SparkNotes Aggregate Demand The Aggregate Demand Curve
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
Problems
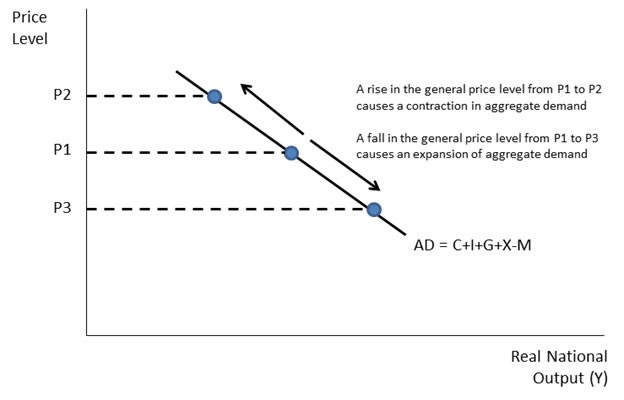
Figure %: Graph of the aggregate demand curve.
The most noticeable feature of the aggregate demand curve is that it is downward sloping, as seen in. There are a number of reasons for this relationship. Recall that a downward sloping aggregate demand curve means that as the price level drops, the quantity of output demanded increases. Similarly, as the price level drops, the national income increases. There are three basic reasons for the downward sloping aggregate demand curve. These are Pigou’s wealth effect, Keynes’s interest-rate effect, and Mundell-Fleming’s exchange-rate effect. These three reasons for the downward sloping aggregate demand curve are distinct, yet they work together.
The first reason for the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve is Pigou’s wealth effect. Recall that the nominal value of money is fixed, but the real value is dependent upon the price level. This is because for a given amount of money, a lower price level provides more purchasing power per unit of currency. When the price level falls, consumers are wealthier, a condition which induces more consumer spending. Thus, a drop in the price level induces consumers to spend more, thereby increasing the aggregate demand.
The second reason for the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve is Keynes’s interest-rate effect. Recall that the quantity of money demanded is dependent upon the price level. That is, a high price level means that it takes a relatively large amount of currency to make purchases. Thus, consumers demand large quantities of currency when the price level is high. When the price level is low, consumers demand a relatively small amount of currency because it takes a relatively small amount of currency to make purchases. Thus, consumers keep larger amounts of currency in the bank. As the amount of currency in banks increases, the supply of loans increases. As the supply of loans increases, the cost of loans—that is, the interest rate—decreases. Thus, a low price level induces consumers to save, which in turn drives down the interest rate. A low interest rate increases the demand for investment as the cost of investment falls with the interest rate. Thus, a drop in the price level decreases the interest rate, which increases the demand for investment and thereby increases aggregate demand.
The third reason for the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve is Mundell-Fleming’s exchange-rate effect. Recall that as the price level falls the interest rate also tends to fall. When the domestic interest rate is low relative to interest rates available in foreign countries, domestic investors tend to invest in foreign countries where return on investments is higher. As domestic currency flows to foreign countries, the real exchange rate decreases because the international supply of dollars increases. A decrease in the real exchange rate has the effect of increasing net exports because domestic goods and services are relatively cheaper. Finally, an increase in net exports increases aggregate demand, as net exports is a component of aggregate demand. Thus, as the price level drops, interest rates fall, domestic investment in foreign countries increases, the real exchange rate depreciates, net exports increases, and aggregate demand increases.
IS-LM model of aggregate demand
There is another major model that is useful for explaining the nature of the aggregate demand curve. This model is called the IS-LM model after the two curves that are involved in the model. The IS curve describes equilibrium in the market for goods and services where Y = C(Y — T) + I(r) + G and the LM curve describes equilibrium in the money market where M/P = L(r,Y). The IS-LM model exists in a plane with r, the interest rate, on the vertical axis and Y, being both income and output, on the horizontal axis. The IS-LM model has the same horizontal axis as the aggregate demand curve, but a different vertical axis.
Figure %: Graph of the IS-LM curves.
The IS curve describes equilibrium in the market for goods and services in terms of r and Y. The IS curve is downward sloping because as the interest rate falls, investment increases, thus increasing output. The LM curve describes equilibrium in the market for money. The LM curve is upward sloping because higher income results in higher demand for money, thus resulting in higher interest rates. The intersection of the IS curve with the LM curve shows the equilibrium interest rate and price level.
The IS curve and the LM curve shift in response to economic activities. The IS curve shifts outward as a result of increased government purchases, exogenous increases in investment, decreases in taxes, and exogenous increases in consumption. The IS curve shifts inward as a result of decreases in government purchases, exogenous decreases in investment, increases in taxes, and exogenous decreases in consumption. The LM curve shifts outward as a result of increases in the money supply and decreases in the price level. The LM curve shifts inward as a result of decreases in the money supply and increases in the price level.
The aggregate demand curve can be derived using the IS-LM model. Recall that the aggregate demand curve relates price level to income and output. The simplest way to derive the downward sloping aggregate demand curve from the IS-LM model is to look at the effects of an increase in the price level on output or income.
When the price level increases, the LM curve shifts inward. An inward shift in the LM curve results in an intersection of the IS-LM model at a lower level of output and income and a higher interest rate. When a line connecting the old price level and the old output and income to the new price level and the new output and income in the price level and output and income space, the downward sloping aggregate demand curve appears. In general, from the IS-LM model, it is clear that aggregate demand slopes downward because as the price level increases, output and income decrease.
The IS-LM curve is a useful way to incorporate the money market into the logic driving the aggregate demand curve. By understanding the basics of the IS-LM model and the three reasons that the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping as presented under the previous heading, the nature of the aggregate demand curve is clear. The next step to work through is how shifts of and shifts along the aggregate demand curve function. In this capacity, the IS-LM model will become very useful.














