Investor Confidence Index
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
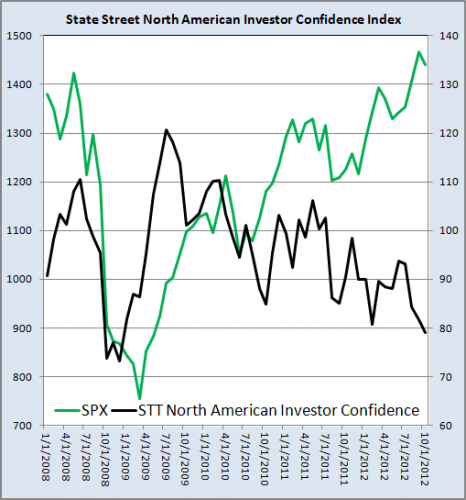
The State Street Investor Confidence Index ® (the index) provides an objective, quantitative measure of global risk tolerance of the world’s sophisticated investors. Regional components measure separately the risk appetites of institutional investors in North America, Europe and the Asia-Pacific region.
The index is published at 10 a.m. local time in Boston, Massachusetts on the last Tuesday of each month.
Global Index on Feb 24, 2015
The Premise
Confidence in the economy and the capital markets is a critical driver of economic and financial fluctuations and of the business cycle. When confidence increases, consumers and investors want to buy consumer goods, durables and invest at prevailing prices. When confidence decreases, spending and risk-taking tend to fall.
Investors are said to be confident when the news about the future is good and stock prices are rising. However, rising prices are related both to good fundamentals, such as growth in industrial production and productivity, as well as to the underlying sentiment or mood of investors. A good confidence measure should indicate whether, for a given set of fundamentals, investors have an increased or decreased appetite for risk.
Quantitatively measuring shifts in investor sentiment presents a unique set of problems to researchers. Investor surveys are often outdated by the time they are released. On the institutional side, accuracy can be compromised as decision makers are often too busy to fill out surveys. In all cases, survey responses, like prices, tend to obscure the effects of fundamentals and investor sentiment.
The Approach
State Street’s approach measures confidence directly and quantitatively by assessing the changes in investor holdings of risky assets, implementing a research model developed by Harvard Professor Ken Froot and Managing Director Paul O’Connell of State Street Global Markets’ research partnership – State Street Associates.
The idea is simple: the more of their portfolios that sophisticated investors are willing to devote to riskier as opposed to safer investments, the greater their risk appetite or confidence. When risk appetite increases, investors move to increase, in the same proportion, their holdings of each risky investment. This process may occur when there is good news and prices are up, but could also happen over a period of bad news and falling prices. As a result, the risk appetite of institutional investors is a separate and distinct measure from the behavior of prices. Actual investor holdings and recent purchases provide a solid foundation on which to base a measure of investor confidence.














