Trade Protectionism Definition Pros Cons
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
Many Americans protested the NAFTA free trade agreement because it cost American jobs. Photo: Getty Images
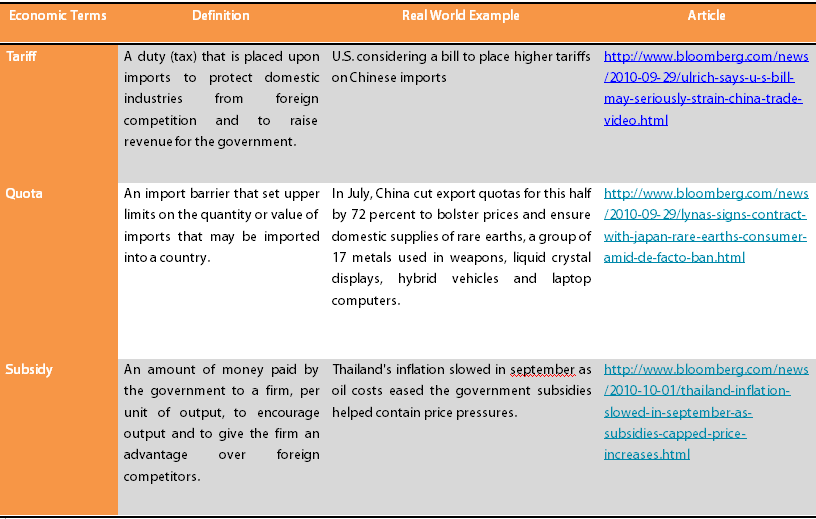
Definition: Trade protectionism is used by countries when they think their industries are being damaged by unfair competition from foreign industries. It’ s a defensive measure, and i s usually politically motivated. It can often work, in the short run. However, in the long run it usually does the opposite of its intentions. It can make the country, and the industries it is trying to protect, less competitive on the global marketplace.
What Exactly Is Trade Protectionism?
Countries use a variety of ways to protect their trade. One way is to enact tariffs. which tax imports. This immediately raises the price of the imported goods, making them less competitive when compared to locally produced goods. This works especially well for a country like the United States, which imports a lot of consumer products and oil.
The most famous example is the Smoot-Hawley Tariff of 1930. It was originally designed to protect farmers from agricultural imports from Europe, which was stepping up farming after the destruction of World War I. However, by the time the bill made it through Congress. it had slapped tariffs on many more imports. As so often happens with tariffs, other countries retaliated. This tariff war restricted global trade, and was one reason for the extended severity of the Great Depression.
A second way of protecting trade is when the government subsidizes local industries with tax credits or even direct payments. This again lowers the price of locally produced goods and services. It works even better than tariffs because now the goods are cheaper even when shipped overseas. This works well for the United States, but even better for countries that rely mainly on exports .
A good example of this is, once again, in the U.S. agricultural industry. The Agricultural Adjustment Act of 1933 allowed the government to pay farmers to not grow crops or livestock, thus restricting supply and raising prices. This subsidy helped farmers who had been devastated by the Dust Bowl .
A third method is by imposing quotas on imported goods. This can one of the most effective methods for protecting trade, since the foreign country cannot ship more goods no matter how low it sets the price through subsidies.
There is a fourth type of trade protectionism that is not usually mentioned in text books, because it is subtle. That is a deliberated attempt by a country to lower its currency value, thereby making its exports cheaper and more competitive. However, this can ultimately result in retaliation, and start up a currency war. Countries can lower their currency’s value through either a fixed-exchange rate, like China’s yuan. or by creating so much national debt that it has the same effect, like the U.S. dollar decline .
Advantages of Trade Protectionism
If a country is trying to grow strong in a new industry, tariffs will protect it from foreign competitors. This allows companies in the new industry time to learn how to produce the good efficiently, and develop their own competitive advantages .
Protectionism also temporarily creates jobs for domestic workers. As domestic companies are protected by tariffs, quotas or subsidies, they will hire locally. This will occur until other countries retaliate by erecting their own protectionism within that industry.
Disadvantages of Trade Protectionism
In the long term, trade protectionism weakens the industry. Without competition, companies within the industry won’t innovate and improve their products or services. There’s no need to. Eventually, consumers will pay more for a lower quality product than they would get from foreign competitors.
Job outsourcing is a result of declining U.S. competitiveness. itself a result of decades of the U.S. not investing in education. This is particularly true for high tech, engineering, and science. Increased trade opens new markets for businesses to sell their products. The Peterson Institute for International Economics estimates that ending all trade barriers would increase U.S. income by $500 billion.
Increasing U.S. protectionism will further slow economic growth and cause more layoffs, not less. If the United States closes its borders, other countries will do the same. This could cause layoffs among the 12 million U.S. workers who owe their jobs to exports.
Free Trade Agreements
Free trade agreements (FTAs) reduce or eliminate tariffs and quotas between trading partners. The largest agreement is NAFTA. or the North American Free Trade Agreement. which is between the United States, Canada and Mexico. If approved, two other agreements would be larger: the Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership .
Other free trade agreements are CAFTA. which is between the United States and Central America. There are bilateral agreements with Chile, Colombia, Panama, Peru and Uruguay, most countries in Southeast Asia, and the Middle Eastern countries of Israel, Jordan, Morocco, Bahrain, and Oman.
However, FTAs don’t eliminate protectionist measures such as subsidies or currency wars. One of the disadvantages of NAFTA was that Mexican farmers were put out of business by subsidized U.S. farm products. For more, see Free Trade Agreements Pros and Cons. Article updated January 8, 2015.














