Mortgage Securitization
Post on: 16 Июнь, 2015 No Comment
Mortgage securitization is the pooling of various mortgage loans and their usage as collateral to issue securities. This process allows the originator of the mortgage loans to restructure its balance sheet by reducing the receivables and using the funds received from the sale of securities to invest elsewhere. Mortgage securitization allows the originators of the loans to diversify their risk besides enabling them to secure immediate liquidity for assets which would otherwise have faced some difficulty in trading.
Process of Mortgage Securitization
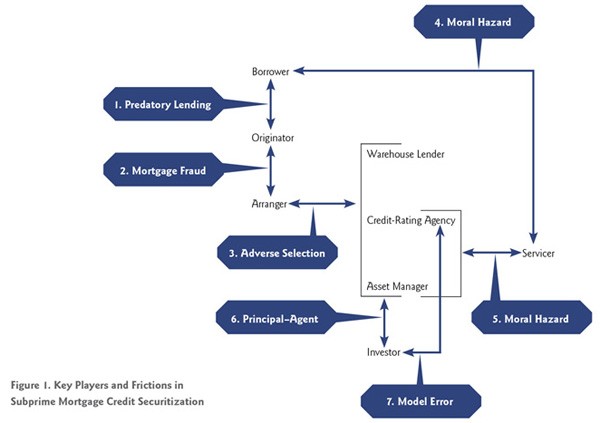
The process of mortgage securitization is similar to that of normal securitization and involves the pooling of various mortgage loans. These mortgage loans are then transferred to a trust or a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) that issues securities backed by this pool of mortgage loans after getting them rated from a credit rating agency. The cash generated by the pooled assets is used to pay the interest and principal on the mortgage backed securities. Cash is generated by the monthly mortgage payments and the prepayment or repayment of the mortgages.
In most cases, the SPV or the trust transfers the right to service the collection of income from the pooled assets to a third party or the originating party itself. The rights to service the mortgage loans are called Mortgage Servicing Rights or MSR. The entity holding the rights to service the mortgage loans in many cases again transfers them to another party and, thus, the actual borrower makes his interest payments to a party that is very often not the originator of the loan. Since the rights to service mortgage assets are also considered as assets with recognized value, they are also sold, assigned and securitized like mortgage loans. Mortgage securitization and its complex transactions have been held responsible for the 2007-2009 housing and financial crisis in the US.
Mortgage Securitization by Public and Private Players
Mortgage securitization is taken up by both public and private players. Public placements are originated by Government Sponsored Entities such as Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and Ginnie Mae and normally involve a single form of an investment bond called Pass-Through Certificates.
Private-label placements represent mortgages that have been aggregated on the secondary market by private investors and are done in tranches to represent the varying levels of risks associated with them.














