If Interest Rates Rise Will Gold Go Down and the Dollar Rise
Post on: 18 Август, 2015 No Comment
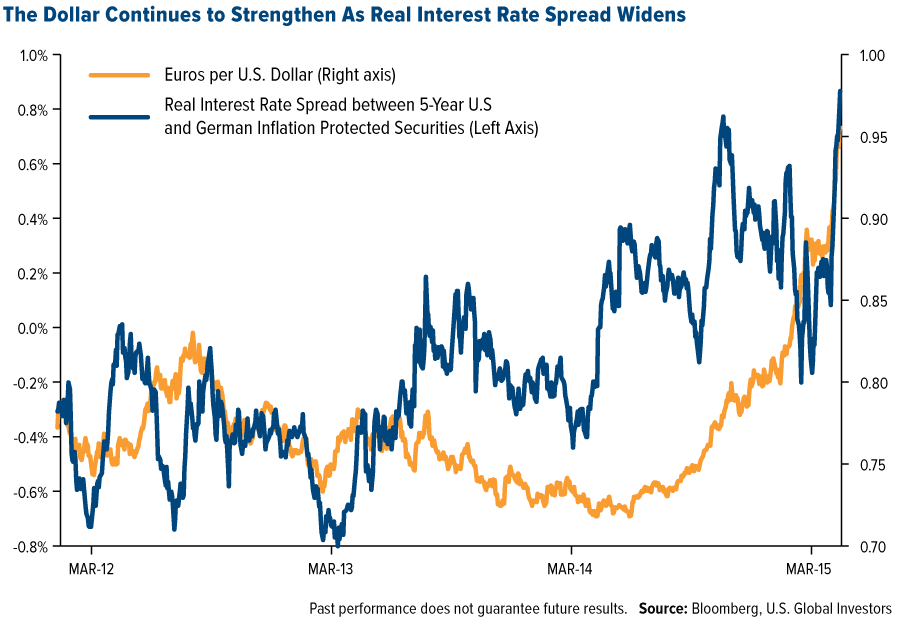
Will Gold Go Down and the Dollar Rise?
Interest Rate Rises in a Growing Economy
In an economy like China borrowers tend to be businesses enjoying the remarkable growth rates at around 10%. Their businesses in general are thriving and income either steady or growing with the potential to grow more of easily pay down debt. If you throw inflation of between 5 and 7% at them on certain items, their ability to absorb those costs is enormous. These may be items such as oil and food which do absorb a large portion of discretionary spending, but are accepted as one of life’s burdens that we all must endure. Usually they can pass them onto their customers without their customers being driven away. In such an environment interest rate rises then have the desired effect of tempering growth without stifling it. Overheating, at the risky end of the market is restrained and that along with a remarkable cooperation with government objectives in the economy has the desired effect of keeping the economy growing without excessive strains in one part or the other.
Interest Rate Rises in a Shrinking Economy
Where an economy is in recession and inflation starts to rise from food and energy inflation, the economy finds it extremely difficult to absorb such inflation whatever level of the economy we are talking about. Traditional economics would have central banks attempt to ensure that such inflation does not flow into other areas, but it can only use interest rates to do it. This is like a misdirected sledgehammer in so many cases as it now imposes yet another burden on businesses that are struggling to keep going and ensure minimum profitability. The effect of interest rate rises in this climate is to curtail business activity even more. At worst it can precipitate a depression eventually. What it does that is so difficult to rectify is to undermine already wavering confidence. If confidence is already undermined then such further cost pressures send it down into a spiral. The U.K. may experience this situation in 2011 and 2012.
