EDHECRisk Amundi ETF ETF and Passive Investment Strategies Research Chair
Post on: 12 Июль, 2015 No Comment
Indices & Benchmarking — March 30, 2009
Amundi ETF ETF and Passive Investment Strategies Research Chair
The Amundi ETF ETF and Passive Investment Strategies research chair will involve three years of academic research into ETFs (exchange-traded funds) and the use of ETFs as part of a core-satellite approach to asset management. The work will be overseen by a joint Amundi ETF/EDHEC-Risk Institute advisory board.
The team of researchers at EDHEC-Risk Institute, under the leadership of centre director Noлl Amenc, will examine advanced forms of risk budgeting in a dynamic core-satellite approach and the use of these techniques by investors and asset managers.
[Press release announcing the creation of the research chair (30/03/09) ]
Research output:
Risk Allocation, Factor Investing and Smart Beta: Reconciling Innovations in Equity Portfolio Construction
July 2014
Noлl Amenc, Romain Deguest, Felix Goltz, Ashish Lodh, Eric Shirbini
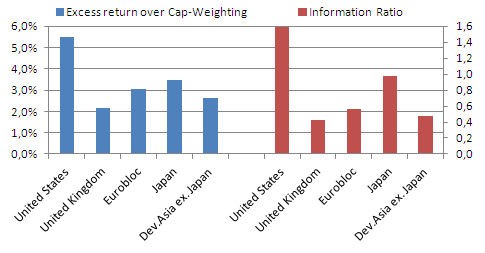
This publication argues that current smart beta investment approaches only provide a partial answer to the main shortcomings of capitalisation-weighted (cap-weighted) indices, and develops a new approach to equity investing referred to as smart factor investing. It provides an assessment of the benefits of simultaneously addressing the two main shortcomings of cap-weighted indices, namely their undesirable factor exposures and their heavy concentration, by constructing factor indices that explicitly seek exposures to rewarded risk factors while diversifying away unrewarded risks.
The results we obtain suggest that such smart factor indices lead to considerable improvements in risk-adjusted performance. For long-term US data, smart factor indices for a range of different factor tilts roughly double the Sharpe ratio of the broad cap-weighted index. Outperformance of such indices persists at levels ranging from 2.92% to 4.46%, even when assuming unrealistically high transaction costs. Moreover, by providing explicit tilts to consensual factors, such indices improve upon many current smart beta offerings where, more often than not, factor tilts result as unintended consequences of ad hoc methodologies. In fact, this publication shows that by using consensual results from asset pricing theory concerning both the existence of factor premia and the importance of diversification, it is possible to go beyond existing smart beta approaches which provide partial solutions by only addressing one of these issues. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 21/10/14]
The EDHEC European ETF Survey 2013
March 2014
Frйdйric Ducoulombier, Felix Goltz, Vйronique Le Sourd, Ashish Lodh
The latest edition of the European ETF Survey, which presents the results of a comprehensive survey of 207 European ETF investors, analyses the current practices and perceptions among ETF users in Europe and intends to shed light on trends within the European ETF market by comparing our results with those of our previous surveys.
This year, the survey results show that ETF investors are still looking to increase or at least to maintain their use of ETFs and have a more favourable outlook on their use of alternative indexing products. The data also shows that respondents are still overwhelmingly in favour of passive ETFs.
The survey further reveals considerable interest in “smart beta” products: around 30% of respondents already use products tracking smart beta indices and more than one third of respondents are considering investing in such products in the near future. Moreover, ETFs based on smart beta indices benefit from a favourable perception as tools for improving their investment process (to outperform cap-weighted indices, to reduce risk, to gain more transparency on methodology and for risk analytics diversification). In total, 39% of investors are interested in further development in ETFs based on smart beta indices. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 26/03/14]
The EDHEC European ETF Survey 2012
February 2013
Noлl Amenc, Felix Goltz, Nicolas Gonzalez, Nikhil Shah, Eric Shirbini, Nikolaos Tessaromatis
The EDHEC European ETF Survey 2012 presents the results of a comprehensive survey of 212 European ETF investors. The aim of the study is to analyse the usage of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in investment management and to provide a detailed account of the current perceptions and practices of European investors in ETFs. Overall, the survey has revealed some interesting trends with regard to investor behaviour, investor perceptions and the general outlook for the ETF industry.
Our results suggest that the ETF market is still growing and that it has potential for further growth. We observe increased levels of usage, satisfaction and demand for product development across a variety of asset classes, especially so for ETFs on emerging market equities, ETFs on fixed income indices, as well as ETFs on new forms of indices. We also find that recent launches of ETFs tracking strategy indices or smart beta indices seem to be blurring the traditional boundaries between active and passive investment. The key requirement for most investors is that an ETF tracks a systematically constructed index rather than implementing discretionary investment decisions. However, the increasing breath of systematic indices now includes strategies which move quite far away from traditional broad-cap-weighted market indices. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 28/03/13]
EDHEC-Risk Asian Index Survey 2011
May 2012
Noлl Amenc, Felix Goltz, Masayoshi Mukai, Padmanaban Narasimhan, Lin Tang
This is the first comprehensive survey of Asian investment professionals that identifies the criteria investors use to assess and select stock and bond indices, measures satisfaction of Asian investors with existing indices, and documents their segmentation practices. It includes comparisons with results from sister surveys of European and North-American investors.
