Why We Could Easily Have Another Flash Crash
Post on: 24 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
Follow Comments Following Comments Unfollow Comments
It’s been a great year for the stock market, which could make some investors complacent or overly confident. Before you run with the bulls, read the guest post below by Brian Korn. and Bryan Y.M. Tham. securities lawyers with Pepper Hamilton. They explain why our markets aren’t safe from a flash crash. Let stock buyers beware.
By Brian Korn and Bryan Y.M. Tham
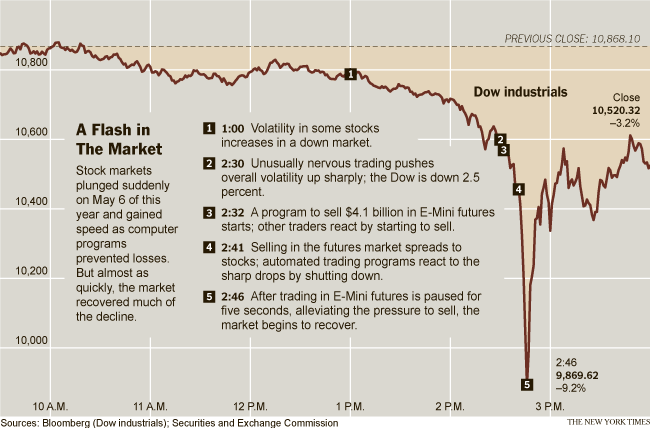
Mind the gap. The flash crash on May 6, 2010 caused a sudden drop in the Dow, followed by a stunning recovery in an otherwise uneventful trading day.
Three years ago, on May 6, 2010, U.S. capital markets experienced the “flash crash,” when the Dow Jones Industrial Average suffered a stunning 1,000-point loss (9%) in five minutes, followed by an equally dramatic recovery. It could happen again.
Moments before the 2010 flash crash, individual stocks were trading at a greater than 90% discount to the price. Accenture PLC, for example, was quoted at $39 just prior to the flash crash, then had trades clear at $32.62, then $5.34, $4.04 and $1.84 before recovering to close at $41.09. The point decline in the Dow within a single day was the largest since the Dow debuted in 1896.
Despite the attention received from various news groups, economists, and the Securities and Exchange Commission, which published its findings jointly with the Commodities Futures Trading Commission in a study on Sept. 30, 2010, the specific cause of the flash crash remains in dispute. It’s bad enough that the flash crash occurred. Worse though, is that the corrective measures have focused on mitigating the effects of the crash, not the cause .
Market crashes and government attempts to prevent future ones, are nothing new. The 1630s Tulip Mania crash at the end of the Dutch golden age led to government efforts to mediate contracts of affected merchants and hostility toward speculators. The U.S. Panic of 1873 resulted in national governments’ embrace of protectionist policies and a shift away from the global silver standard. An investigation into the causes of the Wall Street Crash of 1929 led the Pecora Commission to recommend legislative initiatives which led to the modern securities laws.
Still, the 2010 flash crash exemplifies the risk created by a new and accelerating trend: the market’s shift towards and reliance on automated computer systems in trading; and accordingly, a new class of risk to the markets – the computer-based trading malfunction.
Since this flash crash, other computer-based trading malfunctions, or “glitches,” have transpired, highlighting in each case other at-risk areas in the global trading system. On Aug. 1, 2012, Knight Capital suffered a technical glitch in its algorithmic trading systems, causing more than 140 stocks to be misquoted, eventually costing the firm more than $440 million and forcing it to raise significant capital. On April 25, 2013, a computer glitch in the Chicago Board Options Exchange shut down the exchange for half a day, preventing options trading on two of the U.S. stock market’s most closely-watched indexes.
Similarly, concerns persist that markets remain vulnerable to the rapid dissemination of disinformation, such as cyber-terrorism initiatives aimed at general disruption. One of these was a false report on April 23, 2013, from a hacked Associated Press Twitter account, that the White House had suffered two explosions and that President Obama had been injured. This report resulted in sharp decreases in the Dow and the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index; they rebounded after the AP revealed it had been hacked.
Each incident has prompted careful review and additional changes to regulatory and procedural safeguards by capital markets regulators, including, the SEC, the CFTC and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority. These changes are largely designed to mitigate the potential risk of volatility or damage caused to the markets.
