What Is Driving Oil Prices Realworld Demand and Supply
Post on: 15 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
Richard G. Anderson, Jason J. Buol
If your wallet felt a lot lighter every time you filled up your car with gasoline in 2004, it’s not surprising. During the second half of 2004, the futures and spot prices of oil reached record levels in today’s dollars, not adjusted for the effects of inflation. To what extent are higher prices the result of supply and demand factors? How much has speculation affected oil prices?
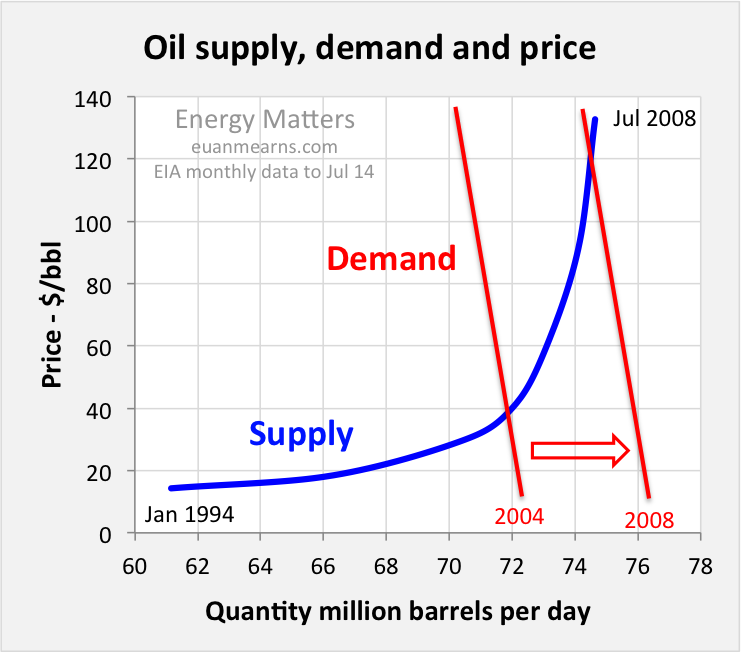
As news reports often say, oil prices are notoriously volatile. As figure one indicates, spot prices (indicated by the solid line) ranged from a low of about $10 per barrel of oil in the 1990s to more than $50 per barrel of oil in 2004. Just as dramatic, however, is the change in futures prices. In November 2003, the futures market expected prices to be approximately $27 by December 2004, but in November 2004, the futures market predicted oil prices of almost $48 by December 2004 and remaining around $40 through 2008. The ongoing conflict in Iraq undoubtedly was a factor in the change in the futures market between November 2003 and November 2004. Nonetheless, the reaction of the futures market suggests that the recent spot price increase is not viewed as a purely temporary shock.
Demand
Many factors affect the price of oil in the world market. Recently, the rapid increase in world oil demand has been a major factor. In August 2004, the International Energy Agency reported that world oil demand was increasing faster than at any other point in the past 16 years. The agency attributes the increase in demand to rapid economic expansion in several countries, particularly China.
In 2003, China became the second-largest consumer of petroleum products behind the United States, which consumed approximately 20 million barrels per day (bbl/d). According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), China accounts for about 40 percent of world oil-demand growth over the past four years and consumes approximately 5.56 million bbl/d. The EIA forecasts continued growth in oil demand by China, expecting China’s demand for oil to more than double in the next 20 years.
India also has fueled increased oil demand. The EIA predicts India’s future consumption will likely increase 75 percent in the next 15 years from its 1995 level of 1.6 million bbl/d. As other developing countries continue to expand, they are likely to follow the same pattern of sharply rising demand for energy.
Supply
Meanwhile, several oil-producing countries have undergone turmoil that has affected their abilities to produce at full capacity. Two such countries are Iraq and Venezuela.
Since the start of the second Iraq war, Iraq’s oil production has been uncertain. Not only have violence and sabotage of facilities contributed to production problems, but also sub-standard production methods during Saddam Hussein’s regime have damaged some reserves so severely that fully recovering pre-war production levels is questionable.
Venezuela has been plagued by political problems exacerbated by a nationwide strike from December 2002 through early 2003. The strike significantly reduced oil production and, although pre-strike production levels are returning, political problems continue to threaten the stability of this country’s oil production.
Speculation
Speculation refers to engaging in financial transactions that involve a high degree of risk. Speculative activities in the oil industry might include holding oil inventories for future sales or increased trading in the oil futures market. Many people, including Acting OPEC Secretary General Maizar Rahman and Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan, believe that speculation has driven up the cost of oil by $10 to $15. Greenspan stated during September 2004 House Budget Committee testimony that one possible source of higher prices was speculators, who influenced prices by taking larger positions in crude oil futures. This theory suggests that more active trading was taking place before and during the period when oil prices were reaching record nominal levels. A cursory examination of petroleum futures volume data from the Wall Street Journal demonstrates that the volume of trades was up during this time period, which indicates that enhanced speculation did contribute to increasing oil prices.














