Floating and Fixed Foreign Exchange Rates Currency Analysis
Post on: 14 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
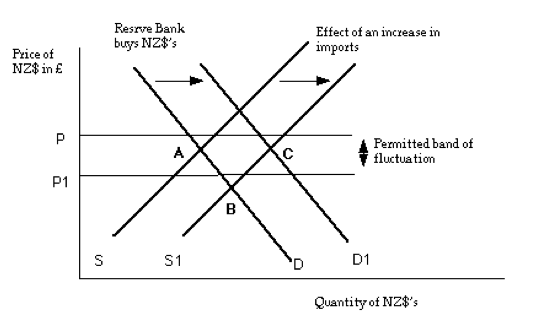
Floating and Fixed Foreign Exchange Rates
When you look at forex trading it is important that you understand what the foreign exchange rates are. You need to understand how they are calculated and how affects them. There are two methods that countries use for their foreign exchange rates and they are fixed and floating. It is important that you know what the differences are.
What Are Foreign Exchange Rates?
Simply put, foreign exchange rates are the value at which one currency is able to be exchange for another currency. It is the value of another country’s currency when compared to your home currency.
The Floating Rates
The floating rate is the one that most countries will use and you need the understand it. This rate is set by supply and demand on the private market. It is often termed as being self-correcting because any variance in the supply and demand will be corrected automatically. For example, if the demand for a certain currency is low, the value of that currency decreases. This makes imported goods expensive and it causes a demand for goods and services that are available locally. This causes the employment rate to increase as it is a job creation mechanism, which will cause the market to auto-correct itself. This exchange rate changes constantly.
No country’s currency is either floating or fixed. Market pressures may influence changes in the foreign currency exchange rate in a fixed system. There are times when a currency will reflect the true value as compared to its pegged value and this may cause the development of a ‘black market’ which better reflects actual demand and supply. When this happens, the national bank will have no choice but to devalue or revalue the rate that was set in order to bring it in line with the unofficial rate. This will stop the ‘black market’ activity. The national bank may also choose to intervene in a floating rate environment if it deems it necessary to do so to avoid inflation and to ensure stability. However, this rarely happens that the national bank interferes in a floating foreign currency exchange environment.
The Fixed Rates
The second way that foreign exchange rates are regulated is through the fixed rate which is also known as the pegged rate. This is the rate that is set by a country’s national bank and it is used as the official foreign currency exchange rate. This fixed price will normally be determined by the use of one of the major currencies in the world. This is normally the US dollar, but it can also be the Euro or any other major currency. To maintain this fixed rate, the national bank will sell and buy its own currency on the forex market and use the pegged currency as an exchange.
An example of this strategy is if the government decides that the value of its local currency is equivalent to $3, the national bank must ensure that it retains sufficient foreign reserves. This is an amount of foreign currency that is reserved by the national bank which will allow it to absorb or release additional funds out of or into the trading market. This will ensure a suitable money supply and suitable fluctuations in the market to maintain the exchange rate at the level required. The national bank may adjust of exchange rate if it deems it necessary.