Regulatory changes generally fall into three categories: circuit breaker modernization, erroneous trade breaking rules, and new rules to strengthen minimum quoting standards. Here’s how they each respond to a flash crash:
Circuit breaker modernization. On May 31, 2012, the SEC approved a “limit up-limit down” mechanism that prevents trades in individual exchange-listed stocks from occurring outside of a specified price band, to replace the single-stock circuit breaker pilot program, which was developed and implemented in response to the flash crash. This mechanism is designed to prevent trades in individual securities from occurring outside of specified price bands (percentage levels above and below a security’s average reference price over a preceding five-minute period). It also implements rules that affect the treatment of such things as market and stop orders; specialist and market maker quoting obligations; declaration of trading halts by exchanges; and obvious or catastrophic errors.
In addition, the SEC approved market-wide circuit breakers that, when triggered, halt trading in all exchange-listed securities throughout the U.S. markets. Recently, the SEC approved modifications to these circuit breakers, including, among other things, replacing the DJIA with the S&P 500 as the determining index for circuit breaking. This would reduce the threshold of decline from 10% to 7%, using change from the previous day’s close instead of the last month of quarter average for decline calculations; reduce halt time to 15 minutes (instead of 30, 60 or 120 minutes); and reduce the triggering time for trading halt time periods from six to two minutes.
Erroneous trade breaking rules. Although contemplated prior to the flash crash, the SEC approved the Clearly Erroneous Pilot Program, which identified new rules following the flash crash outlining when an erroneous trade would be broken. These erroneous trade rules, which clarified when–and at what price–completed trades will be reversed, or “broken,” by the exchanges and FINRA, were designed to foster a sense of certainty to reduce the likelihood of market panic and capital flight when computer glitches occur.
The lack of consistent standards for breaking trades prior to the Clearly Erroneous Pilot Program contributed to uncertainty of application. Clearly erroneous execution rules varied from exchange to exchange, with some breaking trades only if the price exceeded an objective threshold based on the preceding market price, and others relying more heavily on the subjective judgment of exchange officials. On May 6, 2010, the markets, using a process that was not transparent to market participants, only broke trades that were more than 60% away from the reference price.
New rules to strengthen minimum quoting standards. Immediately following the flash crash, the SEC implemented new rules for the exchanges and FINRA designed to strengthen minimum quoting standards and prohibiting certain practices, including “stub quoting” – an offer to buy or sell a stock at a price so far away from the prevailing market that it is not intended to be executed – requiring market makers in exchange-listed equities to maintain continuous two-sided quotations during regular market hours that are within a certain percentage band of the national best bid and offer.
In addition, the SEC required FINRA and the exchanges to develop, implement and maintain a consolidated audit trail system, which collects and accurately identifies every order, cancellation, modification and trade execution for all exchange-listed equities and equity options. This audit trail requirement is the result of speculation that the flash crash began as the result of a “fat finger” keypunch error by a broker-dealer employee, which, despite the appeal of its ease of explanation, has never been substantiated. The audit trails allow for increased measurable data available to regulators for investigations of illegal activities, and for timely forensic investigations and diligence of broad-based market events.
Despite all these efforts, not much has changed. The rapid pace in developing and implementing these protective mechanisms and others will increase the market’s awareness and ability to react to glitch-based crashes. But at best, they will limit the effect of a flash crash — not prevent it.
The precise cause of the flash crash remains unclear. Therefore, the markets are still hostage to episodic technological outages that cannot be predicted or understood. The most recently was the startling half-day outage at the Chicago Board Options Exchange that shut down trading in the S&P 500, the most traded options product, and the S&P Volatility Index.
What’s ahead? Clearly more proposed rules and amendments to existing ones by the SEC. As cyber-terrorism becomes a greater concern, we can also expect government initiatives to address it. For example, in October 2011, the SEC’s Division of Corporation Finance issued a directive to companies to disclose particular risks related to cyber-terrorism and hacking attacks. The market remains susceptible to “non-market” hacking, such as the AP Twitter incident. And none of the regulatory initiatives are designed to protect offending firms from the financial fallout when their systems go awry.
Also On Forbes














