Financial Analysis and Accounting Book of Reference Statement of Financial Position
Post on: 12 Июль, 2015 No Comment
Debt ratios: What is it?
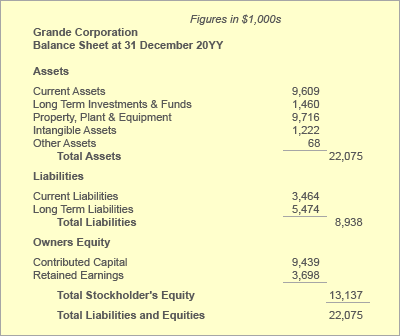
Financial leverage ratios (debt ratios ) measure the ability of a company to meet its financial obligations when they fall due. Financial leverage ratios (debt ratios) indicate the ability of a company to repay principal amount of its debts, pay interest on its borrowings, and to meet its other financial obligations. They also give insights into the mix of equity and debt a company is using.
Financial leverage ratios usually compare the debts of a company to its assets. The common examples of financial leverage ratios include debt ratio, interest coverage ratio, capitalization ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and fixed assets to net worth ratio.
Financial leverage ratios indicate the short-term and long-term solvency of a company. They give indications about the financial health of a company. These ratios give indications whether the company has got enough financial resources to cover its financial obligations when the creditors and lenders seek their payments.
A company with adverse financial leverages ratios may not be able to cover its debts and therefore may go bankrupt. These ratios can give warnings to the shareholders and directors of potential financial difficulties. The shareholders and directors can take actions to prevent the company from going bankrupt.
Financial leverage ratios help to determine the overall level of financial risk faced by a company and its shareholders. Generally speaking, the greater the amount of debt of a company the greater the financial risk is. A company with greater amount of debts and financial obligations is more likely to fail to repay its debts.
Financial leverage ratios are of little use in isolation. To draw meaningful conclusions about the financial health of a company, trend analysis and industry analysis needs to be done. Trend and industry analysis will tell how well the financial position is being managed. Trend analysis will indicate whether the financial position of a company is improving or deteriorating over time. Industry analysis will indicate how well the company is performing as compared to other companies in the same industry.
Companies need to carefully manage their financial leverage ratios to keep their financial risk at acceptable level. Careful management of financial leverage ratios is also important when seeking loans from banks and financial institutions. Favorable ratios can help the company to negotiate a favorable interest rate.
Asset Coverage Ratio
Asset coverage ratio measures the ability of a company to cover its debt obligations with its assets. The ratio tells how much of the assets of a company will be required to cover its outstanding debts. The asset coverage ratio gives a snapshot of the financial position of a company by measuring its tangible and monetary assets against its financial obligations. This ratio allows the investors to reasonably predict the future earnings of the company and to asses the risk of insolvency.
Debt Ratio
Debt ratio is a ratio that indicates proportion between company’s debt and its total assets. It shows how much the company relies on debt to finance assets. The debt ratio gives users a quick measure of the amount of debt that the company has on its balance sheets compared to its assets. The higher the ratio, the greater risk will be associated with the firm’s operation. A low debt ratio indicates conservative financing with an opportunity to borrow in the future at no significant risk.
Debt Service Coverage Ratio
Financial Leverage
Financial leverage can be aptly described as the extent to which a business or investor is using the borrowed money. Business companies with high leverage are considered to be at risk of bankruptcy if, in case, they are not able to repay the debts, it might lead to difficulties in getting new lenders in future. It is not that financial leverage is always bad. However, it can lead to an increased shareholders return on investment. Also, very often, there are tax advantages related with borrowing, also known as leverage.
Fixed Assets to Net Worth
Fixed assets to net worth is a ratio measuring the solvency of a company. This ratio indicates the extent to which the owners’ cash is frozen in the form of fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, and the extent to which funds are available for the company’s operations (i.e. for working capital).
Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
Fixed charge coverage ratio is the ratio that indicates a firms ability to satisfy fixed financing expenses such as interest and leases. This means that the fixed charges that a firm is obligated to meet are met by the firm. This ratio is calculated by summing up Earnings before interest and Taxes or EBIT and Fixed charge which is divided by fixed charge before tax and interest.
Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR)
The interest coverage ratio (ICR) is a measure of a company’s ability to meet its interest payments. Interest coverage ratio is equal to earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) for a time period, often one year, divided by interest expenses for the same time period. The interest coverage ratio is a measure of the number of times a company could make the interest payments on its debt with its EBIT. It determines how easily a company can pay interest expenses on outstanding debt.
Long Term Debt to Capitalization Ratio
A Long Term Debt to Capitalization Ratio is the ratio that shows the financial leverage of the firm. This ratio is calculated by dividing the long term debt with the total capital available of a company. The total capital of the company includes the long term debt and the stock of the company. This ratio allows the investors to identify the amount of control utilized by a company and compare it to other companies to analyze the total risk experience of that particular company.
Long Term Debt to Total Asset Ratio
Long Term Debt to Total Asset Ratio is the ratio that represents the financial position of the company and the companys ability to meet all its financial requirements. It shows the percentage of a company’s assets that are financed with loans and other financial obligations that last over a year. As this ratio is calculated yearly, decrease in the ratio would denote that the company is fairing well, and is less dependant on debts for their business needs.
Non-current Assets to Net Worth
Non-current assets to net worth ratio isa measure of the extent of a company’s investment in low-liquid non-current assets. This ratio is important for comparison analysis because it is less dependent on industry (structure of company assets) than debt ratio or debt-to-equity ratio.














