Dividend Paying Stocks
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
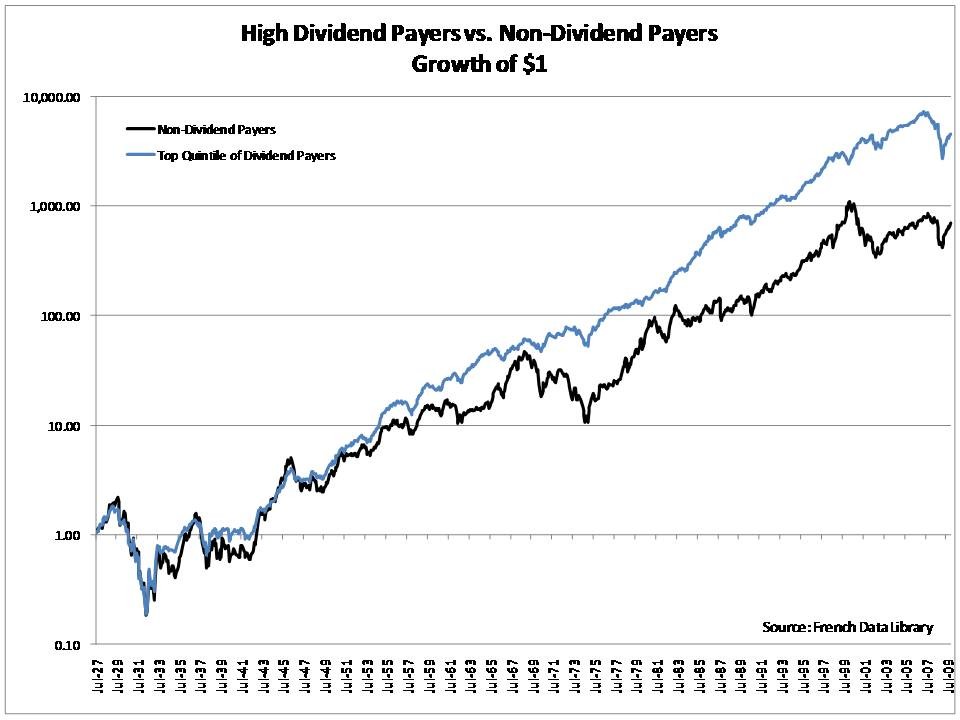
Dividend paying stocks normally pay in a pattern of dividend payments which may suit on type of stock holder more than another.
A retiree may prefer to invest in a dividend paying stock that provides a consistently high dividend yield, whereas a person with a high income from employment may prefer to avoid dividends due to their high tax rate on income. Dividend paying stocks can pay in particular patterns of dividend payments, a corporation may be able to maximize its stock price and minimize its cost of capital by catering to a particular investor. This model may help explain the relatively consistent dividend policies followed by most dividend paying stocks.
When investors have incomplete information about dividend paying stocks they will look for other information that may provide a clue as to the firms future prospects. Managers have more information than investors about the firm, and such information may influence their dividend decisions. When management lacks confidence in the firms ability to generate cash flows in the future they may keep dividends constant, or possibly even reduce the amount of dividends paid out. Conversely, management that has access to information that indicates very good future prospects for the firm are more likely to increase dividend payouts.
Investors can use this knowledge about a dividend paying stock to inform their decision to buy or sell the firms stock, bidding the dividend paying stocks price up in the case of a positive dividend surprise, or selling it down when dividends do not meet expectations. This, in turn may influence the dividend decision a managers know that stock holders closely watch dividend announcements looking for good or bad news. As managers tend to avoid sending a negative signal to the market about the future prospects of their firm, this also tends to lead to a dividend policy of a steady, gradually increasing dividend payment.
There are several key terms to understand when investing in dividend paying companies some of which include:
Dividend Re-Investment Plan: A plan offered by corporations allowing investors to reinvest their cash dividends by purchasing additional shares on the dividend payments date.
Dividend Yield: A financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to
its share price. The dividend yield is calculated as the latest dividend rate divided by the stocks latest closing price.
Dividend Rate: If a company’s board has committed to dividend payments in the future, the latest reported dividend rate equals the number of times the company pays dividends per year times the latest dividend, expressed in dollars. If a company’s board has not committed to dividend payments in the future, the latest reported dividend rate equals the total dividends paid in the past 12 months.
