Adaptive Trading Systems and Their Use in the MetaTrader 5 Client Terminal MQL5 Articles
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
Introduction
Hundreds of thousands of traders all over the world use the trading platforms developed by MetaQuotes Software Corp. The key factor leading to success is the technological superiority based on the experience of many years and the best software solutions.
Many people have already estimated new opportunities that have become available with the new MQL5 language. Its key features are high performance and the possibility of using object-oriented programming. In addition to it, with appearing of the multi-currency strategy tester in the MetaTrader 5 client terminal, many traders have acquired unique tools for developing, learning and using complex trading systems.
Automated Trading Championship 2010 starts this autumn; thousands of trading robots written in MQL5 are going to participate in it. An Expert Advisor that earns the maximum profit during the competition will win. But what strategy will appear the most effective one?
The strategy tester of the MetaTrader 5 terminal allows finding the best set of parameters, using which the system earns the maximum amount of profit during a specified time period. But can it be done in the real time? The idea of the virtual trading using several strategies in an Expert Advisor was considered in the Contest of Expert Advisors inside an Expert Advisor article, which contains its implementation in MQL4.
In this article, we are going to show that the creation and analysis of adaptive strategies has become significantly easier in MQL5 due to the usage of object-oriented programming. classes for working with data and trade classes of the Standard Library.
1. Adaptive Trading Strategies
Markets change constantly. Trade strategies need their adaptation to the current market conditions.
The values of parameters that give the maximal profitability of the strategy can be found without using the optimization through sequential change of parameters and analysis of testing results.
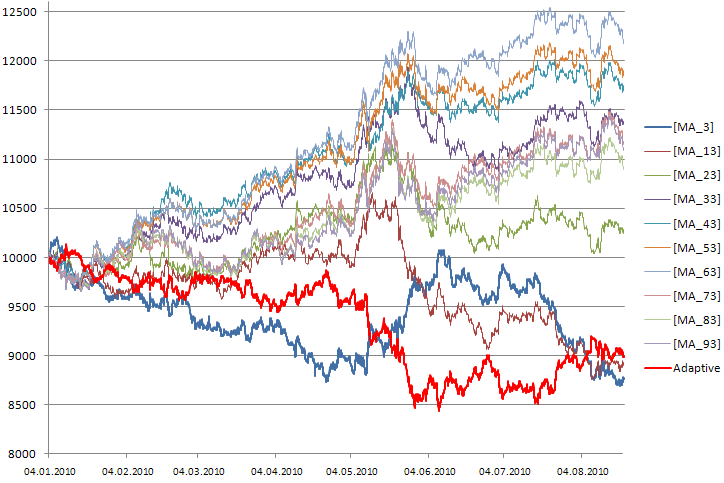
Figure 1 demonstrates the equity curves for ten Expert Advisors (MA_3. MA_93); each of them traded by the strategy of moving averages but with different periods (3,13. 93). The testing has been performed at EURUSD H1, the testing period is 4.01.2010-20.08.2010.
Figure 1. Diagrams of equity curves of ten Expert Advisors at the account
As you can see at the Figure 1, the Expert Advisors had nearly the same results during the first two weeks of working, but further their profits started diverging significantly. At the end of testing period the best trading results were shown by the Expert Advisors with periods 63, 53 and 43.
The market has chosen the best ones. Why shouldn’t we follow its choice? What if we combine all ten strategies in a single Expert Advisor, provide the possibility of virtual trading for each strategy, and periodically (for example, at the beginning of each new bar) determine the best strategy for the real trading and trade in accordance with its signals?
The results of obtained adaptive strategy are shown in the Figure 2. The equity curve of the account with adaptive trading is shown with the red color. Note, that during more than a half of period the form of equity curve for the adaptive strategy is the same as the one of the MA_63 strategy, which has appeared to be the winner finally.
Figure 2. Equity curves at the account with the adaptive strategy that uses signals of 10 trade systems
The balance curves have the similar dynamics (Fig. 3):
Figure 3. Balance curves of the adaptive strategy that uses signals of 10 trade systems
If none of the strategies is profitable at the moment, the adaptive systems shouldn’t perform trade operations. The example of such case is shown in the fig. 4 (period from 4-th to 22-nd of January 2010).