The 127 Asian investment professionals, representing asset managers, institutional investors, investment consultants, and private wealth managers, who responded to the survey are principally from the three asset management hubs in the Asia Pacific region (Australia, Singapore and Hong Kong), but a wide range of other countries are represented, including India, China, Japan and New Zealand.
This new survey-based evidence will be useful to Asian investors who wish to benchmark their indexation practices to research advances as well as to the practices of their peers in the region and globally. It will also provide much-needed information to providers of investment solutions who want to better address the needs of Asian investors. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 10/05/12]
The EDHEC European ETF Survey 2011
March 2012
Felix Goltz, Lin Tang
The EDHEC European ETF Survey 2011 presents the results of a comprehensive survey of 174 institutional investment managers and private wealth managers. In addition to analysing ETF investment, the survey sheds light on the role of ETFs in asset allocation and compares ETFs and other investment products traditionally used as indexing vehicles – namely futures, index funds and total return swaps.
The results of the survey show that the use of ETFs has considerably stabilised. While investors are using ETFs more heavily for dynamic strategies and specific sub-segment exposure than in the past, the main use of ETFs remains long-term buy and hold investing into broad market indices. Investors are also moving towards applying ETFs more for portfolio optimisation as well as for risk management, and they continue to have a demand for ETFs mainly as index replicating products, rather than as active funds. This finding underlines that ETFs are mainly used as beta tools or asset allocation tools, thus allowing investors to focus on the question of beta management which has been pointed out as being of first-order importance in investment management, rather than focusing on security selection issues which are only of third order importance (Amenc et al. 2010c). [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 28/03/12]
Capturing the Market, Value, or Momentum Premium with Downside Risk Control: Dynamic Allocation Strategies with Exchange-Traded Funds
July 2011
Elie Charbit, Jean-Renй Giraud, Felix Goltz, Lin Tang
There is extensive evidence that investment strategies based on momentum and value are attractive for portfolio managers who seek higher performances. Momentum and value are among the most robust return drivers in the cross section of expected returns. Dynamic risk budgeting methodologies such as Dynamic Core Satellite strategies (DCS) are used to provide risk-controlled exposure to different asset classes. We examine how to exploit the value and momentum anomalies using a DCS investment model. This paper shows that the DCS approach can boost portfolio returns while keeping downside risk under control. The implementation of the portfolio strategies is enabled by exchange-traded funds which are natural investment vehicles since they offer a broad exposure to the markets and provide the necessary liquidity to the frequent rebalancing of the DCS model. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 04/10/11]
EDHEC-Risk European ETF Survey 2010
May 2010
Felix Goltz, Adina Grigoriu, Lin Tang
This survey has been taken as part of the second year of the Amundi ETF Core-Satellite and ETF Investment research chair. The findings of the survey were first presented at EDHEC-Risk’s Confйrence de la Gestion Institutionnelle Franзaise (French institutional asset management conference) held in Paris on 9 June, 2010.
The EDHEC European ETF Survey 2010 presents the results of a comprehensive survey of 192 institutional investors, asset managers and private wealth managers conducted between January and March 2010. It analyses the possible uses of ETFs (exchange-traded funds) in investment management and gives a detailed account of current perceptions and practices of European investors in ETFs.
On the whole, the results of the survey suggest that, as a consequence of strong growth, the industry has entered a phase of increased maturity. As ETFs are now very widely used, investors are embracing more advanced ways of trading and using ETFs, such as OTC trading and securities lending, and the positive impact of ETFs on the market as a whole, including their underlying assets and other related instruments, is being felt by an increasing number of market participants.
Despite this maturity, there is still room for growth. In particular, survey respondents see a need for new products on emerging markets and alternative asset classes. Likewise, ETFs are still used mostly in static strategies and on broad market indices; their potential contribution to dynamic asset allocation and to allocation strategies in precisely defined market segments or styles is not yet fully exploited. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 16/06/10]
Risk control through dynamic core-satellite portfolios of ETFs
January 2010
Noлl Amenc, Felix Goltz, Adina Grigoriu
The paper examines the ways dynamic asset allocation techniques can be used to manage portfolios of exchange-traded funds (ETFs). First, dynamic allocation to stock and bond ETFs and traditional static diversification are compared. Second, tactical allocation to stock and bond ETFs and risk-controlled allocation—with both forms of allocation informed by the same return forecasts—are compared. The paper shows that dynamic asset allocation techniques that can be used with frequently traded and broadly diversified instruments such as ETFs make it possible better to address investor concerns over drawdown and intra-horizon risk, whether or not the manager wishes to make return predictions.
EDHEC-Risk European ETF Survey 2009
May 2009
Noлl Amenc, Felix Goltz, Adina Grigoriu, David Schrцder
The first project undertaken as part of the chair was the EDHEC-Risk ETF Survey 2009, an in-depth pan-European survey of the use of ETFs by European investors. The findings of this survey were presented at the third ETF and Indexation Summit at EDHEC-Risk Institutional Days in Paris on 26 and 27 May 2009.
