How to calculate beta
Post on: 20 Апрель, 2015 No Comment
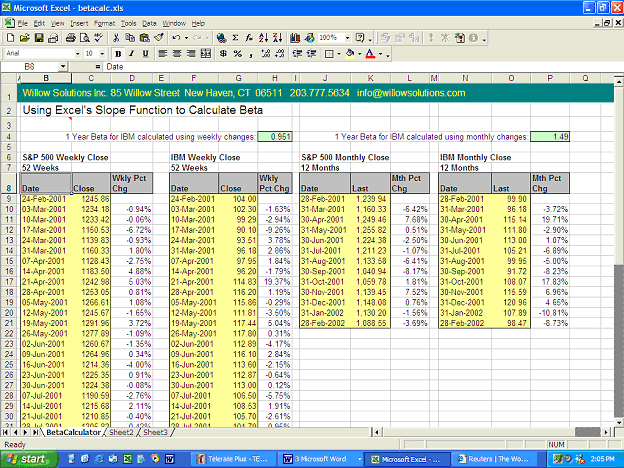
1. Find a company stock that has at least 5 years of quarterly return data (60 data points). Determine what the company Beta is by running a regression, and compare your calculation with what the financial source is reporting for the Beta.
2. Is your calculation of Beta the same as what the financial source reports? If not, why could there be a difference?
Theme 2
1. For the company that you chose in Theme 1, see if you can find data that could be used to calculate a WACC for the company. Typically, this information can be found on the company’s website (financial statements. etc.) and stock rating services. After you have calculated the WACC. share your work with your colleagues on the discussion forum. Describe how you collected the information (where you went to collect it), and how you actually calculated the WACC; show your work.
Theme 3
1. Describe some ideas for how you could go about calculating a discount rate if you weren’t able to calculate a Beta.
2. Discuss the pros and cons to different methods and what would be appropriate for certain types of situations.
3. How would you work with a scenario that requires the valuation of a project in a Third-World country (assuming that the headquarters of the company is in the United States)? What things would you consider in the valuation process?
4. Choose two countries from the African and Asian continents. Discuss how you would value companies (or individual projects) across both. Would you value a project the same or differently? Describe the logic of your approach.
Solution This solution is FREE courtesy of BrainMass!
Please see attached file.
Theme 1
The company chosen is Hershey and the data is monthly returns as per the message I gave you. The calculations are in attached excel file.
Reuters .15
Google Finance .15
MSN Money .15
AOL Money & Finance .378
Is your calculation of Beta the same as what the financial source reports? If not, why could there be a difference?
There is slight difference. This can be due to difference in the time period taken by us and the published data. Overall the Beta of Hershey is low.
Theme 2
1. For the company that you chose in Theme 1, see if you can find data that could be used to calculate a WACC for the company. Typically, this information can be found on the company’s website (financial statements. etc.) and stock rating services. After you have calculated the WACC. share your work with your colleagues on the discussion forum. Describe how you collected the information (where you went to collect it), and how you actually calculated the WACC; show your work.
The cost of capital can also be viewed as the minimum rate of return required keeping investors satisfied. Thus it is used to know the rate of return expected by the investors.
Cost of capital (WACC) =
(Cost of Equity x Proportion of equity from capital)+ (Cost of debt x Proportion of debt from capital)+ (Cost of Preference share x Proportion of preference share from capital).
Equity includes retained earnings and the cost of R/E is taken at cost of equity. Cost of equity capital is the opportunity return from an investment with same risk as the company has. Cost of equity is usually defined with Capital asset pricing model (CAPM ). The estimation of cost of debt is naturally more straightforward, since its cost is explicit. Cost of debt includes also the tax shield due to tax allowance on interest expenses. In case of preference shares, the dividend rate can be taken as the cost since it is the amount, which the company intends paying against preference shares. As is the case of debt the issue expenses or discount/premium on issue has also to be taken into account.
Thus cost of capital is used to evaluate the project. It is also know as discount rate.
A firm’s WACC is the overall required return on the firm as a whole and, as such, it is often used internally by company directors to determine the economic feasibility of expansionary opportunities and mergers. It is the appropriate discount rate to use for cash flows with risk that is similar to that of the overall firm.
The company chosen is Hershey the calculations are in attached excel file.
WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL
1 2 1*2
Amount in mn Proportion Cost
Debts $ 901,176,000.00 0.47 4.24% 1.99%
Common Stock $1,021,076,000 0.53 4.94% 2.63%
1922252000 WACC= 4.61%
Theme 3
1. Describe some ideas for how you could go about calculating a discount rate if you weren’t able to calculate a Beta.
In those cases we will calculate it through dividend Gordon model or Bond risk premium method. It is given in attached excel file.
WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL (Using Dividend gordons model)
1 2 1*2
Amount in mn Proportion Cost
Debts $ 901,176,000.00 0.47 4.24% 1.99%
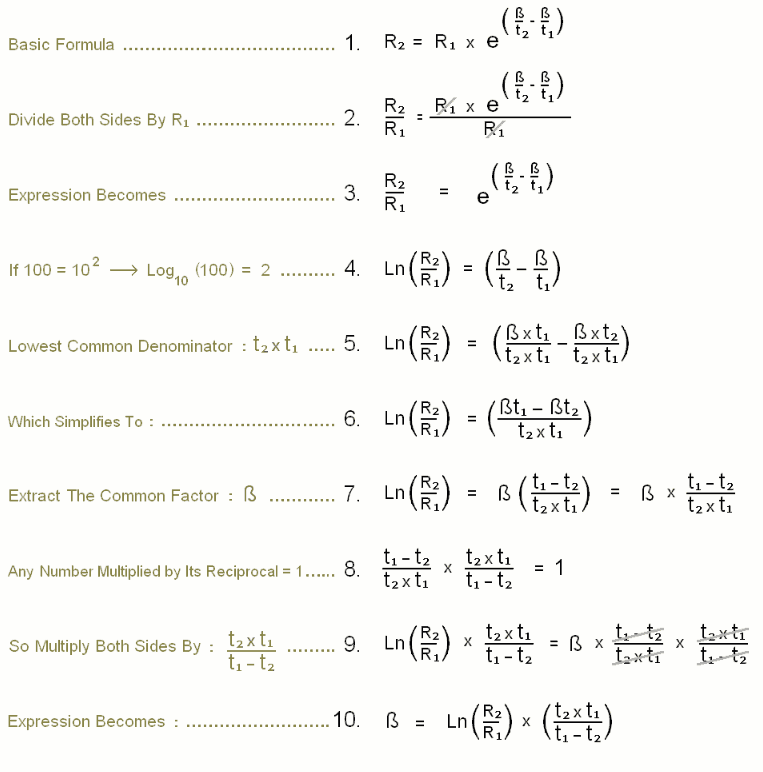
Common Stock $1,021,076,000 0.53 11.42% 6.07%
1922252000 WACC= 8.05%
2. Discuss the pros and cons to different methods and what would be appropriate for certain types of situations.
CAPM method is the most popular method to calculate the cost of equity. It should be used when the data for Beta is reliable. In some case company is new one or it does not pay any dividend, then also this method can be used. Dividend Gordon’s model is used when the beta of a company is not reliable.
The bond yield plus risk premium method of estimating the cost of internal equity:
It begins with an estimate of the firm’s before-tax bond yield. A risk premium is added to the bond yield to estimate the cost of internal equity. The difficulty is in estimating the appropriate risk premium. This risk premium may vary over time and across different firms. This method cannot be used when the organization has very low debt or zero debt.
3. How would you work with a scenario that requires the valuation of a project in a Third-World country (assuming that the headquarters of the company is in the United States)? What things would you consider in the valuation process?
In this the valuation process has to incorporate the country risk.
Risk is an aspect of any organization’s operation. When it is recognized, understood, and managed, risk can set the stage for sustainable growth. Companies need identify risk within their operations and plan a systematic approach to managing it.
According to www.anao.gov.au:
Effective risk management contributes to better decision-making because it develops a deeper insight into risks and their potential impact. It is a structured and disciplined approach: it aligns strategy. processes, people, technology, and knowledge with the purpose of evaluating and managing the uncertainties the enterprise faces as it creates value.
For our current purposes, we can classify the risk of a firm into two types
Business risk and financial risk.
Business risk is the riskiness of the firm without debt, which is due to the uncertainty associated with the firm’s cash flows. This type of risk depends on a number of factors including demand variability, sales price variability, input cost variability, pricing power, R&D efficiency, foreign risk exposure, and the degree of operating leverage
Financial risk is the risk that results from the use of debt. Since debt issues come with the obligation to make fixed payments, regardless of the business fortunes of the enterprise, they introduce a higher degree of uncertainty to NOPAT. Thus a higher degree of financial leverage, while increasing expected return on equity also increases the riskiness of those returns.
Thus it is possible to make a reasonable estimate of the required return. One has to take care of country risk. Organization uses several of methods and tools to assess risks, tools from database integrated software to basic spreadsheet templates. What ever the method used, each driving forces has several categories (Business Investment, Business Development, and Business Operations) which opportunities and risks can be assessed. A country risk is one in which a country will not be able to honor its financial commitments and a political risk is one in which the investor priveleges are affected by the regime in force. The regime may impose restrictions on repatriation of profits. One should first study their culture, come out with a list of do’s and dont’s and prepare its staff to face the eventualities incident in that country.
Adjustments to WACC
WACC means weighted average cost of capital. Here The basic principles applicable to an international investment decision are similar to a domestic investment decision. The incremental cash flow of the investment should be discounted at an opportunity cost of capital appropriate to the risk of the investment. The investment should be accepted if the net present value is positive.
International Risk and Source of Capital
One factor that distinguishes the international investment decisions from the domestic investment decisions is that cash flows are earned in foreign currency. This fact should be considered while estimating the incremental cash flows. Moreover Firms must constantly assess the business environments of the countries they are already operating in as well as the ones they are considering investing in. This WACC should be adjusted by the country risk.
POLITICAL RISK OF FOREIGN INVESTMENTS














