The Ultimate Guide To Natural Gas Investing
Post on: 2 Апрель, 2015 No Comment

Natural gas is a gas that consists primarily of methane and is widely used as an energy source around the world. The natural resource is important for the creation of fertilizers, and is now used to power a wide variety of applications including automobiles. Supplies of natural gas are concentrated in a few regions of the world, and the fuel has historically been the source of political disputes in Eastern Europe and the Middle East as well as in the U.S. The place of natural gas in the domestic energy equation has been widely discussed in recent years, with many advocating for increased adoption as an alternative to crude oil products [see also The Guide To The Biggest Companies In Every Major Commodity Sector ].
Because natural gas is clean burning and found in massive quantities within U.S. borders, it has been hailed as a fuel of the future that will account for an increasingly large energy market share in coming decades. That factor has made natural gas a popular investment destination, as has the generally strong relationship between gas prices and the health of the U.S. economy. There are a number of options for investors to achieve exposure to natural gas, including futures contracts, stocks of companies engaged in extraction and transport of the gas, and ETFs and ETNs .
Physical Properties Of Natural Gas
Natural gas can be found in a variety of different locations. The gas is often found in coal beds, and is also found in both oil fields and natural gas fields. Natural gas located in oil fields is often referred to as associated while natural gas discovered in a dedicated natural gas field is described as unassociated. Natural gas is often a byproduct of producing oil, and disposing of unwanted gas historically posed a problem to oil companies. Because natural gas had to be transferred to end users via pipeline, supplies in remote areas were essentially worthless and were often burned offa process known as flaring that is now illegal in many countries. The development of energy infrastructure in recent decades has made it easier to transport and store natural gas produced from oil-related activities, and technological improvements have also facilitated the capture of this resource [see also Commodity Investing: Physical vs. Futures ].
Natural gas maintains a low density, a physical property that makes it difficult to transport via truck or boat in its gaseous form. Because transocean pipelines are not practical from a cost perspective, natural gas has historically been a local commodity. Whereas oil produced in the Middle East can be shipped around the world, end users of natural gas are generally located in relatively close proximity to the fuel source.
Natural gas can be temporarily converted to liquid form ( liquefied natural gas, or LNG) or compressed (compressed natural gas, or CNG) in order to make long distance transportation through traditional sources such as ships more efficient both from a logistical and cost perspective. Technological developments have increased the use of LNG and CNG, and shipments of natural gas between continents has increased significantly in recent years as a result [see also Three Mining Companies With Robust Yields ].
Natural gas goes through extensive processing before it can be used as fuel; almost all non-methane components must be removed before the commodity can be utilized as a source of energy. Byproducts of natural gas processing include carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, and sulfur.
Uses Of Natural Gas
Natural gas is a source of electricity generation that involves gas and steam turbines, and is used widely by power plants. Compressed natural gas is used as an alternative to automobile fuels, and the number of natural gas vehicles has increased steadily in recent years. Natural gas is also used as a feedstock for the production of ammonia, making it useful in the process of manufacturing fertilizer [see also Invest Like Jim Rogers With These Three Agriculture Stocks ].
Natural Gas Supply And Demand
There are four primary sources of natural gas, including:
- Gas-Rich Shale: This is the source for many natural gas reserves, but until recently had not been a focus of gas production.
- Conventional Gas Accumulations: Occurs when gas migrates from gas-rich shale into an overlying sandstone formation, and then becomes trapped.
- Tight Sand Gas Accumulations: Occurs when gas migrates from a source rock into a sandstone formation, but is limited in its ability to migrate upward.
- Coal Bed Methane: This type of gas is generated during the transformation of organic material to coal.
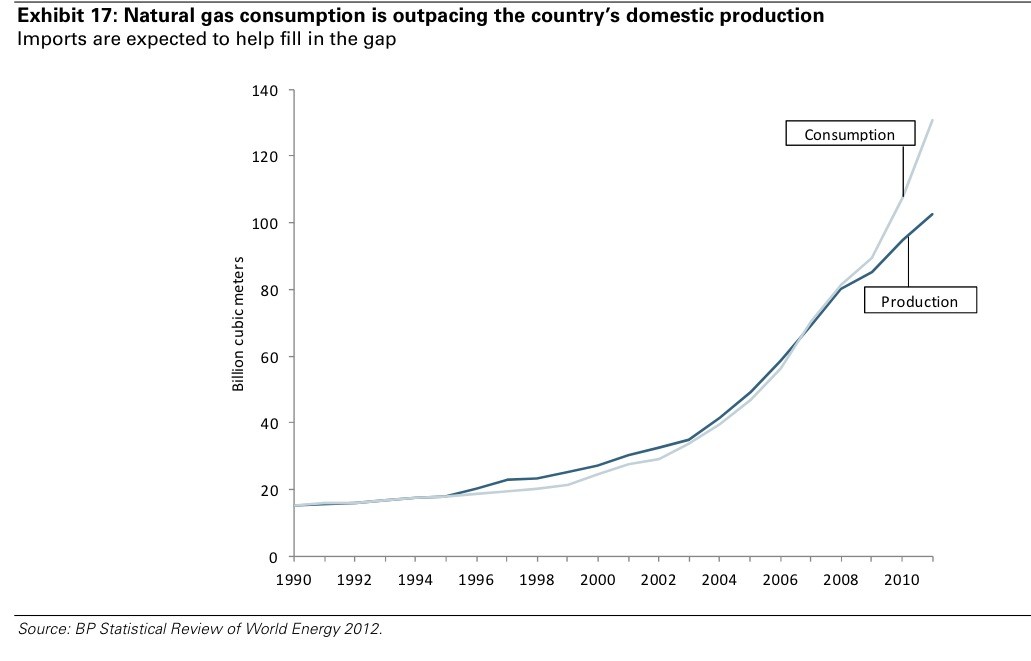
Russia is by far the largest global supplier of natural gas, followed by Iran, Qatar, and a number of other Middle Eastern countries. The worlds largest natural gas field is located off the shore of Qatar; the North Field is estimated to hold about 25 trillion cubic meters. That supply alone is enough to last 200 years at optimum extraction levels. However, because natural gas remains largely a local commodity, prices of natural gas in the U.S. will be impacted primarily by domestic supplies [see also Company Spotlight: Barrick Gold Corporation (ABX) ].
In the U.S. the largest natural gas deposits are found in Arkansas, Louisiana, Alaska, and Texas. Significant natural gas deposits are scattered throughout the western and southern parts of the country, though there are a handful of meaningful reserves located in Michigan, Kentucky, and West Virginia (see a map of the largest U.S. gas reserves ).
Proved Reserves














