Backspread Wikipedia the free encyclopedia_1
Post on: 19 Июль, 2015 No Comment
Contents
Call backspread [ edit ]
The call backspread (reverse call ratio spread) is a bullish strategy in options trading whereby the options trader writes a number of call options and buys more call options of the same underlying stock and expiration date but at a higher strike price. It is an unlimited profit, limited risk strategy that is used when the trader thinks that the price of the underlying stock will rise sharply in the near future.
Put backspread [ edit ]
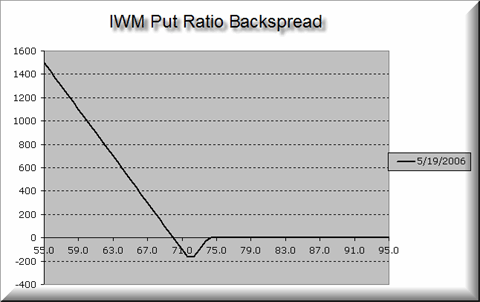
An example profit and loss graph for a Put Backspread options strategy placed at a net credit. The solid black line shows the combined value of the position at expiration. The dashed blue line shows the combined value of the position some time before expiration and when there exists significant implied volatility in the options.
The put backspread is a strategy in options trading whereby the options trader writes a number of put options at a higher strike price (often at-the-money ) and buys a greater number (often twice as many) of put options at a lower strike price (often out-of-the-money ) of the same underlying stock and expiration date. Typically the strikes are selected such that the cost of the long puts is largely offset by the premium earned in writing the at-the-money puts. This strategy is generally considered very bearish but it can also serve as a neutral/bullish play under the right conditions.
The maximum profit for this strategy is achieved when the price of the underlying security moves to zero before expiration of the options. Given these declarations:
The maximum profit per put backspread combination can be expressed as:
The maximum upside profit is achieved if the price of the underlying is at or above the upper strike price at expiration and can be expressed simply as:
The maximum loss for this strategy is taken when the price of the underlying security moves to exactly the lower strike at expiration. The loss taken per put backspread combination can be expressed as:
As a very bearish strategy [ edit ]
The maximum profit from this strategy is realised if the underlying moves to zero before the options expire. The maximum loss for this strategy is realised when, at expiration, the underlying has moved moderately bearishly to the price of the lower strike price. This strategy might be used when the trader believes that there will be a very sharp, downward move and would like to enter the position without paying a lot of premium, as the written puts will offset the cost of the purchased puts.
As a neutral/bullish strategy [ edit ]
The strategy can often be placed for a net credit when the net premium earned for the written puts minus the premium paid for the long puts is positive. In this case, this strategy can be considered a neutral or bullish play, since the net credit may be kept if the underlying remains at or greater than the upper strike price when the options expire.