Dividend Payout Ratio: The current payout is the LTM dividend per share divided by LTM EPS, expressed as a percentage. The percentage indicates the percent of EPS that was paid out as a dividend.
Dividend Screener™: An internet based tool used to screen dividend paying stocks for growth, yield etc.
Dividend Ranking™: An internet based tool used to rank dividend paying companies in terms of the yield, growth etc.
Dividend Top 100™: An internet based tool used to sort the Top 100 Dividend paying companies by exchange or sector etc.
Dividend Analyzer™: An internet based tool used to analyze dividend paying companies.
Dividend Declaration Date: The date on which the next dividend payment is announced by the directors of a company. This statement includes the dividends size, ex-dividend date and payment date.
Ex Dividend Date: The major exchanges require 4 business days prior to the Record Date for recording ownership changes. The day that begins this 4-day period is the Ex-Date. Investors who purchase the stock prior to the Ex-Date are eligible for the latest dividend; investors who purchase the stock on or after the Ex-Date are not entitled to the dividend. Empirical evidence has shown that this is also the date that the market reflects the dividend policy in the stock price.
Dividend Record Date: The date established by an issuer of a security for the purpose of determining the holders who are entitled to receive a dividend or distribution.
Dividend Pay Date: The date on which a declared stock dividend is scheduled to be paid.
Dividend Growth: The amount of dividend payout increase/decrease vs previous payouts.
Cash Dividend: Money paid to shareholders, normally out of the corporations current earnings or accumulated profits.
Dividend Policy: The policy a company uses to decide how much it will pay out to shareholders in dividends.
Special Dividend: A non-recurring distribution of company assets, it is also known as an extra dividend.
Stock Dividend: A dividend payment made in the form of additional shares.
Stock Investing: A term used for the investor that purchases common stocks trading on stock exchanges.
Online Stock Trading: A way to purchase a stock online, normally through online brokers.
Stock Quote: A list of prices for a stock at a particular point during the trading day.
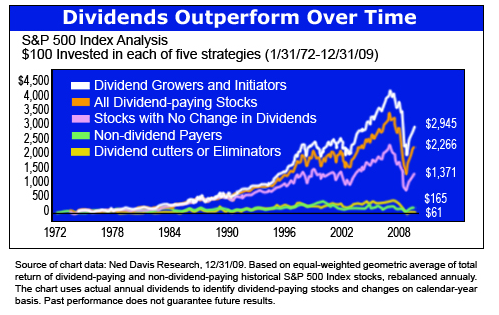
Stock: A type of security that signifies ownership in a corporation. There are two main types of stock: common and preferred.
Dividend History: The length of time a company has paid out dividends.
Dividend ETF: A security that tracks a dividend index, a commodity or a basket of assets like an index fund. An ETF trades like a stock and it is normally bought and sold throughout the trading day.
Dividend Capture: A term used in the process of purchasing a stock prior to the ex-dividend date.
Dividend Calendar: The payment timetable for a corporations annual dividend payouts.
Qualified Dividend: A certain type of dividend to which capital gains tax rates are applied.
Dividend Stock: A security that pays a dividend usually in the form of a cash payout.
Dividend Discount Model: A procedure for valuing the price of a stock by using predicted dividends and discounting them back to present value.
Canadian Dividend Stocks: The Toronto Stock Exchange lists many dividend paying stocks.
UK Dividend Stocks: The London Stock Exchange lists many dividend paying stocks.
Dividend Investing: A certain type of investment strategy focused on dividend paying companies.
DividendInvestor.com™ is a leading worldwide independent provider of dividend information and data for investment professionals. Our mission is to be the First In Dividend Data Worldwide ™ by designing and developing essential tools and systems for the investment community with the highest level of accuracy and integrity. Financial planners, advisors and individual investors worldwide utilize DividendInvestor.com™ to research dividend data in order to make wise investment decisions. With proprietary tools for our members such as the Dividend Analyzer™, Screener™, Ranking™ and others, financial investors have the power to make their own informed dividend stock investment decisions. The worlds best value investors have long understood the power that dividends can provide. Many market analysts agree that historically, over 40% of the total stock markets return has come from dividends. With such an amazing historical performance, it is easy to understand why dividends have become so critical when it comes to investing.
DividendInvestor.com™ provides you with the all of the data and tools to make wise investment decisions. Join now so you can enjoy the exclusive market-edge DividendInvestor.com™ provides!














