Exponential moving average (Stock market) Definition Online Encyclopedia
Post on: 26 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
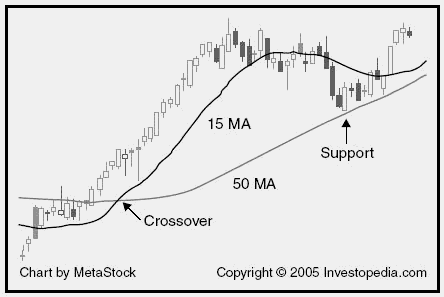
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
Description
EMA stands for Exponential Moving Average. It helps to smooth the price curve for better trend identification. Unlike the SMA. EMA places greater importance on recent data.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
Exponential moving average s place more weight upon the later moves in the time period than the earlier moves.
Exponential Moving Average
An exponential moving average is a type of moving average which gives more weight to more recent stock prices, and less weight to older, historical prices.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
Exponential Moving Average — EMA
What is the definition of Exponential Moving Average — EMA ?
An ‘EMA ‘ is moving average that is used to identify a security ‘s trend. It gives greater weight to more recent data in a bid to reduce the lag of the moving average.
Exponential Moving Average s (EMA )
One of the first indicators that most trader s will learn when finding the fascinating field of Technical Analysis is the Moving Average.
The Exponential Moving Average is the most popular of all the versions of the moving average. The exponentially smoothed moving average gives greater weight to recent price data and also includes all the data in the life of the security.
Exponential Moving Average s (EMA )
The problem with simple moving averages is that the earliest day of the time period has the same weight in the average as the most recent day.
Triple Exponential Moving Average (TEMA) is another smoother and faster version developed by Patrick G. Mulloy in 1994.
His first Double version can be studied here: Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA).
The TEMA, or Triple Exponential Moving Average. was introduced by Patrick Mulloy in Technical Analysis of Stocks & Commodities magazine, February 1994.
It compares two triple smoothed exponential moving average s, and displays the difference as a single line with positive and negative values. The TRIX is displayed on its own chart. separate from the price bars, and is the lower section in the example chart.
Exponential Moving Average Calculation
Exponential moving average s reduce the lag by applying more weight to recent prices. The weighting applied to the most recent price depends on the number of period s in the moving average. There are three steps to calculating an exponential moving average.
Exponential Moving Average
An Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) takes a percentage of today’s price and adds in the prior day’s exponential moving average times 1 minus that percentage. For instance, suppose you wanted a 10% EMA.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) An exponential moving average (EMA ) is another form of a weighted moving average that gives more importance to the most recent prices. Instead of dropping off the oldest prices in the calculation, however, all past prices are factored into the current average.
Exponential Moving Average :
Exponential moving average s give higher importance to recent changes in a stock price. If you want a snapshot of what a stock price is doing in the near present, this is probably the tool for you.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
The EMA is basically the same calculation except more weight is given to the latest data focusing more emphasis on what an index or stock price is doing more recently.
exponential moving average — a moving average smooths the fluctuations in stock prices by averaging the prices over a specified period. An exponential moving average gives heavier weight to the most recent data.
Exponential Moving Average — EMA
A type of moving average that is similar to a simple moving average. except that more weight is given to the latest data. The exponential moving average is also known as exponentially weighted moving average .
Exponential Moving Average s give more weight to the most recent data, and are therefore more sensitive and can react better to sudden price changes. This makes them more suitable for option trading .
Exponential Moving Average Calculation:
Source: Wikipidia.org
Example of an Exponential Moving Average Plotted on a Chart.
EXPONENTIAL MOVING AVERAGE — FIVE PERIOD
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) (above) is one of a number of smoothing techniques.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) A moving average that gives greater weight to more recent data in an attempt to reduce the lag of (or smooth) the moving average .
Exponential Moving Average The EMA for day D is calculated as:where PR is the price on day D and a (alpha ) is a smoothing constant. Alpha may be estimated as 2/(n+1), where n is the simple moving average length. Another form of the formula is.
Exponential Moving Average
Calculated by applying a percentage of today’s closing price to yesterday’s moving average value. As a result, the most recent market action is weighted more heavily enabling the EMA to capture near-term trend changes earlier than a simple moving average.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
exponential moving average. A moving average that is exponentially weighted. Example: for a 9 period EMA. todays close is weighted 20% and yesterdays ma is weighted by the other 80%.
Exponential Moving Average
Similar to a simple moving average. the exponential moving average is the average stock price over a specified time period in which more weight is placed on the latest data. The exponential moving average is also known as ‘exponentially weighted moving average ‘.
exponential moving average (ema)
a moving average That Gives more weight to the latest data (more recent bars), Whereas older bars get Exponentially Decreasing weight.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) — the type of moving average where more weight is given to the most recent data. It is front-end weighted, resulting in the most recent price changes having the greatest impact on its movement.
- exponential moving average (period :34,yellow).
- exponential moving average (period :89,purple).
- Horizontal lines drawing Support s / Resistance s of the past price action.
An Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) gives greater weight to more recent data in an attempt to reduce the lagging properties of the moving average. EMA = PreviousEMA + ((price-PreviousEMA)* (2 / period )).
3) Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
Lets see how EMA is different from WMA.
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
The Exponential MA is a refinement of the SMA that attempts to assign more weight to the most recent data, making it less sensitive to the price that is dropped from the calculation, and reduces lag.
8.1 Exponential Moving Average
And then the exponential moving average. The EMA as its more commonly called, is weighted close r to the current price of the scrip. That makes it follow the candle pattern more close ly as compared to the simple moving average or SMA .
We use Exponential Moving Average s as does the S&P 500 Real-time Signal service. We are also using a 34-period Slow Stochastic set to 34, 7, and 4 period s.
We use a smoothed version of CCI that has 34 period s of CCI smoothed with a 10-period Exponential Average.
3) 44-Period Exponential Moving Average of Close Price (blue)
4) 36-Period Exponential Moving Average of Close Price (orange)
5) Awesome Oscillator (there are no settings to change on this — apart from the colours).
Exponential Moving Average reduces the lag by applying more weight to recent prices relative to older prices. The weighting applied to the most recent prices depends on the specified period of the moving average.
Exponential moving average s gives more weight for the recent price action. So the difference in the EMAs represent the trend as well as the momentum of the stock price action.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) is a weighted average of a price which puts a higher weight on recent data point. Because it gives more weight to the most recent data, EMA enables trader s to react faster to recent currency pair rate changes.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
Similar to SMA. but more weight is given to later time period s. It is calculated by applying a percentage of later time period ‘s closing price to the previous EMA value.
- Exponential moving average s; I use the 8 and 21 day EMAs on the daily chart s to help with trend identification and dynamic support and resistance identification. Both the 8 and 21 EMAs are factors or levels that can add confluence to a price action setup.
2 Exponential Moving Average Cross Metatrader 4 Expert Advisor
Written by Metatrader Corp.
An exponential moving average improves the weighted moving average by weighting past history less and less, without ever removing the data completely. So it eliminates the impact when a data point is dropped from the moving average.
The exponential moving average (EMA ) is a less popular but more sophisticated version of the simple moving averages. You need a computer trading program such as FutureS ource to employ an EMA indicator.
The exponential moving average (EMA ) used in the MACD method is calculated as
where
EMAt. current value of exponential moving average.
The Exponential Moving Average is a type of the moving average study. In a simple moving average. all price data has an equal weight in the computation of the average with the oldest value removed as each new value is added.
6. Use exponential moving average s, or EMAs, for longer time frame s but shift down to simple moving averages. or SMAs, for short er ones. EMAs apply more weight to recent price change, while SMAs view each data point equally.
A 9-day exponential moving average is plotted on top of Litton’s prices. I drew arrows when a reversal bulge occurred (i.e. the Mass Index rose above 27 and then fell below 26.5). If the 9-day moving average was falling, I drew a buy arrow.
The 50EMA (exponential moving average ) line combined with some simple filter s helps me achieve exactly that. It surely does not have the glory of complex mathematical formulae or chart structure s, but it works, which is what I am interest ed in.
Modified Exponential Moving Average . The difference between the Modified Exponential Moving Average (MEME) and an exponential moving average is that MEME calculates the smoothing factor differently.
Module: A component of the CitiFX Pro platform.
What is an Exponential Moving Average ?
Read More
What is a Currency Symbol?
Simple Vs. Exponential Moving Average s
There are also exponential moving average s (EMAs). They work the same as a simple moving average. except they place greater weight on the more recent closing price s.
TRIX is calculated by formula:
Calculation of TRIX is based on EMA3 = triple exponential moving average (EMA of EMA of EMA ). For EMA period is usually used value of 15.
You can theoretically have a moving average for any timeframe. But, the most commonly-used moving average s in stock trading today are 20-day MAs, 50-day MAs, and 200-day MAs. You can have these in two different flavors: simple moving averages and exponential moving average s.
Bar 1 — Fail, failure breakout low of yesterday but tail, 60 minute 20 bar exponential moving average. probably seller s at the high of the bar and probably scaling in higher. 60 minimum or minutes twenty gap bars buy or long. Ok swing. better to wait
This would lead me down the path of using something more colorful like a double exponential moving average and I would take it a step further and displace it by x period s. If you are reading this and have no idea, what I am talking about then great for you.
The most common and popular form (and easiest to calculate) is the simple moving average. followed by the exponential moving average. The difference between the 5 types is purely down to how much ‘weight’ the average applies to recent data, compared to older data.
A 3-day exponential moving average is taken of the net NYSE advance s over declines, measuring the short term condition of the market. When this index moves above +100, a market short term buy signal is generated.
What Is the Exponential Moving Average.
What Are the Different Types of Disability Insurance Policies?
What Is FEMA Flood Insurance?
What Is a Dependency Exemption?
What Are the Best Sources for Budgeting Advice?