Figure 4. The time period when the adaptive strategy stopped opening new positions due to the absence of profitable strategies
Starting from the January 2010 the best effectiveness is shown by the MA_3 strategy. Since the MA_3 (blue) had the maximum amount of money earned at that moment, the adaptive strategy (red) followed its signals. In the period from 8-th to 20th of January all the considered strategies had a negative result, that’s why the adaptive strategy didn’t open new trade positions.
If all the strategies have a negative result, it’s better to stay away from trading. This is the significant thing that allows stopping unprofitable trading and keeping your money save.
2. Implementation of the Adaptive Trading Strategy
In this section, we are going to consider the structure of the adaptive strategy that performs the virtual trading using several trade strategies simultaneously, and chooses the most profitable one for real trading according to its signals. Note that the use of the object-oriented approach makes the solution of this problem significantly easier.
First of all we are going to investigate the code of the adaptive Expert Advisor, then we’re going to take a detailed look into the CAdaptiveStrategy where the functionality of the adaptive system is implemented, and then we will show the structure of the CSampleStrategy class — the base class of the trade strategies where the functionality of virtual trading is implemented.
Further, we’re going to consider the code of two of its children — the CStrategyMA and CStrategyStoch classes that represent the strategies of trading by moving averages and the stochastic oscillator. After analyzing their structure you’ll be able to easily write and add you own classes that realize your strategies.
2.1. Code of the Expert Advisor
The code of the Expert Advisor looks very simple:
The first three lines define the properties of the program. then comes the #include directive that tells the preprocessor to include the CAdaptiveStrategy.mqh file. Angle brackets specify that the file should be taken from the standard directory (usually, it is terminal_folderMQL5Include).
The next line contains the declaration of the Adaptive_Expert object (instance of the CAdaptiveStrategy class); and the code of the OnInit. OnDeinit and OnTick functions of the Expert Advisor consists of the calls of corresponding functions Expert_OnInit, Expert_OnDeInit and Expert_OnTick and the Adaptive_Expert object.
2.2. The CAdaptiveStrategy class
The class of thr adaptive Expert Advisor (CAdaptiveStrategy class) is located in the CAdaptiveStrategy.mqh file. Let’s start with the include files:
The reason why we include the ArrayObj.mqh file is the convenience of working with classes of different strategies using the object of the CArrayObj class, which represents a dynamic array of pointers to the class instances spawned by the base class CObject and its children. This object will the m_all_strategies array, it will be used a container of trade strategies.
Each strategy is represented as a class. In this case, we have included the files that contain the CStrategyMA and CStrategyStoch classes, which represent the strategies of trading by moving averages and trading by the stochastic oscillator.
For requesting properties of current positions and for performing trade operations, we will use the CPositionInfo and CTrade classes of the Standard library, that’s why we include the PositionInfo.mqh and Trade.mqh files.
Let’s take a look into the structure of the CAdaptiveStrategy class.
To implement a united approach to the objects of different classes, the trade strategies (or rather the instances of their classes) are stored in the dynamic array m_all_strategies (of the CArrayObj type), which is used as a container of classes of the strategies. This is the reason why the class of trade strategies SampleStrategy is spawned from the CObject class.
The ProceedSignalReal function implements the synchronization of the direction and volume of a real position with the given direction and volume:
Note that it’s easier to work with the trade position using the trade classes. We used the objects of the CPositionInfo and CTrade classes for requesting the properties of market position and for performing trade operations respectively.
The RealPositionDirection function requests the parameters of the real open position and returns its direction:
Now we’re going to take a look into the main functions of the СAdaptiveStrategy class.
Let’s start with the Expert_OnInit: function
The set of trading strategies is prepared in the Expert_OnInit function. First of all, the object of the m_all_strategies dynamic array is created.
In this case, we created ten instances of the CStrategyMA class. Each of them was initialized (in this case, we set different periods and allowed virtual trading) using the Initialization function.
Then, using the SetStrategyInfo function we set the financial instrument, strategy name and comment.
If necessary, using the Set_Stops(TP,SL) function we can specify a value (in points) of Take Profit and Stop Loss, that will be executed during the virtual trading. We have this line commented.
Once the strategy class is created and adjusted, we add it to the m_all_strategies container.
All classes of trade strategies should have the CheckTradeConditions() function that performs the checks of trading conditions. In the class of the adaptive strategy this function is called at the beginning of each new bar, thus we give the strategies a possibility to check the values of indicators and to make the virtual trade operations.
