What are Tax Deferred and Tax Exempt Investment Accounts
Post on: 4 Июль, 2015 No Comment
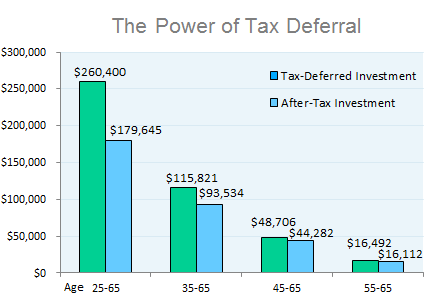
Tax planning is a key part of a retirement planning strategy and the use of the right types of accounts is central to meeting tax planning goals. The decision on what type of investment account to use to hold your retirement funds will have big impacts on what and how you withdraw money at retirement.
Tax deferred accounts are accounts in which the investments in the account are not included in taxable income at the time the investment is made. These investments can then grow tax free in the account until they are distributed or withdrawn at which point they become taxable as regular income to the individual. So you get the benefit of no taxes now for regular taxes in the future, which is where the deferred part comes in.
Tax exempt accounts are accounts in which the investments in the account are included as taxable income when earned and taxes are paid on them at the individuals current rate. The investments then grow tax free in the account and stay that way. At retirement when withdrawals start to happen these withdrawals are not subject to tax since they were taxed prior to investing in the account. So, they are exempt at withdrawal since they were taxed at the time of investment.
Traditional IRAs and 401k plans are the most common tax deferred account investment vehicles for individual investors. Created by legislation to encourage retirement savings, these investment vehicles offer the ability to hold stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other investments in a tax deferred status. The IRA is entirely investor driven as most any investment asset that can be purchased can be held in an IRA, while the 401k is an employer driven feature that usually has a set of predefined investment options usually including a broad mix of mutual funds of different asset classes.
Roth IRAs and Roth 401ks are the most common types of tax exempt account investment vehicles for the individual investor. Also created by congressional action to further the goal of encouraging retirement savings, these two types have similar features as mentioned above for IRAs and 401ks except for the tax treatment at retirement, which is tax exempt.
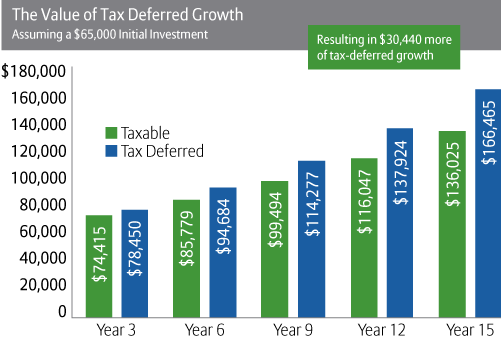
Other savings vehicles that should be mentioned are the Keogh account which is a tax deferred account type that is primarily of interest for self employed individuals or owners of small unincorporated businesses. Some arguments can be made for higher income or net worth individuals to use a Health Savings Account (HSA) which incorporates some benefits of both approaches, allowing pre-tax contributions, but tax free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. With the medical expenses in retirement, and some exemptions after certain ages, this can be a creative idea to consider if other options are already maxed out, but generally either IRAs or 401ks are recommended first.
Not commonly thought of as an investment vehicle for retirement, but worth mentioning in this discussion due to being among the tax advantaged investment types is the 529 plan, which is used for saving for college and is a tax exempt account as long as the earnings are used for qualified education expenses.
Options for both tax deferred and tax exempt savings are available to most people who are either employed or are earning an income and knowing what these options are is an important step in developing a savings plan. The next step is putting it into place with the right mix and executing on that plan.














