The Rise Of The Hedged Mutual Fund
Post on: 16 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
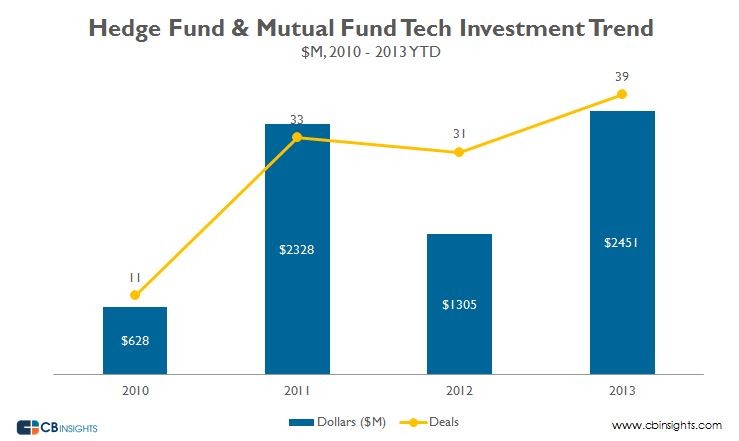
Hedged mutual funds. although previously only available to institutional clients, are now readily available for use in the small retail investor’s toolkit. While these types of mutual funds are gaining acceptance overseas, this article will focus on their relatively new existence in the United States retail investor marketplace. As a result of the repeal of the SEC’s short-short rule in 1997, these funds draw on the decades-old hedge fund strategies within the traditional mutual fund structure. (To read more about traditional hedge funds, see Introduction To Hedge Funds — Part One . Part Two and A Brief History Of The Hedge Fund .)
With this relatively new mutual fund category, the barriers to entry are much lower. Unlike retail hedge funds, which have higher minimums that require some level of investor accreditation, this breed of mutual fund enjoys the same level of accessibility as the more commonplace active and passive strategies available across the traditional equity and fixed income style boxes .
The gradual appearance of such funds over the past 10 years is a result of investors’ ongoing desire to find additional sources of return, diversification and risk management as doing so within more traditional offerings becomes more challenging.
Types of Hedges
Hedged mutual funds are available as a single strategy (such as. a U.S. market neutral fund) option or as a fund of funds. which employs several investment managers offering different strategies in the service of one overriding goal, namely the achievement of a stated return in excess of a risk-free rate with a lower standard deviation .
The strategies are typically active, though some look to match a composite index or a particular strategy index. The hedged mutual fund should be differentiated from its relatives: the occasional hedgers, such as the long-only funds that are allowed to sell short by virtue of their mandate (but may do so only infrequently) and the leveraged or inverse index funds, which offer investors the inverse performance of a given index or leverage on the performance of that index. These two fund types offer a more limited arsenal and less resemble actual hedge funds than the hedged mutual fund. (To keep reading on indexes, see Index Investing . A Market By Any Other Name and The ABCs Of Stock Indexes .)
Benefits
In contrast to their more traditional hedge fund counterparts, these funds appear to enjoy several distinct advantages common to traditional mutual funds including:
- Transparency
- Daily valuation
- Daily liquidity
- Limits on leverage
- Illiquid positions and short-selling
- No lock-ups
- Lower asset management fees relative to the traditional hedge fund
- No performance fees (ex. 20% of profits)
- Simplified tax reporting (1099s v. K-1s)
- Independent audits
- Independent board of directors
- Trustees
- Separate custody
Such features allow for fast and easy implementation with limits on helpful, yet potentially harmful, hedging techniques. Hedged mutual funds also boast competitive costs, third-party oversight and independent safekeeping. The funds’ unique strategies often allow for low correlation with other asset classes, making them a potentially good diversification and risk management tool in changing market environments.
Drawbacks
These funds carry several potential disadvantages as well. Fees are often higher than those of the typical actively managed mutual fund, where the cost of such active management can run from 0.75-2% at the higher end, depending on the strategy and share class. By contrast, the fee range for hedged products can be from 2.5-4% or more. Some investors may view such high hurdle rates with skepticism, as these higher fees may act as a drag on performance (returns may be consumed more rapidly by higher fees).
These funds’ numerous strategies are a potential double-edged sword as well, as they may subject portfolios to greater risks if markets move in an unfavorable direction. The complexity of the strategy may be difficult to grasp for less sophisticated investors, making asset allocation decisions more challenging; therefore, investors may wish to retain the services of an investment advisor familiar with such strategies. (To find out more on asset allocation, read Five Things To Know About Asset Allocation . Achieving Optimal Asset Allocation and Asset Allocation Strategies .)
Not all hedge strategies may lend themselves well to the more highly regulated mutual fund structure either. For example, distressed debt. global macro and fixed-income arbitrage have generally operated with less transparency, invested in less liquid securities and used more leverage. By law, hedged mutual funds are constrained in their ability to use such features, potentially limiting their ability to add alpha. (For related reading, see Adding Alpha Without Adding Risk .)
Analysis and Outlook
When it comes to investing in hedged mutual funds, ordinary retail investors need to do their homework to determine which approach to hedging can best be integrated into their portfolios and enable them to achieve their investment goals, retirement or otherwise. (For more insight, read A Beginner’s Guide To Hedging .)
Consider your goal, time horizon to reach it, risk tolerance and level of sophistication.
Due diligence on the investment team’s leadership, experience with the strategy or strategies in question, philosophy, process and appropriateness of fees are as essential for hedge investors as they are for traditional funds. Because of the relative novelty of the category, investors need to gain an understanding of what the strategy is trying to accomplish and whether it will contribute to their investment objectives. The research and due diligence process needs to reflect this. While some initial research finds value added in these strategies, the jury may still be out for the long-term ability of this subset of the mutual fund world to deliver alpha and manage risk.