Instead of ten specified moving averages (3, 13, 23. 93) we can add hundreds of moving averages (instances if the CStrategyMA class):
Or we can add the classes of strategy that works by the signals of the stochastic oscillator (instances of the CStrategyStoch class):
In this case the container includes 10 strategies of moving averages and 5 strategies of the stochastic oscillator.
The instances of classes of trading strategies should be the children of the CObject class and should contain the CheckTradeConditions() function. It is better to inherit them from the CSampleStrategy class. Classes that implement trade strategies can be different and their number is not limited.
The Expert_OnInit function ends with the list of strategies that are present in the m_all_strategies container. Note that all the strategies in the container are considered as the children of the CSampleStrategy class. The classes of trade strategies CStrategyMA and CStrategyStoch are also its children.
The same trick is used in the Expert_OnDeInit function. In the container, we call the SaveVirtualDeals function for each strategy; it stores the history of performed virtual deals.
We use the name of strategy for the file name that is passed as a parameter. Then we deinitialize the strategies by calling the Deinitialization() function and deleting the m_all_strategies container:
If you don’t need to know about the virtual deals performed by the strategies, remove the line where tStrategy.SaveVirtualDeals is called. Note that when using the strategy tester the files are save to the /tester_directory/Files/ directory.
Let’s consider the Expert_OnTick function of the CAdaptiveStrategy class that is called each time a new tick comes:
The code is very simple. Each strategy, located in the container must be able to recalculate the current financial result of its virtual positions using the current prices. It is done by calling the UpdatePositionData() function. Here, once again we call the strategies as the heirs of the CSampleStrategy class.
All trade operations are performed at the beginning of a new bar (the IsNewBar() function allows determining this moment as well as the other methods of checking new bar). In this case, the end of forming of a bar means that all the data of the previous bar (prices and indicator values) won’t change anymore, so it can be analyzed on the correspondence to the trading conditions. To all the strategies we give the opportunity to perform this check and to perform their virtual trade operations by calling their CheckTradeConditions function.
Now we should find the most successful strategy among all strategies in the m_all_strategies array. To get it done, we used the Performance[] array, values that are returned by the StrategyPerformance() function of each strategy are placed into it. The base class CSampleStrategy contains this function as the difference between the current values of virtual Equity and Balance.
The search of index of the most successful strategy is performed using the ArrayMaximum function. If the best strategy has a negative profit at the moment and it doesn’t have real open positions, then it’s better not to trade, that’s the reason why we exit from the function (see section 1).
Further, we request the direction of the virtual position of this strategy (best_direction). If it differs from the current direction of the real position, then the current direction of the real position will be corrected (using the ProceedSignalReal function) according to the best_direction direction.
2.3. Class CSampleStrategy
Strategies placed in the m_all_strategies container were considered as the heirs of the CSampleStrategy class.
This class is the base one for the trade strategies; it contains the implementation of virtual trading. In this article we will consider a simplified case of virtual trading implementation, the swaps aren’t aken into consideration. The classes of trade strategies should be inherited from the CSampleStrategy class.
Let’s show the structure of this class.
We won’t analyze its detailed description, additional information can be found in the CSampleStrategy.mqh file. There you can also find the function of checking new bar — IsNewBar.
3. Classes of Trade Strategies
This section is devoted to the structure of classes of trade strategies that are used in the adaptive Expert Advisor.
3.1. Class CStrategyMA — Strategy of Trading by Moving Averages
The CStrategyMA class is a child of the CSampleStrategy class where the entire functionality of virtual trading is implemented.
The protected section contains internal variables that will be used in the class of the strategy. These are: m_handle — handle of the iMA indicator, m_period — period of the moving average, m_values[] — array that will be used in the CheckTradeConditions function for getting current values of the indicator.
The public section contains three functions that provide the implementation of the trade strategy.
- Function Initialization. The strategy is initialized here. If you need to create indicators, create them here.
- The signal for opening a long position (SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG)
The concept is simple — on the basis of indicator states and prices, the signal type (new_state) is determined, then the current state of the virtual trading is requested (using the GetSignalState function); and if they’re not the same, the SetSignalState function is called for correcting the virtual position.
