What is Risk Management
Post on: 20 Июнь, 2015 No Comment

Types of Risk
Interest Rate Risk: It is the risk of adverse effect of interest rate movements on a firm’s profits or balance sheet.
Credit Risk: It is the risk which may arise due to default of the counter-party.
Liquidity Risk: It is the risk which arises if the given asset or fund is not traded at right time in the market.
Internal Business Risk: it is due the inefficiency of management in the business.
External Business Risk. This type of risk arises due to external environment in the business.
Financial Risks: This risk originates due to improper composition of the operations.
Market Risk: This is the risk which occurs due to market conditions which results in reduction in returns expected on investment. It is also referred to as price risk
Basis Risk: This risk is due the price of the asset and the hedged instrument are not perfectly correlated.
Volatility risk: Risk of suffering losses from changes in implied volatility of the market.
Personnel Risk: This risk is the one which may occur due to inefficient or incapable personnel in the business.
Country or Sovereign Risk: When a country is in difficulty in terms of making its financial commitments for that country as well as for other countries then this type of risk is Country or Sovereign Risk.
Technology Risk: Type of risk which arises due to failure in technology.
Operational Risk: This risk is due to any type of operational failure like,inadequate monitoring, systems failure, management failure, human error.Operational Risk includes Model risk, people risk, legal and compliance risk.
Foreign Exchange Risk: It is due the changes in the foreign exchange rate, currency values etc. which affects the firm
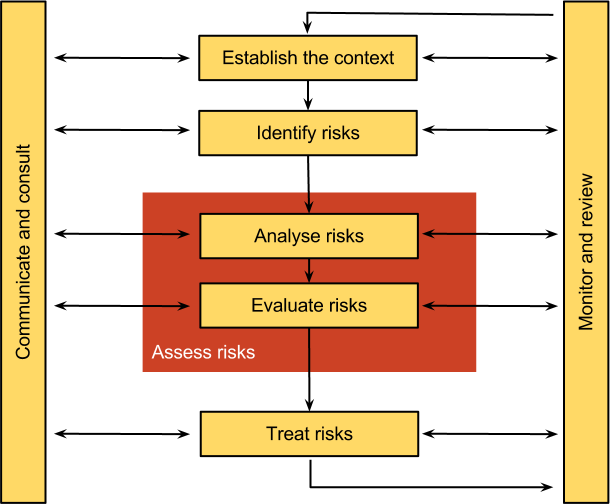
Risk Management Process
Risk Management process deals with the measuring, or assessing risk and developing strategies to manage it.
Approaches to Risk Management
Brief Description of Approaches to Risk Management
- Risk Avoidance – Avoiding of a risk means one should not involve in such activity which involves risk.
- Loss Control – It is altogether making an attempt to reduce either the possibility of a loss or the quantum of loss.
- Combination – It means combining more than one business activity in order to reduce the overall risk.
- Risk Transfer – The business which is originally exposed to risk; transfers when it to another party which is willing to bear the risk.
- Risk Retention – Risk is retained when nothing is done to avoid, reduce or transfer it.
- Risk Sharing – It means the business is itself retaining the risk and also it is sharing that risk with other entity. In short it is a combination of Risk Retention and Risk Transfer.
Value at Risk (VAR)
It is a technique which is used to measure the level of financial risk in the firm. Risk managers make its use, to calculate or measure the level beyond which risks are not taken.
VAR is defined as the maximum loss over a defined period of time at a stated confidence level, given normal market conditions.
Risk Management Tools
The various risk management tools are as follows:
Forward Contract as the name suggests, is a customized contract between two parties where an asset can be bought or sold at a specified price on a specified date.
Futures contract is an exchange-traded contract to buy or sell a predetermined quantity and quality of an asset on a predetermined future date at a predetermined price.
An option is a contract, which gives the holder, the right but not the obligation to buy or sell, an agreed amount of financial instrument on or before an agreed future date, at an agreed price.
Hedging means making an investment to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in an asset.Any technique designed to reduce or eliminate financial risk; for example, taking two positions that will offset each other if prices change
English meaning of Swap is to trade one thing for another‖ or To exchange one thing for another‖
Swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange cash flows in future
- The agreement defines the dates when the cash flows are to be paid and the way in which they are to be calculated.
- The cash flows are calculated over a notional principal amount, which is usually not exchanged between counter-parties.
- Unlike standardized options and futures contracts, swaps are not exchange-traded instruments.
- Swaps are customized contracts that are traded in the over-the-counter (OTC) market between private Parties
Hybrid Debt Securities
Hybrid Debt Security is a debt security combined with any other types of derivatives. Convertible bonds are the types of Hybrid Debt Securities.
Credit Derivative is a derivative, whose value is derived from the credit risk on an underlying bond, loan or other financial asset.
- Credit derivatives are bilateral contracts between a buyer and seller under which the seller sells protection against the credit risk of the reference entity
Career Overview in Risk Management:
Risk management is the part of financial services industry, and it is associated with assessing, measuring and managing of risk.
Responsibilities of Risk Manager:
Risk managers may work in specific area or may concentrate in particular arena. This person has to develop, implement the procedures in order to minimize these risks.
In financial industry risk, the risk can be:
- Default on the loans taken by the firm.
- Market uncertainties,
- Losses on Securities held by traders.
- Losses on investment securities
Qualification:
For working as a Risk Manager, minimum requirement is Bachelor’s degree and often post graduates like MBA is preferred by the firms,
Nowadays, many institutes are offering Certification in risk management in national as well as international level. At international level one can go for the certification of PRM (Professional Risk Manager), FRM (Financial Risk Manager). As these designations are highly respected in the job market.














