What is an etf
Post on: 4 Май, 2015 No Comment
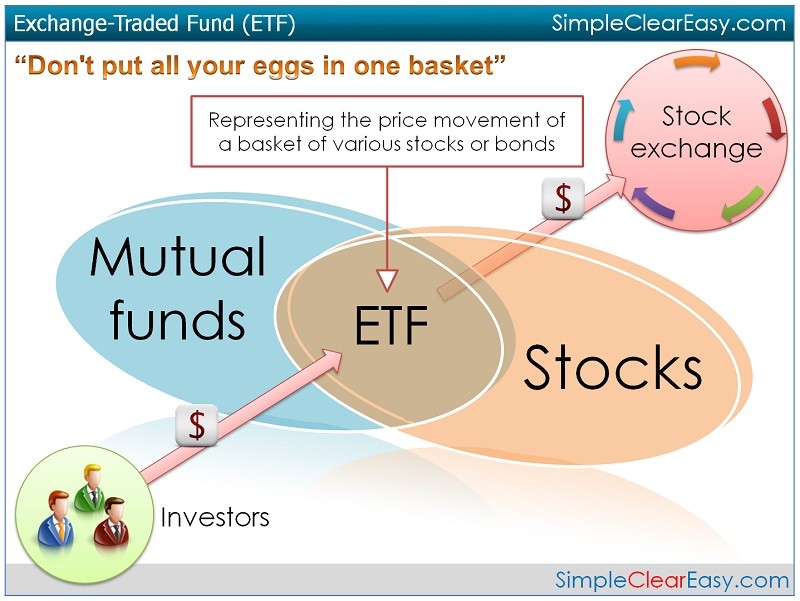
What is an ETF? It is an exchange traded fund (ETF), an investment product that allows investors to buy or sell shares of a single security representing your undivided interest in a portfolio of securities and other assets. ETFs are designed to track the performance of a benchmark, an index; for example buying shares in the SPDR S&P 500 (NYSEArca: SPY) will provide you with exposure to hundreds of stocks & sectors in a single transaction.
While ETFs are in many ways similar to traditional mutual funds in terms of providing easy diversification they are different from mutual funds in that they can be bought and sold throughout the day like stocks on a securities exchange through a broker. An ETF is expected to closely track an underlying index or portfolio that trade throughout the day at market prices.
As publicly traded securities, you can trade ETFs just like a stock: buy it on margin or short it, use stop orders or limit orders. On many ETFs, you also have the ability for options (puts and calls) to be written against them. It’s important to take a fund’s liquidity (how many shares it trades per day) in consideration before buying in if you’re looking for short term exposure.
ETFs have been growing at a phenomenal rate every year as investors recognized many advantages in buying ETFs for investment or even for trading purposes. ETFs have become popular investment products as new funds are issued regularly. The global market is forecasted to surpass the US $2 trillion mark by the end of 2011.
This shouldn’t surprise you at all as ETFs will cost you less in fees because most of them are not actively managed. You will pay the same transaction fee to your brokerage firm just like you would have for a stock when buying or selling. The ETF issuers (banks, financial institutions) charge a management fee that is deducted from the assets of the fund. The Net Asset Value (NAV) of an ETF is calculated by adding the value of the total assets of the fund minus the management expense and divided by the number of outstanding shares.
On top of easy diversification, ETFs can also offer you exposure to a sector as a whole or to a specific sub-sector. For example you can buy shares in a Commodity Index Tracking Fund (NYSEArca: DBC) which tracks the most important physical commodities in the world: crude oil, heating oil, gold, aluminum, corn and wheat. Or you can buy shares in a crude oil ETF like the United States Oil Fund (NYSEArca: USO) if you wish to track West Texas Intermediate (WTI) light sweet oil performance.
Customizing your market exposure is one of the biggest advantages to an individual investor, you get to pick the building blocks of your portfolio in a cost efficient way. Whatever your investment preference or style you have access to a wide array of Index ETFs, Dividend ETFs, Agriculture ETFs. Commodity ETFs, Bond ETFs, currency ETFs and leveraged ETFs .
In conclusion, what is an ETF? Its Gold, Corn, microchips, or really whatever you want it to be. A simple way to think of it is as commodity or basket of assets that is a tradable vehicle, such as stock within an exchange, which exposes you to a broad market or to a narrow niche sector. ETFs are popular because the expense ratio paid is often lower than your average mutual fund, leaving more money in the fund and less paid in fees to your broker. It is up to you to decide how to use your trades, just remember that there are risks when it comes to investing, so build your portfolio wisely.