3.2. Class CStrategyStoch — the Strategy of Trading by Stochastic
The code of the class that performs trading on the basis of intersection of the main and signal lines of the iStochastic oscillator is given below:
As you see, the only differences between the structure of the CStrategyStoch class and the one of CStrategyMA are the initialization function (different parameters), the type of indicator used and the trade signals.
Thus, to use your strategies in the adaptive Expert Advisor, you should rewrite them in the form of classes of such type and load them to the m_all_strategies container.
4. Results of Analysis of the Adaptive Trade Strategies
In this section, we’re going to discuss several aspects of practical use of the adaptive strategies and the methods of improving them.
4.1. Enhancing the System with Strategies that Use Inversed Signals
Moving Averages are not good when there are no trends. We’ve already met this kind of situation — in the figure 3, you can see that there was no trend within the period from 8-th to 20-th of January; so all 10 strategies that use moving averages in trading had a virtual loss. The adaptive system stopped trading as a result of absence of a strategy with positive amount of money earned. Is there any way to avoid such negative effect?
Let’s add to our 10 strategies (MA_3, MA_13. MA_93) another 10 classes CStrategyMAinv. whose trade signals are reversed (the conditions are the same but SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG/SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT and SIGNAL_CLOSE_LONG/SIGNAL_CLOSE_SHORT exchanged their places). Thus, in addition to ten trend strategies (instances of the CStrategyMA class), we have another ten counter-trend strategies (instances of the CStrategyMAinv class).
The result of using the adaptive system that consists of twenty strategies is shown in the figure 5.
Figure 5. Diagrams of equity at the account of the adaptive strategy that uses 20 trade signals: 10 moving averages CAdaptiveMA and 10 mirrored ones CAdaptiveMAinv
As you can see at the figure 5, during the period when all the CAdaptiveMA strategies had a negative result, following the CAdaptiveMAinv strategies allowed the Expert Advisor to avoid unwanted drawdowns at the very beginning of trading.
Figure 6. Time period when the adaptive strategy used the signals of counter-trend CAdaptiveMAinv strategies
This kind of approach may seem unacceptable, since losing the deposit is just a question of time when using a counter-trend strategy. However in our case, we’re not limited with a single strategy. The market knows better which strategies are effective at the moment.
The strong side of adaptive systems is the market suggests by itself which strategy should be used and when it should be used.
It gives a possibility to abstract from the logic of strategies — if a strategy is effective, then the way it works is of no significance. The adaptive approach uses the only criterion of success of a strategy — its effectiveness.
4.2. Is It Worth to Invert the Signals of the Worst Strategy?
The trick with inversion shown above leads to a thought about the potential possibility of using the signals of the worst strategy. If a strategy is unprofitable (and the worst one at that), then can we get a profit by acting in reverse?
Can we turn a losing strategy into a profitable one by a simple change of its signals? To answer this question, we need to change ArrayMaximum with ArrayMinimum in the Expert_OnTick() function of the CAdaptiveStrategy class, as well as to implement the change of directions by multiplying value of the BestDirection variable by -1.
In addition, we need to comment the limitation of virtual trading in case of negative effectiveness (since we are going to analyze the result of the worst strategy):
Diagram of equity of the adaptive Expert Advisor that uses the reversed signals of the worst strategy is shown in the figure 7:
Figure 7. Diagrams of equity at the accounts of ten strategies and the adaptive system that uses the reversed signals of the worst system
In this case, the least successful strategy for most of the time was the one based on intersection of moving averages with period 3 (MA_3). As you can see at the figure 7, the reverse correlation between MA_3 (blue colored) and the adaptive strategy (red colored) exists. but the financial result of the adaptive system doesn’t impress.
Copying (and reversing) the signals of the worst strategy doesn’t lead to improving the effectiveness of trading.
4.2. Why the Bunch of Moving Averages is not so Effective as it Seems?
Instead of 10 moving averages you can use lots of them by adding another hundred of CStrategyMA strategies with different periods to the m_all_strategies container.
To do it, slightly change the code in the CAdaptiveStrategy class:
However, you should understand that close moving averages will inevitably intersect; the leader will constantly change; and the adaptive system will switch its states and open/close positions more frequently than it is necessary. As a result, the characteristics of the adaptive system will become worse. You can make sure in it on your own by comparing the statistical characteristics of the system (the Results tab of the strategy tester).
