What is an ETF
Post on: 22 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
Categories
The full form of ETF is exchange-traded fund which is an investment fund. This investment fund is traded like stocks or shares in stock exchanges. During the activities of a trading day, ETF comprises different types of financial assets nearest to its NAV (net asset value ). These different types of financial assets might include bonds, commodities and other types of stocks or shares.
ETF also tracks index like NIFTY and like SENSEX. An ETF might provide handsome returns or profits. This is because ETF is traded like stocks and it has tax efficiency. Investors might get good profit because ETFs are invested through low cost investment strategy. In the world of exchange-traded products, ETF is the most common and most popular name.
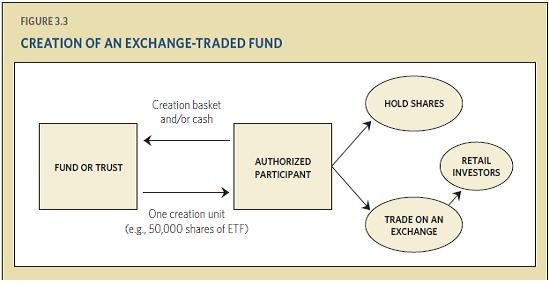
Actually shares of an ETF is bought and sold by large institutional investors. They are the authorized participants who trade directly in relation with the fund manager. Institutional Investors exchange thousands of ETFs in creation units (a host of underlying securities). There is option for these investors to invest in ETF for long-term.
Most authorized investors act like market makers only on the open market. So, ETF share exchange in creation units also depend on the ability of these investors. This is important because this process provides liquidity and ensures balanced state between NAV and intraday market price. Whereas, other investors like retail traders invest with underlying financial assets on secondary market (where pre-issued financial instruments are bought and sold).
Every ETF has an ability to combine a close-end fund with a unit investment trust or a mutual fund. A unit investment trusts valuation feature has NAV and this can be bought or sold at the end of an intraday trading. On the other hand, a close-end fund has all day tradability feature with its fluctuating prices in relation to its NAV. So, these two are combined by an ETF for exchange. It is to be remembered that a close-end fund is not an ETF in its single stand.
There might be different types of ETF. Let us understand them one by one. Index ETFs are in stock market that comprise financial securities and imitate stock market index performance. These ETFs are also known as index funds. Some of them are also called inverse ETF or leveraged ETF. Inverse ETFs focus on the inverse or opposite performance of the daily index by investing in derivatives .
Other types of ETFs are commodity ETFs (also known as ETCs) that invest in commodities only. For example, commodity ETf might invest in metals that are regarded as precious. One of the popular commodity ETFs is gold exchange traded funds . Like that silver exchange-traded funds are also commodity ETFs. A commodity ETF does not invest in securities and therefore this type of ETF is regarded as index funds (they tracks generally non-security indices).
Then there are bond ETFs which invest in bonds. Bond ETFs grow vigorously in a steady manner during the period of economic recession. This is because at the time of recession investors rely to invest only in bonds and not in to share market. For example, government treasury bonds and also any stable financial bonds that a reputed company issues for investors. Thus, one thing is clear that a bond ETF can give an indication of an economic condition of a stock market.
Currency ETF is first launched in 2005 in New York which was then called Euro Currency Trust. Right from that point currency ETFs get returns and track all major currencies from share index. Recently another name has come in ETFs world that is actively managed ETF. This type of ETF is updated daily online and displayed a fully transparent (means at risk with investment that is arbitrage ) current security portfolio.
An exchange-traded grantor trust is one of the types of ETF which engage in a host of stocks of an industry or a particular sector. This type of ETFs are neither index funds and nor actively managed funds. Under an exchange-traded grantor trust ETF, an investor shows his or her direct interest in financial assets of a particular industry.
Apart from all these there are leveraged ETFs. Leveraged ETFs try to get sensitive market movements returns or profits. To achieve double and triple market returns, leveraged ETFs use technique like derivatives, rebalancing, equity swaps and financing engineering. The trading done with future contracts are the most common form of leveraged ETF technique.