Interest Rate Rises in a ‘Stagflating’ Economy
Now let’s take a situation not quite as drastic as that above. There is little to no growth in an economy and it suffers food and energy inflation. Energy inflation is imported, so there is usually no way to restrain such price increases. Food inflation in economies that are not self-sufficient has the same effect. Now along the lines of traditional economics, inflation is the one factor that prompts rate increases. Whether it is a one-off spike, or a persistent raising of the oil price does matter, but these days there appears to be no respite from these, which now stand at around $113 per barrel. An interest rate increase when it comes, becomes and additional taker of income, so adding to the burden of a business that is struggling to survive and cannot see any relief from a growing economy. The result is that the business now begins to suffer. It targets cost cutting, which in turn ensure the overall economy of the nation either continues to stagnate or declines into recession or worse.
The Impact on Currencies of Rising Interest Rates
The theory that is usually accepted is that if you raise interest rates you raise the value of a currency internationally. This is true where an economy is growing in a sustainable way, provided exchange rates are not managed by the central bank or government. The ‘carry’ trade has the function of borrowing money from a low interest rate nation and placing it on deposit in a high interest rate paying nation, so placing downward pressure on one exchange rate and upward pressure on the recipient currency. It is another source of gain if the prospects for the currency where the funds are borrowed are poor and it is declining anyway. This allows interest gains to be enlarged by a capital gain on the exchange rate.
Where interest rates are rising but inflation is higher there will exists a ‘negative real’ interest rate which will lead to an exchange rate decline. Where the decline is due to economic fundamentals are such that there is a Balance of Payments deficit overall, then rising or just high interest rates may well not look attractive to outside lenders. This negates any benefits from interest rate hikes.
Illustration
Take for instance an individual that is over-borrowed and his business declines to the point where he cannot service his loans, the bank would usually call in those loans and if not able to, will sell the clients assets in an attempt to cover the debt. If that man were to approach another bank for more loans with which to delay sequestration it may be that he gets the loan, but what impact on his balance sheet. He will, of course be made to pay a higher interest rate. This will ensure the eventual likelihood of repayment is reduced. The higher interest rate will by no means raise his credibility in the market place. Greece, Ireland, Portugal and Spain have moved into that category. The U.S. debt situation has been likened to Greece recently. So to attract more foreign capital, would higher interest rates add credibility to the U.S. debt position? In that case no.
The U.S.
If the U.S. were to attempt to ensure zero ‘real’ interest rate levels by raising interest rates to that of internal inflation [including food and energy inflation], the impact would not be to make the dollar more attractive but to at best stave off the speed at which the dollar is falling in foreign exchanges. What would happen is that state and federal borrowing would have to offer higher interest rates. This would hammer the bond market and frighten off foreign lenders as well as cause the economy to move into ‘stagflation’.
Certainly no such rate hikes will take place until the U.S. economy is able to maintain growth in the face of such rises. This may well take some time longer.
The Eurozone
The E.C.B. has let it be known that they will impose three interest rate hikes in 2011 in an attempt to rein in inflation from primarily food and energy. The E.C.B. is clearly of the opinion that the stronger Eurozone economies are able to bear these rises. Economic activity is concentrated in the stronger E.U. economies. While the E.C.B. is aware that such interest rate hikes will hurt the southern members, their relevance to the overall E.U. economies is not of significance. They are trading on the belief that the woes of these nations will not undermine confidence in the euro itself. In fact, the joy of having weak members in the Eurozone is that they help to keep the euro exchange rate down and the stronger members competitive internationally.
We feel they may have miscalculated in that the confidence in the euro may well prove mercurial should any more members need financial assistance to meet their debt obligations. Their inability to date, to finalize the composition and strategy of the bailout fund, may well lead to them being overextended on their balance sheet. Should the Eurozone subsequently slip into stagnation, they will be seen to be overextended.
Will the Gold Price Go Down as Interest Rates Rise?
Again it comes back to confidence and the waning of instability. If U.S. interest rates move into real positive territory on the back of a sustainable recovery then the dollar will offer value. If the recovery has not gained real traction and rising interest rates still leave them negative ‘real’ rates, then the dollar will not offer value. In the former case U.S. gold investors may well liquidate their holdings to some extent. In the latter case there is little reason to sell gold holdings.