Earlier editions of the EDHEC-Risk European ETF Survey showed how institutional investors could manage a portfolio of ETFs actively. The support from Amundi ETF will enable EDHEC-Risk Institute to take this work into the field of dynamic portfolio management, and to do so to the advantage of investors.
The EDHEC-Risk European ETF Survey 2009 presents the results of a comprehensive survey of 360 institutional investors and private wealth managers conducted in January and February 2009.
It is divided into two parts. The first part is an overview of the ETF market and of the mechanisms behind ETFs. It then goes on to show how advanced techniques involving dynamic allocation strategies can be carried out with ETFs. In particular, this part shows how ETFs can be used to implement the core-satellite approach to investment.
The second part presents the results of our in-depth pan-European survey of the current use of ETFs. In general, the results suggest that European investors make wide use of ETFs and consider them superior to other indexing vehicles. However, we also find that investors seem to be somewhat wary of ETFs in such illiquid asset classes as hedge funds, real estate and corporate bonds. And it seems that ETFs are predominantly used for broad market exposure over long time horizons, a use that is at odds with the plentiful opportunities they provide for strategies that are dynamic and/or apply to specific market segments. [Press release announcing the publication of the research: 27/05/09]
Related research:
Core-satellite investing
In March 2004, within the context of a study dedicated to the use of EuroMTS trackers in institutional investment, EDHEC-Risk Institute began to advocate the core-satellite approach to investment management, by predicting that it would revolutionise asset management, not only in France but also in Europe.
Related events:
ETFs in Institutional Investment—EDHEC-Risk European ETF Survey:
22 June, 2012 — Trieste, Italy
A presentation of the EDHEC European ETF Survey 2011 by Felix Goltz, Head of Applied Research at EDHEC-Risk Institute.
Amundi ETF/EDHEC-Risk Institute European Seminar Series 2010:
Recent research drawn from the Amundi ETF Core-Satellite and ETF Investment research chair will be jointly presented by Amundi ETF and EDHEC-Risk Institute at a series of seminars organised throughout Europe between April and June, 2010:
- 28 April — Frankfurt
Sofitel Munich Bayerpost, Bayerstrasse 12, 80335 Munich
08:30 Breakfast
Renaissance Hamburg Hotel, GroЯe Bleichen, 20354 Hamburg
16:00 — Group meeting
16:00 — Group meeting
Mandarin Oriental, Quai Turrettini 1, 1201 Geneva
16:00 — Group meeting
Park Plaza Victoria Amsterdam, Damrak 1-5, 1012 Amsterdam
09:00 — Breakfast
Le Royal Luxembourg, 12 boulevard Royal, 2449 Luxembourg
16:00 — Group meeting
Hotel Amigo, Brussels, Rue de L’Amigo 1-3, 1000 Brussels
Asset managers generally focus on diversification or returns prediction to create added value in portfolios of exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Recent EDHEC-Risk Institute research draws on dynamic risk-budgeting techniques to emphasise the importance of risk management when decisions to allocate to ETFs are made. Absolute return funds, in which the low-risk profiles of government bond ETFs and conditional allocations to riskier equity ETFs can be combined to obtain portfolios that—beyond the natural diversification between stocks and bonds—provide upside potential while protecting investors from downside risk, are an initial application of ETFs to allocation decisions.
A second application is risk control of tactical strategies. Dynamic risk budgeting is used to provide risk-controlled exposure—taking the manager’s forecasts as a given—to an asset class. EDHEC’s research shows that, even if the manager is an excellent forecaster, this approach yields intra-horizon and end-of-horizon risk-control benefits considerably greater than those of standard tactical asset allocation.
The results of this research will be presented at the seminars by Felix Goltz, Head of Applied Research, and Jean-Renй Giraud, Research Associate, EDHEC-Risk Institute.
The seminar programme may be downloaded here.
Please contact Stйphanie Parenty at sparenty@cheuvreux.com for further information.
About Amundi ETF:
With 100 ETFs* and Ђ9.6bn in assets under management at 28 February 2013, Amundi ETF covers the main asset classes and geographical exposures (Europe, US, emerging markets, and world). As one of the pioneers in the ETF market with its first products launched in 2001, Amundi ETF is characterised by its quality products, continuous innovation and its low cost policy and relies on a wide network of “Authorised Participants” (more than 50* market makers).
Amundi ETF is present in 7* European countries: France, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland and United Kingdom.
Amundi ETF designates the ETF business of Amundi Investment Solutions. Amundi ETF received a Special Commendation in the “European ETF Provider of the Year” category by Funds Europe in 2011. Amundi Group was awarded “Best Europe Equity ETF Manager 2010”, “Best Fixed Income – Cash (Money Market) ETF Manager 2011” and “Best Fixed Income – Cash (Money Market) ETF Manager 2013” as voted by the readers of ETF Express .
* As of 28/02/2013. The Funds described in this document may not be authorised for distribution in all countries. It is the investor’s responsibility to ensure that they are authorised to invest in a Fund.














