How to Calculate VAR for Bond
Post on: 8 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
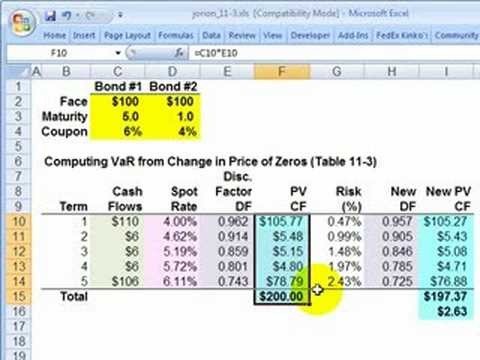
Instructions
Determine the period you want to use for the VaR. The VaR is always calculated with respect to a particular period—usually one day, but sometimes a week or more—and it reflects the amount of loss that may occur in that time period.
Use your interest rate model to determine the 99th percentile (or 95th percentile if you chose 5% in Step 2) interest rate increase that could occur in your market within the period you chose in Step 1. If your interest rate model is bell-curve shaped (as most are), then this will be the value 2.33 standard deviations to the right of the mean (1.65 standard deviations if you chose 5% in Step 2).
Tips & Warnings
References
More Like This
How to Calculate Value At Risk
How to Compute the Effective Rate of a Bond
How to Measure Return on Investment
You May Also Like
Variable rate bonds have a floating or variable interest rate, or coupon rate. The rate adjusts according to a predetermined formula outlined.
Value-at-Risk (VAR) is a method of calculating the maximum potential losses for an investment during a specific time period. The VAR is.
Yield to maturity (YTM) is one of the main ways investors compare the investment potential for bonds. Yield refers to the return.
Risk of Treasury Bonds. or she can sell the bonds. When interest rates rise, the market value of Treasury bonds falls.
How to Calculate Bond Risk. Higher interest rates cause the value of bonds to fall. There is also a risk that.
War bonds were issued by the U.S. government to finance World War II. Previously called Defense Bonds, almost $1 billion dollars' worth.
. receives correct security prices in stock or bond transactions. a trading assistant at an investment bank's corporate bond desk can.
Use VaR or value at risk for the most popular. How to Calculate Municipal Bonds. There are several bond calculations that.
While fixed- and variable-rate bonds have a dramatically different coupon structure, the underlying credit of the two financing forms are generally the.
Recompute every bond value at their current estimated value plus 1 percent. Analyze VaR or Value at Risk techniques by using.
Complex power S in volt-amperes (VA) is the sum of real power P in Watts (W) and reactive power Q in volt-amperes.
Portfolios are a collection of financial instruments, perhaps including disparate assets such as bonds, futures, shares, and more. Investors invest in portfolios.














