Structured Investments Structured Investments
Post on: 2 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
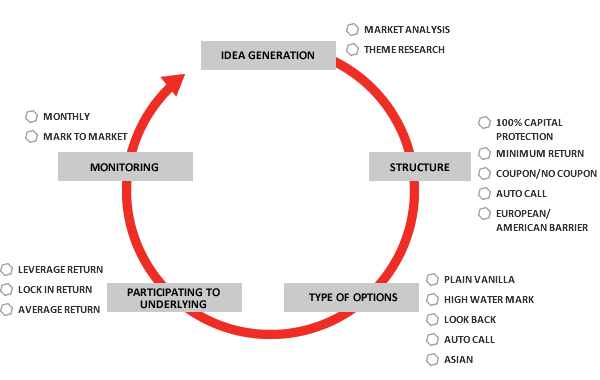
Why Structured Investments?
Access
The packaged nature of structured investments allows investors to invest in certain geographic markets or asset classes which might otherwise be accessed only through the use of options or futures markets or altogether restricted to foreign individuals. In some cases, access is to a particular investment or trading strategy which would otherwise require significant portfolio rebalancing and quantitative analysis.
By investing in a note or deposit issued by a bank, the investor is taking advantage of the breadth of trading capabilities that a bank has relative to those of an individual. In addition, some investments would require a minimum size to implement on a cost effective basis. While the underlying risks associated with each structure remains, the packaging and offering of structured investments to a broad investor base provides the necessary scale.
Customization
Because each investor is unique in their tolerance for risk, their financial goals and the market views, “one-size fits all” investments do not always meet an investor’s objective. For example, an investor planning retirement in five years may potentially have a lower risk tolerance for equity investing than an individual in the early years of their career. However, all other investor profile criteria remaining the same, both individuals may desire the potential for high positive returns which equities can provide. Of course, equities can be volatile investments and there is no guarantee of appreciation or return of principal.
Equity index linked certificates of deposit would provide a return linked to the appreciation or depreciation of an equity index while providing principal protection at maturity. subject to market risk and FDIC insurance limits. The CD may provide a lower participation in the appreciation of the equity index than a direct purchase of a portfolio of diversified equities or an equity index fund, but for the soon to be retiree, with a shorter horizon to make up for any losses in the value of their portfolio, return of principal at maturity may be worth sacrificing some upside.
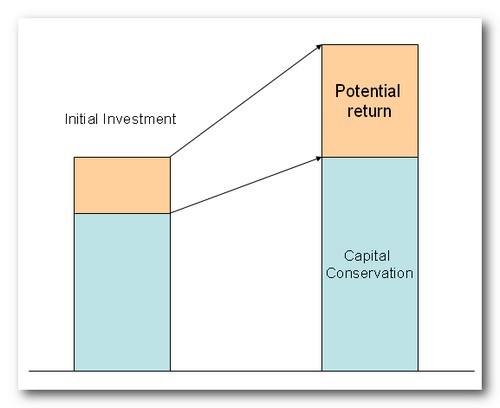
Some investors may be seeking to monetize a market view to generate high periodic yield in exchange for sacrificing any potential upside in the underlying asset. Others are willing to accept a longer investment horizon or some risk to principal in return for greater participation in the underlying asset. Structured investments allow an investor to focus (or dial-in) on the risks that they are willing to accept in exchange for potential returns that they seek.
Risk Factors
As with all financial products, structured investments carry certain risks respective to the underlying investment and structure, which may include complexity of payout, market risk, counterparty risk and additional considerations. Prior to making structured investments part of a well diversified portfolio, investors and advisors should consider the following questions in connection with the evaluation of a structured investment:
- What is the product’s investment objective? Can less costly, complex or risky products achieve the objectives of this product?
- What assumptions underlie the product, and how sound are they? What market or performance factors determine the investor’s return?
- If the product is expected to generate increased yield, does the yield justify any risk to principal?
- What costs and fees for the investors are associated with this product? Are the costs and fees transparent? How do the fees compare with comparable products?
- Does the product present any novel legal, tax, market investment, or credit risks?
- What is the complexity of the product in structure, function and description? Is this product understandable and transparent enough to explain in layman’s terms? Are there caps, barriers or contingencies associated with the payout of the structure?
- What is the incentive of the advisor or brokerage firm offering the product? How liquid is the product? How active is the secondary market?
- What is the expected liquidity of the product?
- Is the product FDIC insured and what is the coverage limit?