5. What Should Be Considered
The m_all_strategies container can have thousands of instances of suggested strategies included, you can even add all the strategies with different parameters; however, to win the Automated Trading Championship 2010. you need to develop the advanced money management system. Note that we have used the trading volume equal 0.1 lots for testing on history data (and in the code of classes) .
5.1 How to Increase the Profitability of the Adaptive Expert Advisor?
The CSampleStrategy class has the virtual function MoneyManagement_CalculateLots :
To manage the volume for trading, you can use the statistical information about the results and characteristics of virtual deals that is recorded in the m_deals_history[] array.
If you need to increase the volume (for example, to double it if the last virtual deals in m_deals_history[] are profitable; or to decrease it), you should change the returned value in the corresponding way.
5.2 Using the Deals Statistics for Calculation of Strategy Performance
The StrategyPerformance() function, implemented in the CSampleStrategy class is intended for the calculation of the strategy performance,
The formula of effectiveness of a strategy can be more complex and, for example, include the effectiveness of entering, exiting, the effectiveness of deals, profits, drawdowns, etc.
The calculation of the effectiveness of entering, exiting and the effectiveness of deals (the entry_eff, exit_eff and trade_eff fields of structures of the m_deals_history[] array) is performed automatically during the virtual trading (see the CSampeStrategy class). This statistical information can be used for making your own, more complex rates of the effectiveness of strategy.
For example, as a characteristics of effectiveness you can use the profit of last three deals (use the pos_Profit field from the archive of deals m_deals_history[]):
If you want to change this function, change it only in the CSampleStrategy class, it must be the same for all trade strategies of the adaptive system. However, you should remember that the difference between Equity and Balance is also a good factor of effectiveness.
5.3 Using Take Profit and Stop Loss
You can change the effectiveness of trading systems by setting fixed stop levels (it can be done by calling the Set_Stops function; it allows setting the stop levels in points for virtual trading). If the levels are specified, closing of virtual positions will be performed automatically; this functionality is implemented in the CSampleStrategy class.
In our example (see 2.2, the function of classes of moving averages), the function of setting stop levels is commented.
5.4. Periodic Zeroizing of Cumulative Virtual Profit
The adaptive approach has the same disadvantage as common strategies have. If the leading strategy starts losing, the adaptive system starts losing as well. That is the reason why sometimes you need to zeroize the results of working of all strategies and to close all their virtual positions.
To do it, the following functions are implemented in the CSampleStrategy class:
CheckPoint of this kind can be used from time to time, for example after each N bars.
5.5. No Miracles
You should remember that the adaptive system is not a grail (USDJPY H1, 4.01.2010-20.08.2010):
Figure 8. Balance and equity curves of the adaptive system that uses the signals of the best of 10 strategies (USDJPY H1)
Equity curves of all the strategies are shown in the figure 9.
Figure 9. Equity curves at the account with the adaptive system based on 10 strategies (USDJPY H1)
If there are no profitable strategies in the adaptive system, using them is not effective. Use profitable strategies.
We should consider another important and interesting thing. Pay attention to the behavior of the adaptive strategy at the very beginning of trading:
Figure 10. Equity curves at the account with 10 strategies of the adaptive strategy
At first, all the strategies had negative results and the adaptive strategy stopped trading; then it started switching between strategies that had a positive result; and then all the strategies became unprofitable again.
All the strategies have the same balance in the beginning. And only after a while, one or another strategy becomes a leader; thus it’s recommended to set a limitation in the adaptive strategy to avoid trading at first bars. To do it, supplement the Expert_OnTick function of the CAdaptiveStrategy class with a variable, which value is increased each time a new bar comes.
In the beginning, until the market chooses the best strategy, you should stay away from real trading.
Conclusions
In this article, we have considered an example of the adaptive system that consists of many strategies, each of which makes its own virtual trade operations. Real trading is performed in accordance with the signals of a most profitable strategy at the moment.
Thanks to using the object-oriented approach, classes for working with data and trade classes of the Standard library, the architecture of the system appeared to be simple and scalable; now you can easily create and analyze the adaptive systems that include hundreds of trade strategies.
P.S. For the convenience analysis of behavior of adaptive systems, the debug version of the CSampleStrategy class is attached (the adaptive-systems-mql5-sources-debug-en.zip archive). The difference of this version is creation of text files during its working; they contain the summary reports on the dynamics of changing of virtual balance/equity of the strategies included in the system.














