Concept of compound interest refers to A)earning interest on the original investment
Post on: 21 Июль, 2015 No Comment

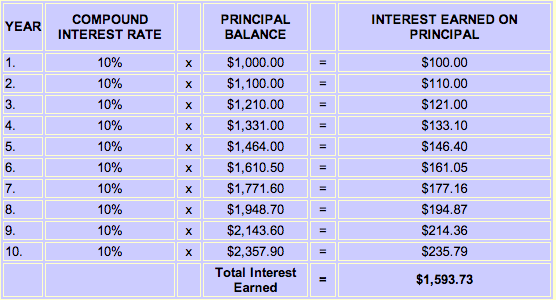
1. The concept of compound interest refers to:
A)earning interest on the original investment.
B)payment of interest on previously earned interest.
C)investing for a multi year period of time.
D)determining the APR of the investment.
A)the interest rate is lower than on comparable investments.
B)the future value of the investment will be low.
C)the earned interest is non taxable to the investor.
8. What is the required return for a stock that has a 5% constant growth rate, a price of $25, an expected dividend of $2, and a P/E ratio of 10?
Capital Structure and Long Term Financing Strategies
A)the maturity value of the stock.
B)the price at which each share is recorded.
C)the price at which an investor could sell the stock.
D)the price received by the firm when the stock was issued.
10. Additional paid in capital refers to:
A)a firm s retained earnings.
B)a firm s treasury stock.
C)the difference between the issue price and the par value.
D)funds borrowed from a bank or bondholders.
11. Which of the following equity concepts would you expect to be least important to a financial analyst?
A)risk of owning equity securities.
B)risk faced by equityholders when debt is used.
C)general business risk of the firm.
A)its expected return on assets.
B)its expected return on equity.
C)the sum of expected return on equity and expected return on debt.
B)60.0%
C)66.7%
D)75.0%
16. A firm has an expected return on equity of 16% and an after tax cost of debt of 8%. What debt equity ratio should be used in order to keep the WACC at 12%?
A).50
B).75
C)1.00
D)1.50
17. Which of the following is not found in John Lintner s stylized facts of corporate dividend policies?
A)Firms have long run target dividend payout ratios.
B)Managers focus more on dividend absolute levels than on its changes.
C)Dividend changes follow shifts in long run, sustainable levels of earnings rather than short run changes in earnings.
D)Managers are reluctant to make dividend changes that might have to be reversed.
18. An increase in dividends might not increase price and may actually decrease stock price if:
A)the dividend increase cannot be sustained.
B)the firm does not maintain an exact dividend payout ratio.
C)the firm has too much retained earnings.
D)markets are weak form efficient.
19. A policy of dividend smoothing refers to:
A)maintaining a constant dividend payout ratio.
B)keeping the regular dividend at the same level indefinitely.
C)maintaining a steady progression of dividend increases over time.
D)alternating cash dividends with stock dividends.
20. What is the most likely prediction after a firm reduces its regular dividend payment?
A)Earnings are expected to decline.
B)Investment is expected to increase.














