How Are Stock Options Priced by
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
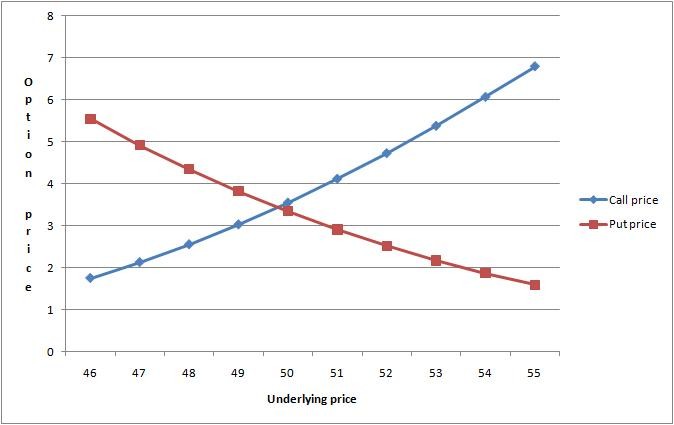
Stock Option Pricing — 2 Main Components, Intrinsic Value & Extrinsic Value
The price of an option contract, or sometimes known as the option premium. consists of 2 main components. Intrinsic Value and Extrinsic Value, governed by the principle of Put Call Parity.
Stock Option Pricing — What Is Intrinsic Value?
Example: If a stock is currently trading at $50, a Call option with a Strike Price of $40 will have a $10 value already built into it as it allows you to buy a $50 stock at $40. Therefore, that option will be priced at $10 + Extrinsic Value. Similarly, if that same stock is currently trading at $50, a Put option with a Strike Price of $60 will have $10 value already built into it as it allows you to immediately sell that same stock at $60 the moment you bought it. That option will also be priced at $10 + Extrinsic Value. Such an Option Contract with intrinsic value built into it is known as an In The Money Option (ITM Option).
How To Calculate Intrinsic Value?
The intrinsic value of a call option is obtained simply by deducting the prevailing market price of the underlying stock by the strike price of the call option.
The intrinsic value of a put option is obtained simply by deducting the strike price of the put option by the prevailing market price of the underlying stock.
A negative value indicates that there is no intrinsic value. An option which contains intrinsic value is known as an In The Money (ITM) Option.
Read the full tutorial on Intrinsic Value.
STOCK PICK MASTER!
Probably The Most Accurate Stock Picks In The World.
Stock Option Pricing — What Is Extrinsic Value?
Extrinsic Value, or sometimes known as the Premium Value or Time Value, of an option is the part of the price that is determined by factors other than the price of the underlying stock. This is what you are paying the seller of the option for the risk that the seller is undertaking for selling you the option contract. This risk money you are paying the seller is justified and determined by 4 main factors. Time to expiration, Interest Rates, Volatility and Dividends payable. One would need a pricing model such as the Black-Scholes Model to accurately calculate the Extrinsic Value of a stock option.
The price of a stock option consists only of it’s Extrinsic Value when there is no built in value at the moment you bought it (hence no intrinsic value).
Example: If a stock is currently trading at $50, a Call option with a Strike Price of $60 will have no intrinsic value built into it. Similarly, a Put option on that same stock with a strike price of $40 will have no intrinsic alue built into it. Such an option contract with no intrinsic value built into it is known as an Out of The Money (OTM) Option.














