Enterprise risk management Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Post on: 23 Август, 2015 No Comment
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Enterprise risk management (ERM ) in business includes the methods and processes used by organizations to manage risks and seize opportunities related to the achievement of their objectives. ERM provides a framework for risk management. which typically involves identifying particular events or circumstances relevant to the organization’s objectives (risks and opportunities), assessing them in terms of likelihood and magnitude of impact, determining a response strategy, and monitoring progress. By identifying and proactively addressing risks and opportunities, business enterprises protect and create value for their stakeholders, including owners, employees, customers, regulators, and society overall. (ERM).
ERM can also be described as a risk-based approach to managing an enterprise, integrating concepts of internal control. the Sarbanes–Oxley Act. and strategic planning. ERM is evolving to address the needs of various stakeholders, who want to understand the broad spectrum of risks facing complex organizations to ensure they are appropriately managed. Regulators and debt rating agencies have increased their scrutiny on the risk management processes of companies.
Contents
ERM frameworks defined [ edit ]
There are various important ERM frameworks, each of which describes an approach for identifying, analyzing, responding to, and monitoring risks and opportunities, within the internal and external environment facing the enterprise. Management selects a risk response strategy for specific risks identified and analyzed, which may include:
- Avoidance: exiting the activities giving rise to risk
- Reduction: taking action to reduce the likelihood or impact related to the risk
- Alternative Actions: deciding and considering other feasible steps to minimize risks.
- Share or Insure: transferring or sharing a portion of the risk, to finance it
- Accept: no action is taken, due to a cost/benefit decision
Monitoring is typically performed by management as part of its internal control activities, such as review of analytical reports or management committee meetings with relevant experts, to understand how the risk response strategy is working and whether the objectives are being achieved.
Casualty Actuarial Society framework [ edit ]
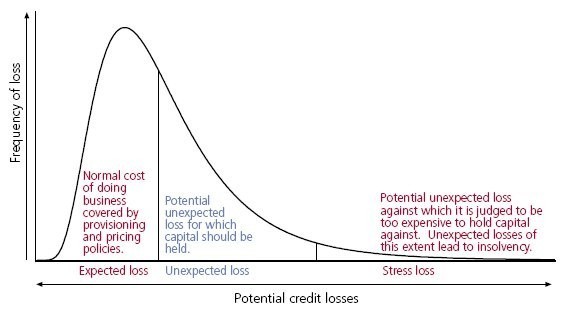
In 2003, the Casualty Actuarial Society (CAS) defined ERM as the discipline by which an organization in any industry assesses, controls, exploits, finances, and monitors risks from all sources for the purpose of increasing the organization’s short- and long-term value to its stakeholders. [ 1 ] The CAS conceptualized ERM as proceeding across the two dimensions of risk type and risk management processes. [ 1 ] The risk types and examples include: [ 2 ]
Hazard risk Liability torts, Property damage, Natural catastrophe Financial risk Pricing risk, Asset risk, Currency risk, Liquidity risk Operational risk Customer satisfaction, Product failure, Integrity, Reputational risk Strategic risks Competition, Social trend, Capital availability
The risk management process involves: [ 3 ]
- Establishing Context: This includes an understanding of the current conditions in which the organization operates on an internal, external and risk management context.
- Identifying Risks: This includes the documentation of the material threats to the organization’s achievement of its objectives and the representation of areas that the organization may exploit for competitive advantage.
- Analyzing/Quantifying Risks: This includes the calibration and, if possible, creation of probability distributions of outcomes for each material risk.
- Integrating Risks: This includes the aggregation of all risk distributions, reflecting correlations and portfolio effects, and the formulation of the results in terms of impact on the organization’s key performance metrics.
- Assessing/Prioritizing Risks: This includes the determination of the contribution of each risk to the aggregate risk profile, and appropriate prioritization.
- Treating/Exploiting Risks: This includes the development of strategies for controlling and exploiting the various risks.
- Monitoring and Reviewing: This includes the continual measurement and monitoring of the risk environment and the performance of the risk management strategies.
