Types of Mutual Funds Asset Class Categories
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
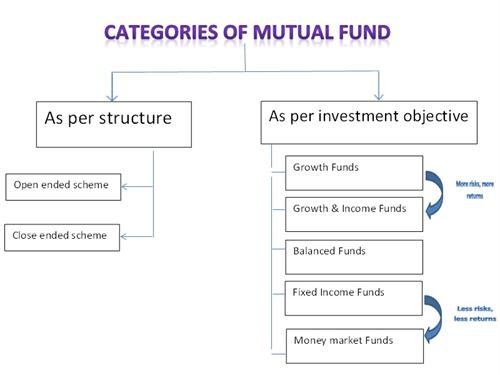
How Funds Are Categorized
You can opt-out at any time.
Mutual funds are organized into categories by asset class (stocks, bonds and cash) and then further categorized by style, objective or strategy. Learning how mutual funds are categorized helps an investor learn how to choose the best funds for asset allocation and diversification purposes. For example, there are stock mutual funds, bond mutual funds and money market mutual funds. Stock and bond funds, as primary fund types, have dozens of sub-categories that further describe the investment style of the fund.
Stock Fund Categories:
Stock funds are first categorized by style in terms of the average market capitalization (size of a business or corporation equal to the share price times the number of outstanding shares):
- Large-cap Stock Funds invest in stocks of corporations with large market capitalization (greater than $11 billion, according to Morningstar ). These companies are so large that you have probably heard of them or you may even purchase goods or services from them on a regular basis. Some large-cap stock names include Wal-Mart, Exxon, GE, Pfizer, Bank of America, Apple and Microsoft. Morningstar also has a market cap group, called Giant, that represents mutual funds investing in corporations of average market capitalization greater than $47 billion.
- Mid-cap Stock Funds invest in stocks of corporations of mid-size capitalization (between $2.5 billion and $11 billion, according to Morningstar ). Many of the names of the corporations you may recognize, such as Harley Davidson and Netflix, but others you may not know, such as SanDisk Corporation or Life Technologies Corp.
- Small-cap Stock Funds invest in stocks of corporations of small-size capitalization (between $750 million and $2.5 billion, according to Morningstar ). While a billion-dollar corporation may seem large to you, it’s relatively small compared to the Wal-Marts and Exxons of the world. Morningstar also has a market cap group, called Micro-cap that represents mutual funds investing in corporations with average market capitalization of less than $750 million.
Stock funds are next categorized according to their objective, which will primarily be divided into Growth, Value or Blend objectives:
- Growth Stock Funds invest in growth stocks, which are stocks of companies that are expected to grow at a rate faster than the market average.
- Value Stock Funds invest in value stocks, which are stocks of companies that an investor or mutual fund manager believe to be selling at a price lower than the market value. Value Stock Funds are often called Dividend Mutual Funds because value stocks commonly pay dividends to investors, whereas the typical growth stock does not pay dividends to the investor because the corporation reinvests dividends to further grow the corporation.
- Blend Stock Funds invest in a blend of growth and value stocks.
Now that you have learned the basics of stock mutual fund categorization, you will understand what it means, for example, if you see a particular mutual fund that is categorized as a Mid-cap Value fund. It is a fund that invests in a group of stocks that represent corporations of mid-sized capitalization with a value objective.
Stock funds can also be categorized as International or Foreign Stock. into geographic region, such as European or Pacific Rim, or into specialty areas, which are usually called sector funds. such as Health, Real Estate, Technology, Energy, Consumer Staples, Utilities and so on.
Bond Fund Categories:
The types of bond funds and how they are categorized may be best understood by revisiting the basics of bonds. Bonds are essentially IOUs issued by entities, such as the US Government or corporations, and bond mutual funds are primarily categorized by those entities who want to borrow money by issuing bonds:
- Government Bond Funds invest in various types of US Treasury bonds.
- Municipal Bond Funds invest in various types of Municipal bonds. The bond issuer—the municipality—is usually a state within the United States (i.e. California Municipal Bond).
- Corporate Bond Funds invest in various bonds issued by corporations.
Bond funds are also categorized by the average duration (similar to, but not always the same as, maturity) of the bonds held in the mutual fund:
- Long-term Bond Funds will primarily purchase bonds with a duration greater than 10 years.
- Intermediate-term Bond Funds will primarily purchase bonds with durations between 3.5 and 6 years.
- Short-term Bond Funds will primarily purchase bonds with durations of one to 3.5 years.
- Ultra-short term Bond Funds will primarily purchase bonds with durations less than one year.
Bond mutual funds may be further distinguished by the credit quality of the underlying bonds held in the particular bond fund. For example, US Treasury bonds are among the highest of credit quality (low risk to bond holder) and Junk Bonds are among the lowest of credit quality (higher relative risk to bond holder) and are often called high income bonds.
Money Market Funds:
Money Market Funds are typically categorized as either taxable or tax-free.














