable economic growth, Boost employment, raise living standards, maintain financial stability, assist other countries economic development, and contribute to growth in world trade.
The Plaza Accord is a 1985 agreement among the G-5 nations (France, Germany, the United States, the United Kingdom and Japan) to manipulate exchange rates by depreciating the U.S. dollar relative to the Japanese yen and the German Deutsche mark. Also known as the Plaza Agreement, the Plaza Accords intention was to correct trade imbalances between the U.S. and Germany and the U.S. and Japan, but it only corrected the trade balance with the former.
The Richmond Fed is one of 12 Reserve Banks that, including the Board of Governors, encompasses the Federal Reserve System with offices located in Richmond, Baltimore and Charlotte. Our regions include Virginia, Maryland, the Carolinas, the District of Columbia and most of West Virginia.
The Statutory Debt Limit
The Statutory Debt Limit was established under the Second Liberty Bond Act of 1917 that limits the amount of public debt that can be outstanding. The Statutory Debt Limit, or debt ceiling, prevents the U.S. Treasury from issuing new debt once the limit has been reached. However, the debt limit can be raised, and has often been raised, with approval from the U.S. Congress.
The Supplementary Financing Program (SFP)
The Federal Reserve working with the Treasury Department launched the SFP during the fall of 2008 in response to the financial crisis. The SFP allowed for a vast increase in t-bill issuance and was intended as an emergency measure to improve liquidity in the financial system. As liquidity improved and financial markets recovered the SFP gradually declined before its recent increase.
The United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau is a division of the federal government of the United States Bureau of Commerce that is responsible for conducting the national census at least once every 10 years, in which the population of the United States is counted. The Bureau of Census is also responsible for collecting data on the people, economy and country of the United States.
Tracking Error: A measure of the consistency or volatility (standard deviation) of excess returns relative to a benchmark.
The sum of a companys price-to-earnings, calculated by taking the current stock price and dividing it by the trailing earnings per share for the past 12 months. This measure differs from forward P/E, which uses earnings estimates for the next four quarters.
Treasuries are a marketable, fixed-interest U.S. government debt security. Treasury bonds make interest
payments semi-annually and the income that holders receive is only taxed at the federal level.
Treasury Bill (T-Bill)
A Treasury Bill, or T-Bill is a short-term obligation with a maturity of less than one year backed by the U.S. Government. T-Bills are issued at a discount from par, while the investor receives full par value at maturity. T-Bills don’t pay interest payments like conventional bonds, and instead the price appreciation is the return the investor receives.
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
Treasury inflation-protected securities (TIPS) help limit inflation risk to your portfolio, as the principal is adjusted semiannually for inflation based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI)-while providing a real rate of return guaranteed by the U.S. government. However, a few things you need to be aware of is that the CPI might not accurately match the general inflation rate; so the principal balance on TIPS may not keep pace with the actual rate of inflation. The real interest yields on TIPS may rise, especially if there is a sharp spike in interest rates. If so, the rate of return on TIPS could lag behind other types of inflation-protected securities, like floating rate notes and T-bills. TIPs do not pay the inflation-adjusted balance until maturity, and the accrued principal on TIPS could decline, if there is deflation.
Treasury International Capital (TIC)
Treasury International Capital (TIC) is select groups of capital which are monitored with regards to their international movement. Treasury international capital is used as an economic indicator that tracks the flow of Treasury and agency securities, as well as corporate bonds and equities, into and out of the United States. TIC data is important to investors, especially with the increasing amount of foreign participation in the U.S. financial markets.
Unemployment occurs when people without jobs are actively seeking, but unable to find, work. The unemployment rate is a measure of the prevalence of unemployment and it is calculated as a percentage by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by all individuals currently in the labor force. An unemployment report is an economic report that shows the number of employed and unemployed workers, and may also include an unemployment rate. In the European Union this data is released monthly by Eurostat.
The unemployment rate is the percentage of the total labor force that is unemployed but actively seeking employment and willing to work.
Underemployment Rate
Underemployment Rate A measure of employment and labor utilization in the economy that looks at how well the labor force is being utilized in terms of skills, experience and availability to work. Labor that falls under the underemployment classification includes those workers that are highly skilled but working in low paying jobs, workers that are highly skilled but work in low skill jobs and part-time workers that would prefer to be full-time. This is different from unemployment in that the individual is working but isnt working at their full capability.
Up Capture / Down Capture: Measure the percentage of the benchmark’s return captured by the portfolio in up / down periods.
U.S. Institute for Supply Managers (ISM) manufacturing index
The U.S. Institute for Supply Managers (ISM) manufacturing index is an economic indicator derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies, and is intended to show the economic health of the U.S. manufacturing sector. A PMI of more than 50 indicates expansion in the manufacturing sector, a reading below 50 indicates contraction, and a reading of 50 indicates no change.
Vehicle sales is the number of domestically produced units of cars, SUVs, minivans, and light trucks that are sold. These sales are reported on the first business day of the month.
The VIX is a measure of the volatility implied in the prices of options contracts for the S&P 500. It is a market-based estimate of future volatility. When sentiment reaches one extreme or the other, the market typically reverses course. While this is not necessarily predictive it does measure the current degree of fear present in the stock market.
The Volcker Rule is a specific section of the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act originally proposed by American economist and former United States Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker to restrict United States banks from making certain kinds of speculative investments that do not benefit their customers.
World Agriculture Supply and Demand Estimates (WASDE)
The World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates (WASDE) report is a monthly report published by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) providing comprehensive forecast of supply and demand for major crops (global and United States) and livestock (U.S. only).