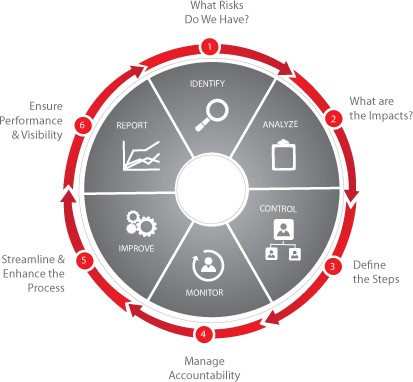
COSO ERM framework [ edit ]
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management-Integrated Framework published in 2004 defines ERM as a …process, effected by an entity’s board of directors, management, and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its risk appetite. to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives. [ 4 ]
The COSO ERM Framework has eight Components and four objectives categories. It is an expansion of the COSO Internal Control -Integrated Framework published in 1992 and amended in 1994. The eight components — additional components highlighted — are:
- Internal Environment
- Objective Setting
- Event Identification
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Response
- Control Activities
- Information and Communication
- Monitoring
The four objectives categories — additional components highlighted — are:
- Strategy — high-level goals, aligned with and supporting the organization’s mission
- Operations — effective and efficient use of resources
- Financial Reporting — reliability of operational and financial reporting
- Compliance — compliance with applicable laws and regulations
RIMS Risk Maturity Model [ edit ]
The RIMS Risk Maturity Model (RMM) for Enterprise Risk Management, published in 2006, is an umbrella framework of content and methodology that detail the requirements for sustainable and effective enterprise risk management. [ 5 ] The RMM model consists of twenty-five competency drivers for seven attributes that create ERM’s value and utility in an organization. The 7 attributes are:
- ERM-based approach
- ERM process management
- Risk appetite management
- Root cause discipline
- Uncovering risks
- Performance management
- Business resiliency and sustainability
The model was published by the Risk and Insurance Management society and developed by Steven Minsky, CEO of LogicManager in collaboration with the RIMS ERM Committee. The Risk Maturity Model is based on the Capability Maturity Model, a methodology founded by the Carnegie Mellon University Software Engineering Institute (SEI) in the 1980s. [ 6 ]
Implementing an ERM program [ edit ]
Goals of an ERM program [ edit ]
Organizations by nature manage risks and have a variety of existing departments or functions (risk functions) that identify and manage particular risks. However, each risk function varies in capability and how it coordinates with other risk functions. A central goal and challenge of ERM is improving this capability and coordination, while integrating the output to provide a unified picture of risk for stakeholders and improving the organization’s ability to manage the risks effectively.
Typical risk functions [ edit ]
The primary risk functions in large corporations that may participate in an ERM program typically include:
- Strategic planning — identifies external threats and competitive opportunities, along with strategic initiatives to address them
- Marketing — understands the target customer to ensure product/service alignment with customer requirements
- Compliance & Ethics — monitors compliance with code of conduct and directs fraud investigations
- Accounting / Financial compliance — directs the Sarbanes-Oxley Section 302 and 404 assessment, which identifies financial reporting risks
- Law Department — manages litigation and analyzes emerging legal trends that may impact the organization
- Insurance — ensures the proper insurance coverage for the organization
- Treasury — ensures cash is sufficient to meet business needs, while managing risk related to commodity pricing or foreign exchange
- Operational Quality Assurance — verifies operational output is within tolerances
- Operations management — ensures the business runs day-to-day and that related barriers are surfaced for resolution
- Credit — ensures any credit provided to customers is appropriate to their ability to pay
- Customer service — ensures customer complaints are handled promptly and root causes are reported to operations for resolution
- Internal audit — evaluates the effectiveness of each of the above risk functions and recommends improvements
Common challenges in ERM implementation [ edit ]
Various consulting firms offer suggestions for how to implement an ERM program. [ 7 ] Common topics and challenges include: [ 8 ]
Identifying executive sponsors for ERM.
- Establishing a common risk language or glossary.
- Describing the entity’s risk appetite (i.e. risks it will and will not take)
- Identifying and describing the risks in a risk inventory.
- Implementing a risk-ranking methodology to prioritize risks within and across functions.
- Establishing a risk committee and or Chief Risk Officer (CRO) to coordinate certain activities of the risk functions.
- Establishing ownership for particular risks and responses.
- Demonstrating the cost-benefit of the risk management effort.
- Developing action plans to ensure the risks are appropriately managed.
- Developing consolidated reporting for various stakeholders.
- Monitoring the results of actions taken to mitigate risk.
- Ensuring efficient risk coverage by internal auditors, consulting teams, and other evaluating entities.
- Developing a technical ERM framework that enables secure participation by 3rd parties and remote employees.














