Oil Exchange Traded Fund ETFs Crude Oil Futures Trading Disadvantages Investments
Post on: 7 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
Diversification is the key for safe investing. Investing in only one kind of instrument or sector is always risky. Investments restricted to the stock market or a particular commodity or currency would be akin to keeping all the eggs in one basket. For instance, if you are invested only in the currency market, you would suffer a loss in the event of weakness in the dollar. But if you are simultaneously invested in crude oil, this investment would appreciate as oil is generally negatively correlated with the dollar.
Till the introduction of the oil exchange traded fund, a person who wished to invest in crude oil, had to buy crude oil futures.
Trading in Crude Oil Futures had its Disadvantages
- The lot size of crude oil futures is huge and was too risky for the retail investor.
- Crude oil futures contracts of the month expire at the end of the month. So traders have the additional task of rolling over the positions that is selling the current month futures and buying the futures contracts of the next month.
- There is invariably a difference between prices of futures contracts of different months. So the investor has to study the prices and roll over his position at the most opportune time.
All this changed with the Oil Exchange Traded Fund
- By buying units of an oil exchange traded fund, an investor can make small investments according to his risk appetite.
- He can buy and sell the ETF units on the exchange itself, just like he buys and sells shares.
- Since he does not have to roll over positions, a person investing in an oil exchange traded fund does not have to repeatedly pay brokerage fees.
- An oil exchange traded fund is managed by experts in that sector.
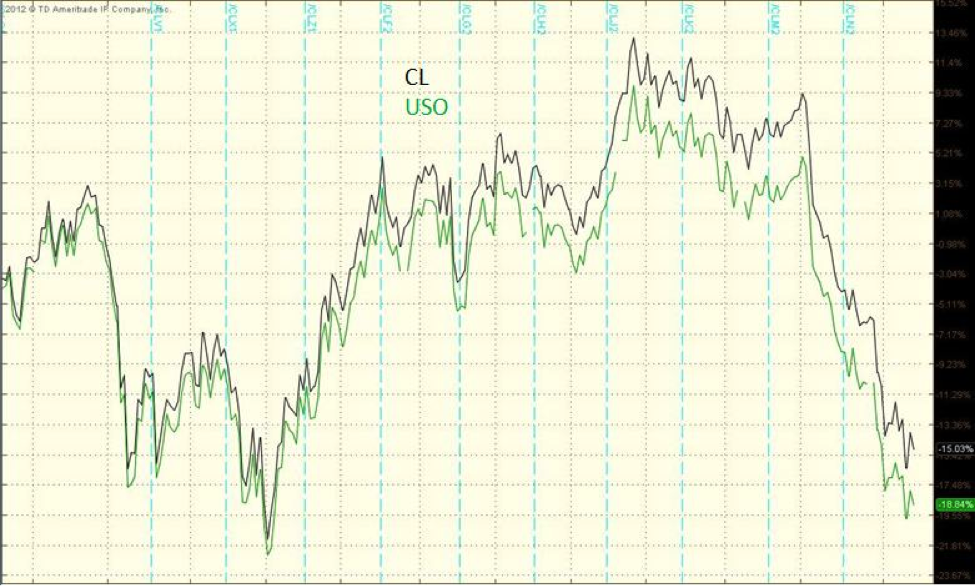
The United States Oil Fund was the first crude oil exchange traded fund in the U.S. market. At its inception in 2006, the price of the ETF was $68.25. After a year, it closed at $52.01. Though the price of crude fell only 6% during that period, the price of the ETF fell as much as 24%. This was because of the negative roll yield. Most oil ETFs make investments in crude oil futures. Generally, the price of the current month futures is less than the price of the future month contracts. So rolling over positions often leads to a negative role yield called as contango.
An Oil Exchange Traded Fund may invest in the following
- Physical asset: In this case, the oil exchange traded fund will invest in the commodity itself, that is, crude oil. However, this is rare because storage of oil in bulk would be difficult and expensive.
- Commodity futures: Most of the oil exchange traded funds invest in oil futures. They tried to ensure that the price of the ETF moves in tandem with crude oil prices. Since positions in the futures market are leveraged, the excess money is usually invested in interest yielding instruments.
- Oil companies: Some oil exchange traded funds invest in companies which manufacture and process crude oil.
One can also invest in oil exchange traded notes (ETNs). These are debt instruments which come with a credit risk.
For a retail investor, buying units of an oil exchange traded fund would be the best way to invest in the sector.














