Difference Between MBS and CDO
Post on: 9 Июль, 2015 No Comment
Difference Between MBS and CDO
Structured Finance is a type of financing that uses securitization. There are several types of Structured Finance Instruments, some of them are: Credit Derivatives, Collateralized Fund Obligation (CFO), Asset-Backed Security (ABS), Mortgage-Backed Security (MBS), and Collateralized Debt Obligation (CDO).
Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) are securities or bonds that derive income from mortgage loans which are backed by the assets of the borrower and insured by a trust which can be sponsored by the government or by private entities such as investment banks and real estate investment trusts or conduits.
Mortgage loans or notes are purchased from banks and lenders and are assigned to a trust which assembles and securitizes these loans into pools and issues the MBS. An MBS has high liquidity, has lower cost, and allows issuers to manage their capital more efficiently.
They were first issued in 1981 and can be:
Stripped Mortgage-Backed Security (SMBS) wherein the payment is used to pay both the principal and the interest.
Pass-through Security which has two types: Residential Mortgage-Backed Security (RMBS) which is backed by a residential property mortgage, and Commercial Mortgage-Backed Security (CMBS) which is backed by a commercial property mortgage.
Collateralized Mortgage Obligation (CMO) which is backed by the owner’s assets.
Collateralized Debt Obligation (CDO), on the other hand, is an Asset-Backed Security (ABS) that derives income from a borrower’s pool of underlying assets which include corporate loans, MBS, credit cards, auto loan payments, leases, royalty payments, and revenues.
A Special Purpose Entity (SPE) is created to secure capital from investors by issuing bonds in tranches. The capital is then used to acquire and hold assets as collateral. The payout structure to investors is more complex providing investors with different returns depending on their utilized tranches.
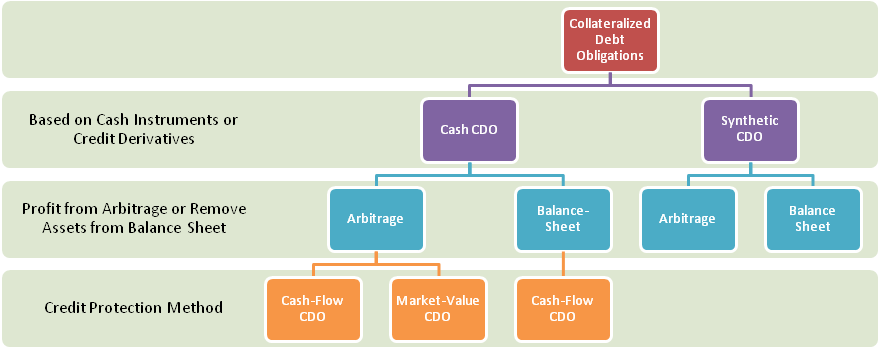
CDOs were first issued in 1987 and are classified according to:
Source of funds: cash flow CDO wherein investors are paid using the cash flows of its assets and market value CDO wherein investors get higher returns from trading and sale of assets.
Motivation: CDOs can be arbitrage or balance sheet transactions.
Funding: CDOs may have a portfolio of cash assets (Cash CDO), fixed income assets (Synthetic CDO), or both (Hybrid CDO).
There is also a Single Tranche CDO and several other variants.
Summary:
1.Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) are securities that generate income from mortgage loans while a Collateralized 2.Debt Obligation (CDO) is a type of Asset-Backed Security (ABS) that generates income from the underlying assets of the borrower.
3.An MBS is issued to investors by a government-sponsored or private entity who purchase them from banks and lenders while a CDO is issued by a Special Purpose Entity (SPE) which secures funds from investors in exchange for bonds issued in tranches.
4.The MBS payout to investors is less complex than that of a CDO which involves several tranches and gives out different amounts of returns depending on the tranche that is utilized.
5.An MBS is secured only by the mortgage loan while a CDO is secured by several other underlying assets such as corporate loans, MBS, credit card payments, royalties, leases, and other assets used as collateral.