Yield is the income return on an investment. This refers to the interest or dividends received from a security and is usually expressed annually as a percentage based on the investments cost, its current market value or its face value.
Yield Curve is a line that plots the interest rates, at a set point in time, of bonds having equal credit quality, but differing maturity dates. The most frequently reported yield curve compares the three-month, two-year, five-year and 30-year U.S. Treasury debt. This yield curve is used as a benchmark for other debt in the market, such as mortgage rates or bank lending rates. The curve is also used to predict changes in economic output and growth.
Yield Spread is the difference between yields on differing debt instruments, calculated by deducting the yield of one instrument from another. The higher the yield spread, the greater the difference between the yields offered by each instrument. The spread can be measured between debt instruments of differing maturities, credit ratings and risk.
ZEW Survey is a main indicator of investors confidence. It is calculated on basis of 350 analysts and institutional investors polling. The indicator reflects the difference between analysts who are optimistic about forthcoming economic development of Germany within six months and those who are pessimistic. The Survey is used for German economic prospects estimation. ZEW Survey growth causes the euro growth.
Sector Definitions
The Consumer Discretionary Sector
Companies that tend to be the most sensitive to economic cycles. Its manufacturing segment includes automotive, household durable goods, textiles and apparel, and leisure equipment. The service segment includes hotels, restaurants and other leisure facilities, media production and services, consumer retailing and services, and education services.
Consumer Staples Sector
Companies whose businesses are less sensitive to economic cycles. It includes manufacturers and distributors of food, beverages and tobacco, and producers of non-durable household goods and personal products. It also includes food and drug retailing companies.
An equity security whose price is affected by ups and downs in the overall economy. Cyclical stocks typically relate to companies that sell discretionary items that consumers can afford to buy more of in a booming economy and will cut back on during a recession. Contrast cyclical stocks with counter-cyclical stocks, which tend to move in the opposite direction from the overall economy, and with consumer staples, which people continue to demand even during a downturn.
Companies whose businesses are dominated by either of the following activities: The construction or provision of oil rigs, drilling equipment and other energy-related service and equipment, including seismic data collection. The exploration, production, marketing, refining and/or transportation of oil and gas products, coal and consumable fuels.
Companies involved in activities such as banking, consumer finance, investment banking and brokerage, asset management, insurance and investment, and real estate, including REITs.
Companies are in two main industry groups—Health care equipment and supplies or companies that provide health care-related services, including distributors of health care products, providers of basic health care services, and owners and operators of health care facilities and organizations. Companies primarily involved in the research, development, production, and marketing of pharmaceuticals and biotechnology products.
Companies whose businesses manufacture and distribute capital goods, including aerospace and defense, construction, engineering and building products, electrical equipment and industrial machinery. Provide commercial services and supplies, including printing, employment, environmental and office services. Provide transportation services, including airlines, couriers, marine, road and rail, and transportation infrastructure.
Manufacturing Sector
Companies engaged in chemical, mechanical, or physical transformation of materials, substances, or components into consumer or industrial goods.
Companies that are engaged in a wide range of commodity-related manufacturing. Included in this sector are companies that manufacture chemicals, construction materials, glass, paper, forest products and related packaging products, metals, minerals and mining companies, including producers of steel.
Companies include those that primarily develop software in various fields such as the Internet, applications, systems and/or database management and companies that provide information technology consulting and services; technology hardware & Equipment, including manufacturers and distributors of communications equipment, computers and peripherals, electronic equipment and related instruments, and semiconductor equipment and products.
Telecommunications Services Sector
Companies that provide communications services primarily through a fixed line, cellular, wireless, high bandwidth and/or fiber-optic cable network.
Companies considered electric, gas or water utilities, or companies that operate as independent producers and/or distributors of power.
S&P 500 Coal & Consumable Fuels
Companies that are engaged in the mining, production, processing and export of coal.
S&P 500 Health Care Facilities
Companies that own or operate health care facilities such as hospitals, long-term care facilities, and medical office properties.
S&P 500 Diversified Financial Services
Diversified financial services companies that provides a range of financial products and services to consumers, corporations, governments, and institutions worldwide including consumer and commercial lending and capital markets services.
S&P 500 Food & Staples Retailing
Companies that own and operate various retail formats including supermarkets, supercenters, warehouse clubs and drug stores.
S&P 500 Oil & Gas Exploration & Production
Companies that are engaged in the discovery, production, processing and refining of oil and natural gas.
S&P 500 Gas Utilities
Companies involved in the gathering, storage and distribution of natural gas for power generation.
S&P 500 Oil & Gas Drilling
Companies that provide drilling services for oil and gas production.
S&P 500 Health Care Services
Companies involved in the delivery of health care services.
S&P 500 Managed Health Care
Companies involved in providing health care benefits including group insurance and other diversified health care services.
S&P 500 Life Sciences Tools & Services
Companies that provide drug development and other product development services, equipment, software and services for research, manufacturing discovery and medical diagnostics.
S&P 500 Electric Utilities
Companies involved in electricity generation from nuclear, fossil, hydro, renewable and other sources.
S&P 500 Construction Materials
Companies that provide raw and intermediate stage materials for use in construction of infrastructure such as roads and bridges.
S&P 500 Specialty Retail
Retailers in the sales of specialty products such as apparel, accessories, jewelry and other luxury goods.
S&P 500 Homebuilding
Companies involved in the development and construction of single-family homes and housing developments.
S&P 500 Telecommunications Services
Companies that provide communications services to retail and commercial customers.
S&P 500 Constructions and Farm Machinery
Companies involved in the manufacturing of heavy equipment for use in construction and farming industries.














