Forex Market Structure
Post on: 15 Май, 2015 No Comment
Forex Market Structure
I n this lesson, we will learn how forex market is structured and who are players as well as their roles. Its good to know where you are playing and who you are playing with, right?
Forex Market Structure
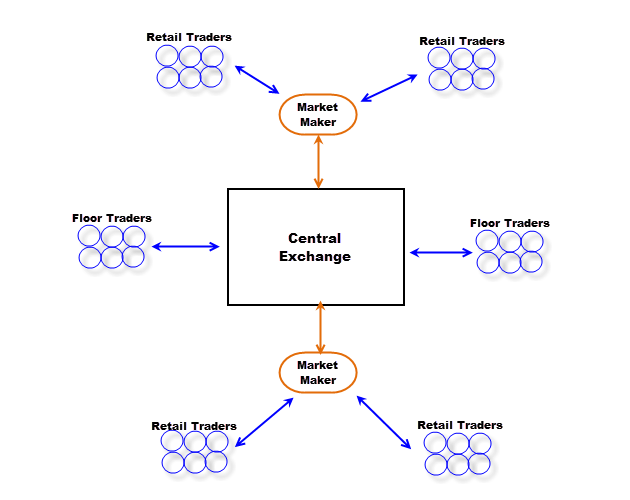
Unlike the stock market, which usually has a monopolistic exchange central. for ex market does not have a physical central. Instead, it have multi exchange centrals around the world in New York, Tokyo, Hongkong, Sydney, Frankfurt and many more. Structure of forex market is described base on the classification of its participants. Following is the market hierarchy:
On the top of the market, major banks and a number of commercial banks (about over 1000 members) make interbank market, where the currencies exchange rates are made (or set) by its members. They exchange currencies with each other base on their needs of supply and demand. To do this, members trade currencies directly or communicate through one of two electronic networks called Thomson Reuters Dealing 3000-Spot Matching and Electronic Brokering Services (EBS), which allow any member to see how much currencies are available in the network and the price that other members asks or offers. Price in interbank market is the best price (primary price) that generally only its members have the privilege to benefit from.
Next are participants who receive liquidity from banks or can reach the interbank market for their purpose. This group of participants frequently deal enormous amount of money with liquidity provider in the interbank market. They includes forex brokers (includes market maker and STP/ECN), large companies, hedge funds, asset managers, institutional traders and high net-worth speculators.
At the bottom of the market, individual traders (like you and me) deal with forex brokers, who are liquidity providers in the retail market. In the past, it was very difficult for an individual to trade forex because he/she have to call telephone in order to make a trade as well as it required he/she a wealthy capital to join the market. But nowaday, thanks to the internet and competitive low requirement from brokers, anyone can join the market with a capital as low as $100 or even less.
Beside of those participants, Govements and Central Banks (whose actions usually reflect governments policy) make effects on the forex market by giving their currency policy and interest rate.
Who Are Players?
The overall forex market players relations can be described by this illustration:
The Major Banks and Other Commercial Banks
At the very top of the market, the major banks and commercial banks exchange money with each other, thus they determine and provide the exchange rate to the market. Large international banks in this group such as Deutsche Bank, Barclays Bank, Union Bank of Switzerland, Citibank, Chase Manhattan Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, etc. affect the exchange markets in the world considerably by the daily operations at the amount of billions dollars. Such dramatic volumes can have an influence on the currency price or the quotation.
The interbank market deals with the commercial turnover majority as well as speculative trading considerable amounts carried out daily. Billions of dollars is possible turnover for a large bank. Besides the customers transactions, the majority of the operations are made for the banks own account and by proprietary desks.
Only banks that have credit relationships with each other can engage in transactions. The larger banks tend to have more credit relationships, which allow those banks to receive better foreign exchange prices. The smaller the bank, the fewer credit relationships it has and the lower the priority it has on the pricing scale.
The Government and Central Banks
They are responsible for regulating inflation and interest rates. They also play an important role in the forex market since they try to control the supply of their currency in order to reach their economic target. Central banks are able to create the stability as well as fluctuation for their currency in the forex market by altering interest rates, an indirect way to set currency exchange rate. By increasing/reducing interest rates, they stimulate traders to buy/sell their currency as it provides a high/low return on investment and this drives the value of the corresponding central banks currency higher/lower with comparison to other currencies.














