Financial Ratios You Need to Know When Buying a Business
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
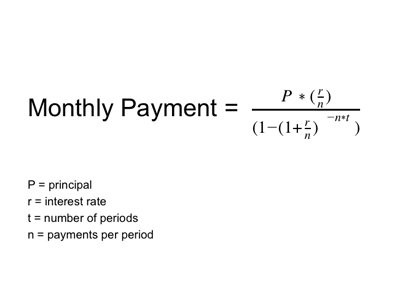
If you want to become educated on business matters, then one of the things that you should know is the financial statement of companies. You need to know how to read numbers because numbers dont lie.
Financial statements are the health check up of businesses. Just like humans, businesses can be subject of certain diseases that you should know before its too late. Here are some of the financial ratios that you should know to examine the health of a business. This would be beneficial too if you are planning to buy an existing business as an investment.
Here are some of the financial ratios that you should know:
Debt to Equity Ratio . Debt to equity ratio is simply defined as total debt divided by total equity. Liabilities are the portion of the companys capital financed by outsiders (bank loans, etc.) where as equities are the portion financed by the insiders or owners (shareholders). A high debt to equity ratio means that the business rely heavily on debt in financing its operations. If the business is not generating much revenue, the burden of interest expenses on debts can seriously damage its health which can lead to bankruptcy. Generally, you should look for LOW Debt to Equity Ratio .
Current Ratio. Current ratio is simply defined as current assets divided by current liabilities. Current assets are generally liquid assets of the company. These assets are so-called liquid because they are easily convertible to cash. Examples of current assets are cash, inventory and accounts receivables.
For investors looking for businesses to buy, look for one with high current ratio. A high current ratio indicates that the business has enough current or liquid assets to pay its liabilities.
Quick Ratio. A more enhanced current ratio is the quick ratio. Quick ratio is simply defined as current assets less inventory divided by current liabilities. This is taking into consideration more liquid assets by taking out inventory. Inventory is excluded here since it might include items that are difficult to liquidate quickly and that have uncertain liquidation values.
Cash Ratio. The best liquidity ratio is the cash ratio. It is simply defined by cash plus marketable securities divided by current liabilities. Marketable securities are shares of the company that is publicly listed. If the creditor of the company, i.e. a bank, demanded payment anytime they want to, then this ratio is how fast can the company pay the bank.
Average Collection Period. A lot of times, businesses allow payment terms on their clients especially companies providing supplies. Their clients can have their products but they can pay on 30, 60 or even 90 days after. Average collection period is the way to gauge the average days on how it takes a company to collect their accounts receivables from their clients. It is defined as accounts receivables divided by average daily credited sales. Credited sales mean that the proceeds of the sale are collected in the form of cash. You should look for businesses that can collect accounts receivables as early as possible.
Gross Profit Margin. Gross profit margin is a ratio of profitability for every sales the company generates. It is simply defined as sales less cost of goods sold divided by sales. We all know that before companies can produce a certain product, they need to encounter some DIRECT costs such as expenses used to purchase raw materials and labor costs.
Cost of goods sold pertains to direct expenses that the company has for every product they produce. However, it EXCLUDES INDIRECT costs such as sales commission of agents, etc. If you are eyeing a business to purchase, then you must look for high gross profit margin.
Return on Assets. A business may have a lot of assets in its possession. However, these assets may become idle because they are not being utilized to generate profits. An example of this is the company may have purchased a real estate, say a warehouse, but it is not being used. Therefore, it could be subject for devaluation if no further improvement is made on its location and termites and rust eat the warehouse itself as time passes by.
Return on assets is a measure of how effectively the companys assets are being used to generate profits. It is defined by net income divided by total assets. When youre buying a business, always look for a higher return on assets. Theres no use even if the company has a lot of assets if its not being used to generate profits.
In addition, there are two other important measures of how profitable a business is. These are working capital and net income.
Working Capital. Working capital is not much of a ratio but it gives you an idea of the cashflow of the company. It is defined as total current assets minus total current liabilities. The result of this calculation must be a positive number.
Net Income. Finally, one of the most important gauge is the net income. It pertains as to how much the business is making. It is defined by total revenues minus total expenses.
In accounting, there are other financial ratios out there but for me, here are the most important ratios that you should know when buying a business.
Furthermore, you should be comparing these ratios on a year to year level. Generally, if you want to buy a business, an increasing net income year over year is the best gauge.
To get articles, you can subscribe using your favorite RSS feed reader or have them delivered directly to your email address .
Incoming search terms:
- ratios to look at when buying a business
- average collection period
- buying a business ratio to use
- financial ratios when buying a business
- buying a business financial ratios
- buying a business ratios
- financial ratios due diligence
- ratios for buying a business
- ratios for purchasing a business
- average collection period formula














