What is a Mutual Fund
Post on: 3 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
What is a mutual fund? This article seeks to answer this question by providing examples and explanations of mutual funds and their investments.
Answering the Question: What is a Mutual Fund?
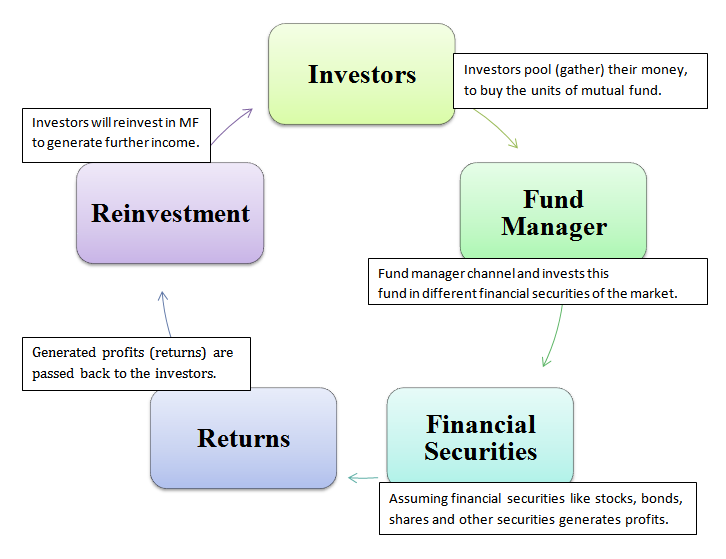
Have you ever asked yourself “what is a mutual fund?” If so, here’s your answer: a mutual fund is a vehicle that enables a number of investors to pool their money and have it jointly managed by a professional money manager.
The fund is divided into units and each holder is entitled to a proportionate share of the fund. Each “unit holder” has the right to their share of the assets of the fund and any income that the fund earns. Under tax law, the fund must distribute all of its income each year to avoid taxation. These “distributions” of realized capital gains, interest and dividend income are made as frequently as monthly.
What is a Mutual Fund Characteristics
Regulation
Mutual funds are regulated by governments, which ensure that adequate information is available to prospective purchasers and unit holders regarding the fund characteristics and its performance. The major fund disclosure document is called the prospectus. Each fund is required to be audited and to provide statements to the unit holders. Major changes to the fund require unit holder approval.
A mutual fund is legally governed by its “trust indenture”. This states how the fund will work. It establishes the role of the fund manager, who provides the investment management for the fund; the trustee and custodian, which holds the actual assets of the fund; and many other things such as investment policy for the fund, who values the fund and how this is done, and how the fund will distribute its income. Since mutual funds are financial investments called “securities” which can be bought and sold, they are regulated by governments.
Investment
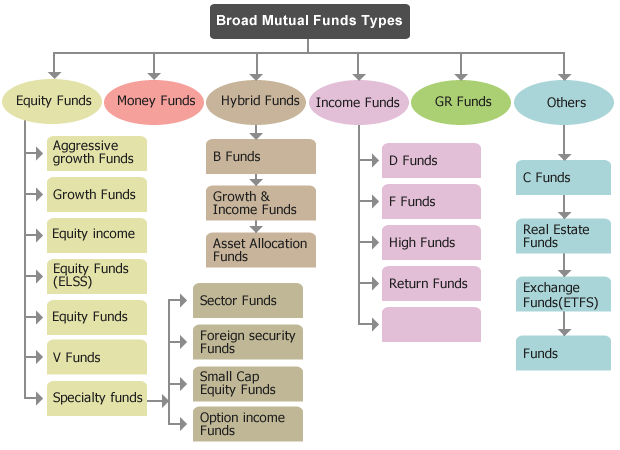
Mutual funds may invest in almost anything, according to what is provided for in the fund documents. Equity mutual funds invest in the common shares of corporations. Bond or income funds invest in the bonds of governments and corporations. Mortgage funds invest in residential and commercial mortgages. Money market or short-term funds invest in government treasury bills and corporate commercial paper, all with a term of under one year. Balanced funds invest in a mixture of bonds. stocks and money market instruments and alter the proportion of these investments according to the manager’s view of these investments.
Related Article
Mutual funds are a very popular investment for retail investors. They package the investment management skills of professional money managers in an economical manner for smaller amounts. Their current popularity has increased to the point where they are starting to replace traditional savings instruments like bank and trust deposits and even direct investment in stocks and bonds.
With a mutual fund, individual investors buy units of the fund. These units give them a “pro rata” share of the value of the investments of the fund. The unit value of the fund is struck by adding up the values of all the investments at their market prices, subtracting amounts owed by the fund and dividing by the number of units outstanding.
The most popular type of mutual fund is an “open-ended” unit trust. This means that the fund sponsor has agreed to buy and sell units at the unit value established at particular times. Valuation used to be monthly or weekly, but now is almost universally done by major funds on a daily basis.
More About Mutual Funds
In Canada, mutual fund regulation is a responsibility of the provincial governments. In Ontario, for example, mutual funds and the people who sell them are regulated by the Ontario Securities Commission (OSC). Mutual Funds must have a “prospectus” (a legal description of the fund) which ensures disclosure of all relevant information concerning the fund. Mutual fund companies and sales agents are also regulated to ensure that they provide the proper information to potential investors.
Mutual funds are established by fund sponsors, who are usually the company in charge of managing the fund. They go through the legal work of having a fund approved and make the initial investments in the fund. In return, the fund structure usually allows for the fund company to recover their costs and administration expenses and receive a “management fee” for providing the investment management of the fund. These expenses are taken out of the fund on an ongoing basis. The level of these fees compared to the total assets of a fund is referred to as the “Management Expense Ratio,” or “M.E.R.,” and usually ranges between 0.5% and 3.5% of fund assets. Any significant changes to the fund require approval by a vote of the unit-holders, as set out in the trust indenture.
There are many types of mutual funds, such as equity, bond, balanced and money-market, which invest in domestic or foreign marketable securities. There are also mutual funds that invest in real estate, mortgages, and other less liquid types of investments. Labor-sponsored funds often take advantage of Canadian Income Tax legislation, which allows investors to shelter invested monies from income tax in exchange for investment in smaller start-up companies.
So, What is a Mutual Fund?
To pose the question again, what is a mutual fund? We should now have a clear idea of how to answer this question. Mutual funds are pools of money jointly managed by a professional money manager that are invested in order to provide the group of investors with returns. The guidelines of a fund can differ, but all regulations and guidelines are spelled out in the fund’s trust indenture and monitored by government regulators.
(Visited 65 times, 59 visits today)














