Putcall parity
Post on: 11 Июль, 2015 No Comment
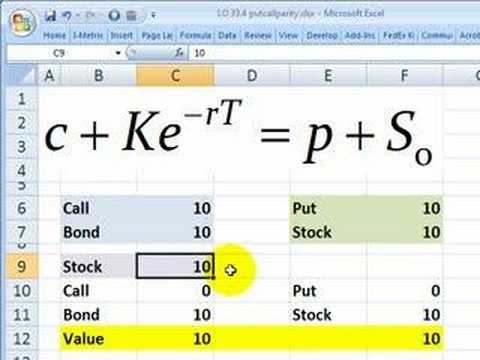
Basically, put-call parity provides a way to check if your pricing is correct or not if they are exercised at expiration.
Something else such as helping us to find the delta of an European put option given 28t%2CS_t%29&bg=ffffff&fg=333333&s=0 /%, that is 5Cfrac%7B%5Cpartial+P%28t%2CS_t%29%7D%7B%5Cpartial+S_t%7D%3D%5Cfrac%7B%5Cpartial+C%28t%2CS_t%29%7D%7B%5Cpartial+S_t%7D%2B1&bg=ffffff&fg=333333&s=0 /%.
Might fail!
1) American option
2) dividends
3) not ideal market
3)bid-ask spread
5)state price
Put-call parity is an important principle in options pricing first identified by Hans Stoll in his paper,The Relation Between Put and Call Prices. in 1969. It states that the premium of a call option implies a certain fair price for the corresponding put option having the same strike price and expiration date, and vice versa. Support for this pricing relationship is based upon the argument that arbitrage opportunities would materialize if there is a divergence between the value of calls and puts. Arbitrageurs would come in to make profitable, riskless trades until the put-call parity is restored.
To begin understanding how the put-call parity is established, lets first take a look at two portfolios, A and B. Portfolio A consists of a european call option and cash equal to the number of shares covered by the call option multiplied by the calls striking price. Portfolio B consist of a european put option and the underlying asset. Note that equity options are used in this example.
Portfolio A = Call + Cash, where Cash = Call Strike Price
Portfolio B = Put + Underlying Asset
It can be observed from the diagrams above that the expiration values of the two portfolios are the same.
Call + Cash = Put + Underlying Asset
Eg. JUL 25 Call + $2500 = JUL 25 Put + 100 XYZ Stock
If the two portfolios have the same expiration value, then they must have the same present value. Otherwise, an arbitrage trader can go long on the undervalued portfolio and short the overvalued portfolio to make a riskfree profit on expiration day. Hence, taking into account the need to calculate the present value of the cash component using a suitable risk-free interest rate, we have the following price equality:
Put-Call Parity and American Options
Since American style options allow early exercise, put-call parity will not hold for American options unless they are held to expiration. Early exercise will result in a departure in the present values of the two portfolios.