What Is a Joint Bond.
There are different types of moving average s-simple moving average (explained above) and exponential moving average. The Exponential Moving Average differs from a Simple Moving Average both by calculation method and in the way that prices are weighted.
There are simple and exponential moving average s with the latter helping to smooth the particular average. Trends are established when your short. intermediate and longer term average s are moving in the same direction. The 10, 50, 100 and 200 day average s are often used.
It is merely the 8 exponential moving average. A major advantage provided by the trading chat room on the website is the exchange of ideas for improving someone’s trading technique. The 8 exponential moving average has very consistent analytical features.
A hybrid indicator which is an oscillator. but used primarily as a trend following tool.
When using indicators that use exponential moving average s a trader needs to always be concerned about dramatic rises and falls in price in a single day as it skews the data used in calculating the average s.
Notice the labels for the momentum and its exponential moving average. Also notice that the momentum indicator is plotted in histogram format (positive green vertical lines and red negative vertical lines). The exponential moving average is plotted in blue in a linear format.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA )
Saya tidak akan menjelaskan lagi mengenai perbedaan SMA dan EMA. Silahkan pelajari sendiri di Babypips School. Intinya EMA biasanya lebih sensitif dan cepat sedangkan SMA lebih halus dan kurang sensitif. Lantas mana yang lebih bagus di antara SMA dan EMA. Tergantung.
In this example two exponential moving average s are used to defined the trend. This is the simplest way to define the parent trend.
Exponential Moving Average (Close. 05) cuts the BLUE line i.e. Exponential Moving Average (Close. 13) from the TOP in a downward direction, exit 30% from the counter.
4.2. When the RED line i.e. Exponential Moving Average (Close. 05) cuts the GREEN line i.e.
The main advantage of the Exponential Moving Average (EMA ) is that it discount s both prices of the previous and current period s. Every subsequent value becomes more significant.
Appel attempted to improve on that concept by using 3 Exponential Moving Average s to form 2 indicator lines. What MACD does is it plots the point spread between 2 different Exponential Moving Average s-a slower and a faster one. This is the first line.
Trader s tend to stick to two main forms of moving average s: simple moving averages (such as those mentioned above) and exponential moving average s. Some trader s get more fancy than these alone, but let’s not stray too far off the beaten path.
In other words, it is the difference between a 26-day and 12-day exponential moving average (EMA ). A 9-day exponential moving average. called the signal (or trigger) line, is then plotted on top of the MACD to show buy/sell opportunities.
I typically use a 10 day exponential moving average. Be sure to give room for play. Do not place the stop at the moving average line. It must be place below. Moving average s are dynamic and change as time progresses.
Exponential moving average
Although varying aspects of Dows comprehensive theory have been disputed, the fact remains that the overall philosophy remains sound.
Same as above but with a 20-day exponential moving average. This index is considered the most important of the three. Market buys and sells are determined in this index by the cross ing of trend lines or support /resistance levels depending on the particular market in question.
McClellan Oscillator is the difference between two exponential moving average s of the advance decline spread. The time period s are typically 19 and 39 days. The values of the indicator oscillate around zero, and generally range from -100 to +100.
The MACD is the difference between a 26-day and 12-day exponential moving average. A 9-day exponential moving average. called the signal (or trigger) line is plotted on top of the MACD to show buy/sell opportunities. (Appel specifies exponential moving average s as percentages.
The answer is, Moving Average s are of different types linear moving average and exponential moving average ; depending on which type of Moving average does one wants to go with (based on his particular needs), the formulas for calculating it will differ.
This is therefore an Exponential Moving Average. on which another Exponential Moving Average was calculated, with yet another Exponential Moving Average calculated on top. Moreover, an ROC is applied to this curve.
Another one utilized in technical analysis is the Exponential Moving Average. Essentially this moving average allocates more importance to more recent prices.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence /Divergence ): An indicator developed by Gerald Appel that is calculated by subtracting the 26-period exponential moving average of a given security from its 12-period exponential moving average.
So a pullback to the 40 day Exponential Moving Average (red line) and/or the Bottom Acceleration Band (aqua), both of which are uptrend ing around the round 1300 level, wouldnt be surprising at this point.
The McClellan Oscillator calculated by subtracting the difference between 39 day exponential moving average and the 19 day exponential moving average of advancing minus declining stocks (smoothing of the Advance/Decline line ).
An oscillator that consists of two exponential moving average s (other inputs may be chosen by the trader as well) plotted against the zero line. The zero line represents the times the values of the two moving average s are identical.
The most popular formula for the MACD is the difference between a securities 26- day exponential moving average and its 12- day exponential moving average. A 9-day exponential moving average. called the signal (or trigger) line is then plotted on top of the MACD to show buy/sell opportunities.
Traditionally, this indicator is constructed by using a 12 and 26 exponential moving average and calculating the difference. The difference is plotted and called the MACD line. A 9 period simple moving average of this MACD line is plotted and called the signal line.














