Accounting 101 Balance Sheet Definition
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
Balance Sheet Defined
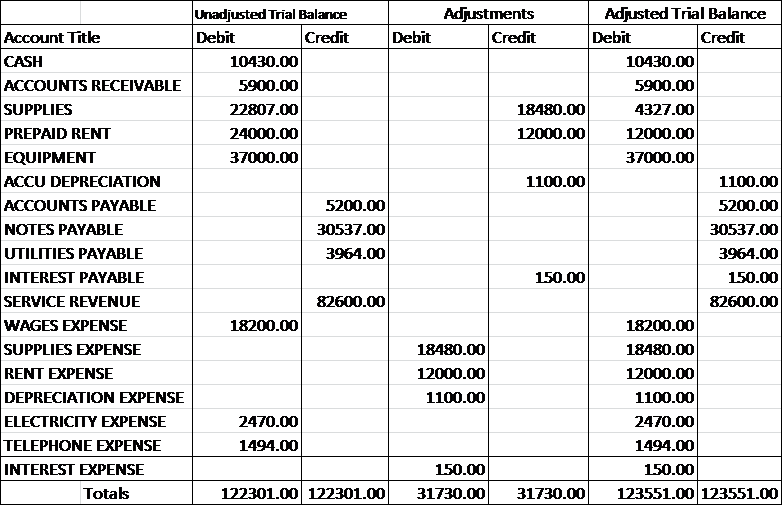
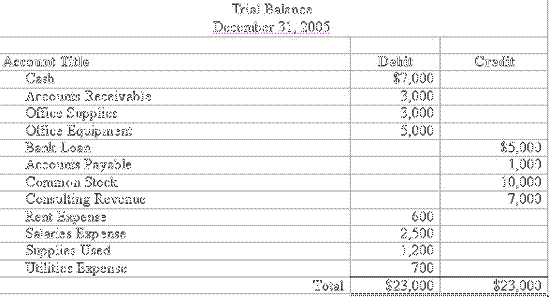
The balance sheet is commonly defined as the financial report that lists (quantifies) the total assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity of a business on a specified date, usually the last day of the accounting period. The balance sheet is divided into three primary sections or categories: assets, liabilities, net worth or owner’ equity. The liabilities of the company subtracted from the assets shows the net worth. Net worth can be a negative figure if the liabilities are greater than the company’s assets.
Assets
Assets are any items of economic value that can be converted into cash. Assets are shown on the debit side of the balance sheet while the credit side shows liabilities and owners’ equity. The two sides must be equal, or balance which is why it is called a balance sheet.
Assets are listed in descending order of liquidity, from most liquid (cash) to the least liquid (property, facilities and equipment). They include current assets, which are cash in hand and cash equivalents such as t-bills and money market funds. Next are the accounts receivables, followed by inventories of supplies and materials including raw materials, work in progress and finished goods. Current assets are usually defined as assets that can be converted into cash within 12 months. The fixed assets are durable assets with a life span greater than 12 months. This category includes properties, facilities, equipment and machinery, and whatever else the company uses to conduct business. Fixed assets need to reflect depreciation in the value of equipment, such as machinery, that has a limited expected useful life
Liabilities
Liabilities include all outstanding debts payable to employees, suppliers and creditors. They may include taxes, interest payments, and other unpaid expenses that the company has incurred but has not been paid at the time the books were closed. The first category of liabilities is accounts payable. These are the assets the company has received that have not yet been paid for. As with assets, liabilities are sub-divided into current liabilities, debt payable within 12 months (mostly comprised of accounts payable) and long-term liabilities—payable in the future—after 12 months. Liabilities are also listed in descending order of due dates.
Net Worth (Owners’ Equity)
Subtracting liabilities from assets shows the net worth or the owners’ equity. This represents the investment in the business by the owners’ including the original start-up investment plus subsequent investments such as retained earnings. A basic tenet of double-entry bookkeeping is that total assets (what a business owns) must equal liabilities (what the business owes) plus equity.














