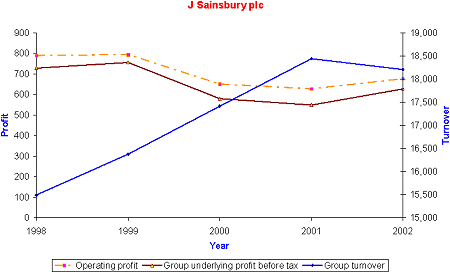
Financial Ratios and profitability measure
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
If we want to know if the profits are sufficient relative to the assets being invested, it is recommended to compare our question to the free-risk interest rate that we can we earn on a savings account or long-term deposit at the bank or Treasury bill at central bank.
To answer the above question, we should apply profitability ratios that helps shareholders or owners of a business to find out the profitability of the operation, as well as return on their investments. Profitability ratios are also called activity ratios because they indicate the ability of company to earn profits in relation to the sales made, assets employed, or equity, the numerator can be net profit, operating profit or gross profit.
Gross Profit Margin represents the limit beyond which fall in sales prices are outside the tolerance limit. Further, the gross profit margin can also be used in determining the extent of loss caused by theft, spoilage, damage, and so on in the case of those firms which follow the policy of fixed gross profit margin in pricing their products. A high ratio of gross profits to sales is a sign of good management as it implies that the cost of production of the firm is relatively low, or to be indicative of a higher sales price without a corresponding increase in the cost of goods sold. It is also likely that cost of sales might have declined without a corresponding decline in sales price. Netherless, a very high and rising gross margin may also be the result of unsatisfactory basis of valuation of stock, that is, overvaluation of closing stock and or undervaluation of opening stock. A relative low gross margin is definitely a danger signal, warranting a careful and detailed analysis of the factors responsible for it. The important contributory factors may be 1) high cost of production reflecting acquisition of raw materials and other inputs on unfavorable terms, inefficient utilization of current as well as fixed assets, and so on, 2) a low selling price resulting from severe competition, inferior quality of the products, lack of demand.
Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue – Operating Cost) / Revenue * 100
Net Profit Margin is indicative of management’s ability to operate the business with sufficient success not only to recover from revenues of the period, the cost of merchandise or services, the expenses of operating the business (including depreciation) and the cost of the borrowed funds. A high ratio would ensure adequate return to the owners as well as enable a firm to withstand adverse economic conditions when selling price is declining, cost of production is rising and demand for the product is falling. A low ratio has the opposite implications. However, a firm with a low profit margin, can earn a high rate of return on investments if it has a higher inventory turnover.
Also, Gross profit margin and net profit margin indicates to the ability of company to control operating cost and non-operating expenses
Operating Profit Ratio = EBIT/Revenue
Net Profit Margin Ratio = Net income/Revenue
The gross margin may show a substantial increase over a period of time but the net profit margin may a) have remained constant, or b) may not have increased as fast as the gross profit margin, or may actually have declined. It may be due to the fact that increase in the operating expenses individually may behave abnormally. And the gross margin may show a decrease over a period of time but the net profit margin may have remained or may have increased faster than gross profit margin, that may be due to the firm generate income other than the revenue of ordinary business.
Return on Investments (ROI) Such ratios are popularly termed as return on investment. There are three different concepts of investments in vogue in financial literature: Total Assets, Capital employed and shareholder’s equity.
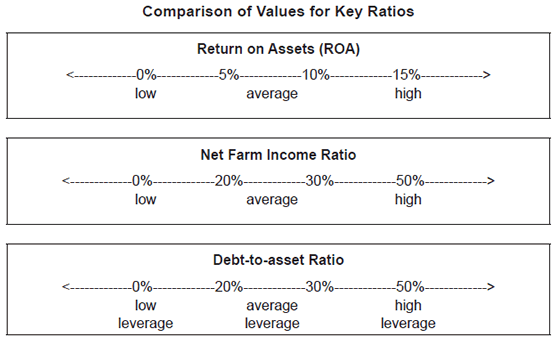
Return on Assets (ROA) is indicative of management’s ability to operate the assets including fixed assets, and how much the efficiency of the utilizing assets. Comparing to the industry average ratio, a high ratio indicates that the assets are utilized efficiently and low ratio indicates to the inefficient assets utilization and more profitable is the assets in producing income.
ROA = Net income/Average total assets *100
ROA = Profit Margin * Assets turnover
Also, the investment turnover can be considered along with the net profit margin. Investment turnover is a revenue divided by average total assets which shows how much one dollar contribute to generate the revenue. High sales-to-assets ratio (Assets Turnover) may have several causes: 1) the company uses its assts efficiently; 2) it is working close to capacity, so that it may be difficult to increase sales without additional invested capital; or 3) The company produces high volume, low margin products
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE). The capital employed is net working capital plus fixed assets. Comparing this ratio to the industry average and over time would provide sufficient insight into how efficiently the long-term funds of owners and creditors are being used. The higher ratio the more efficient is the use of the capital employed.
Return on ordinary Shareholder’s Equity (ROE) measures the profitability exclusively the return on the real owners’ funds. Stockholders are primarily interested in the relationship between net income and their investment in the company. This is probably the single most important ratio to judge whether the firm has earned a satisfactory return for its equity-holders or not. Its adequacy can be judged by comparing it with the past record of the same firm, inter-firm comparison and comparisons with the overall industry average. The higher rate is, the more efficiency in utilizing the owners’ funds.














